The drive shaft is the most important part of the vehicle that transmits torque from the transmission to the differential, and then the differential transmits that torque to the front wheels to drive the vehicle. The drive shaft is also called the Cardan shaft, propeller shaft, or prop shaft.
Simply put, the main function of the propeller or drive shaft is to transmit engine torque from the differential to the vehicle’s wheels.
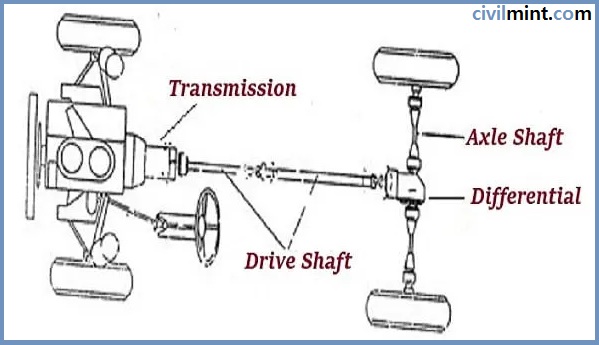
The position of the drive shaft varies depending on the vehicle model and configuration of front-wheel drive, all-wheel drive, and rear-wheel drive. Many other vehicles such as boats, locomotives, motorcycles, trucks, and vans also have drive shafts. These shafts have a number of different prismatic, leaf, universal, or jaw joints to allow varying spacing and engagement between the drive and bearing elements.
Table of Contents
How does it Work?
The main purpose of a drive or transmission shaft is to transmit torque from the engine of the differential or transmission to the wheels of the vehicle. In addition, any variation in angle or length caused by manipulation or misalignment must be compensated for to ensure excellent synchronization between shaft joints.
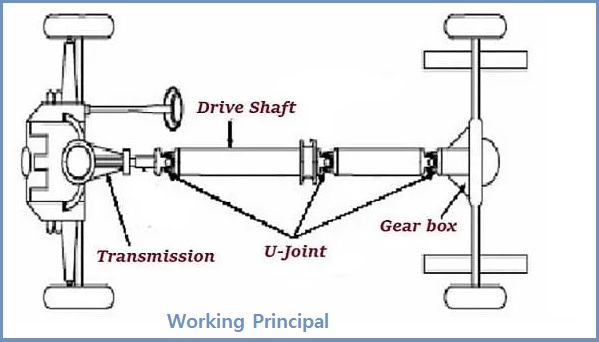
The front-wheel-drive shaft has a connecting shaft, an internal constant-speed joint, and an external stationary joint. It also has other components such as torsion dampers and anti-lock system rings. Vehicles equipped with a flexible bearing or bracket are used to connect the transmission and the engine. However, the suspension springs play the role of connecting the wheels, differential, and rear axle.
Look at the arrangement above; the drive input shaft and the rear axle box output shaft are in several planes. This arrangement allows the drive shaft to connect the input and output shafts at an angle. When the rear wheel hits an uneven surface, the rear axle moves up and down, expanding and compressing the suspension spring. This changes the angle between the post shaft and the drive output shaft.
Due to this process, the length of the post shaft changes. This change occurs because the drive shaft and rear axle rotate in an arc with a point on their axis of rotation.
Parts of the Drive Shaft
- Flanges
- Slip yoke and Tube yoke
- End yoke
- Midship shaft
- Universal joint
- Centre bearing
- Tube
Types of Drive Shafts
- Single Piece shaft
- Two or Three Piece shaft
- Front Wheel Drive
Pros
- There is little or no power loss.
- These shafts are highly durable.
- The drive shaft is not a complicated structure.
- It produces very low noise with high torque.
- It requires less maintenance than a chain system.
- The drive system does not get clogged easily.
Drawbacks
- This shaft is heavier than the chain system.
- Chain systems are more efficient than Cardan shafts.
- Cardan shafts can be very damaging at very high speeds.
- These have the problem of oil leaks in gearing.
- Hollow drive shafts are expensive.
- These are not the best shafts to counter the bending forces.
