The periodic table can be segregated broadly into two types of elements, commonly referred to as metals and non-metals. Each of these elements has varying properties and can be found in a wide range of places, such as buildings, bridges, roads, electric cables, cars, mobile phones, laptops, and aircraft. These are also found in the oxygen we breathe and the carbon dioxide we exhale as well.
Metals and Non-metals are elements that exist in our surroundings. So, it is essential to know whether a particular element is either a metal or nonmetal. Materials can be further divided into metals and non-metals. The characteristic feature of metals like aluminium and copper is a high thermal and electrical conductivity, whereas non-metals like sulfur and phosphorus metal are the insulators. These elements are distinguished based on their properties.
The largest group of elements on the periodic table is that of the transition metals, which is found in the middle of the table. Also, the two rows of elements below the main body of the periodic table (the lanthanides and actinides) are special subsets of these metals. These elements are called “transition metals” because the electrons of their atoms make the transition to filling the d subshell or d sublevel orbital. Thus, the transition metals are also known as the d-block elements.
Here is a list of elements that are considered to be transition metals or transition elements. This list does not include the lanthanides or actinides, just the elements in the main part of the table.
Table of Contents
Metals:-
Most elements are metals. This includes the alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, transition metals, lanthanides, and actinides. On the periodic table, metals are separated from nonmetals by a zig-zag line stepping through carbon, phosphorus, selenium, iodine, and radon. These elements and those to the right of them are nonmetals. Elements just to the left of the line may be termed metalloids or semimetals and have properties intermediate between those of the metals and nonmetals. The physical and chemical properties of the metals and nonmetals may be used to tell them apart.
Metal Physical Properties:–
1.Lustrous (shiny)
2.Good conductors of heat and electricity
3.High melting point
4.High density (heavy for their size)
5.Malleable (can be hammered)
6.Ductile (can be drawn into wires)
7.Usually solid at room temperature (an exception is mercury)
8.Opaque as a thin sheet (can’t see through metals)
9.Metals are sonorous or make a bell-like sound when struck
10.Metals forms an alloy with other metals or non-metals
11.Metals like sodium, potassium are stored in oil as they react with air in seconds and are highly reactive
More metals produce the metal oxide, and highly reactive metals react violently by burning in the oxygen of the air
Metal Chemical Properties:–
1.Have 1-3 electrons in the outer shell of each metal atom and lose electrons readily
2.Corrode easily (e.g., damaged by oxidation such as tarnish or rust)
3.Lose electrons easily
4.Form oxides that are basic
5.Have lower electronegativities
6.Are good reducing agents
Nonmetals:-
Non-metals do not hold the characteristics of metals; it means they are not hard, shiny, fusible, malleable, ductile, and so on. Many materials like Sulphur, coal are too soft and dull in appearance. They can be broken down into very fine thin powdery mass when tapped with a hammer. They are neither sonorous nor very poor conductors of heat and electricity. Non-metal examples are oxygen, carbon, Sulphur, and more.
Physical Properties of Non-metals:-
1.Non-metals may be of solids, liquids, or gases
2.except for Graphite, non-metals are poor conductors of heat and electricity
3.They don’t possess metallic lustre
4.Non-metals do not produce a ringing sound and are not sonorous
5.Non-metals possess no malleability and are not ductile
6.Except for iodine, they have a dull lustre
7.Examples of non-metals are oxygen, carbon, Sulphur, phosphorous, and many more
8.nonductile solids, brittle solids.
9.Transparent as a thin sheet
Nonmetal Chemical Properties:–
1.Usually have 4-8 electrons in their outer shell
2.Readily gain or share valence electrons
3.Form oxides that are acidic
4.Have higher electronegativities
5.Are good oxidizing agents
6.These react more with metals compared to non-metals.
7.Most non-metals don’t react with air at room temperature
8.The only non-metal is white phosphorus which reacts with air to form its oxide by burning
Both metals and nonmetals take different forms (allotropes), which have different appearances and properties from each other. For example, graphite and diamond are two allotropes of the nonmetal carbon, while ferrite and austenite are two allotropes of iron. While nonmetals may have an allotrope that appears metallic, all of the allotropes of metals look like what we think of as a metal (lustrous, shiny).
The Metalloids:-
The distinction between metals and nonmetals is somewhat fuzzy. Elements with properties of both metals and nonmetals are called semimetals or metalloids. A stair-step line roughly divides metals from nonmetals on the periodic table. But, chemists recognize that naming one element a “metal” and the one next to it a “metalloid” is a judgement call. In truth, most metals display the properties of nonmetals under certain conditions, and nonmetals act like metals in some situations.
Hydrogen is a good example of an element that acts as a nonmetal some times, but as a metal other times. Under normal conditions, hydrogen is a gas. As such, it acts like a nonmetal. But, under high pressure it becomes a solid metal. Even as a gas, hydrogen often forms the +1 cation (a metallic property). Yet, sometimes it forms the -1 anion (a nonmetal property).
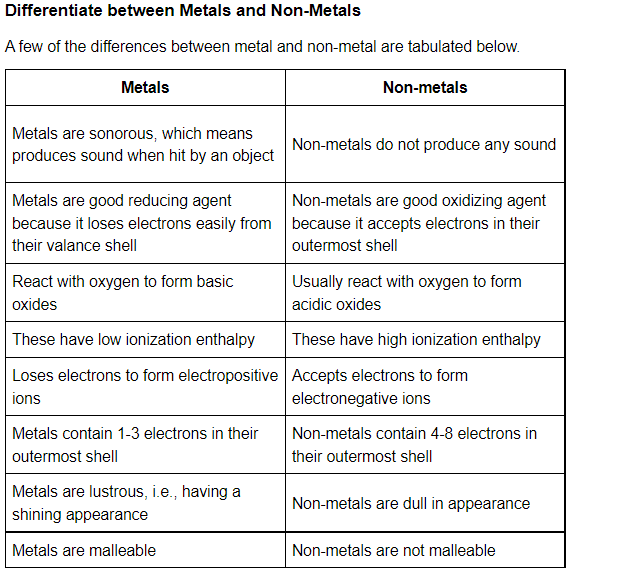
Conclusion:-
In chemistry, Elements can be divided into metals and nonmetals and it is important to know whether a particular element is a metal or nonmetal before performing any chemical research. Metals (like copper and aluminium) are good conductors of heat and electricity, while nonmetals (such as phosphorus and sulfur) are considered insulators. A nonmetal is a chemical element that usually gains electrons when reacting with metal, and which forms an acid if combined with oxygen and hydrogen. Nonmetals display more variety in colour and state than metals do.
Chemistry is really important and efficient for the research and study of living organisms because it helps students and scientists to understand the life processes of every living thing on earth at the molecular level. At any molecular level, every process of life takes place due to the involvement of various minor or major chemical reactions.
Thus, the students need to learn their chapters well and understand all the chemistry concepts by practising with a maximum number of past years’ question papers and sample question papers available on the Vedantu website. This will help them to understand the time management skill and learn the marking schemes that carry maximum marks and plan which question needs what type of answers. Break down larger portions into smaller effective points and write them down in a separate notebook so it will help you in revising before the exams. Make note of the important questions that keep repeating in the recent past year question papers give more weightage to those questions and prepare a little extra because it might repeat in the current year also. If you have any doubts about the equations and chemical formulations that are taught during the classes then try to spend some extra time in the lab and get to understand all the concepts by trying out the experiments and practising them well. This will help you write your formulas and equations well.
