Table of Contents
Introduction of Electrical Grounding
Electrical grounding is a electrical discharge technique to the earth. In this process, instantaneous discharge of electrical energy by conducting the charge directly to earth through a low impedance wire.
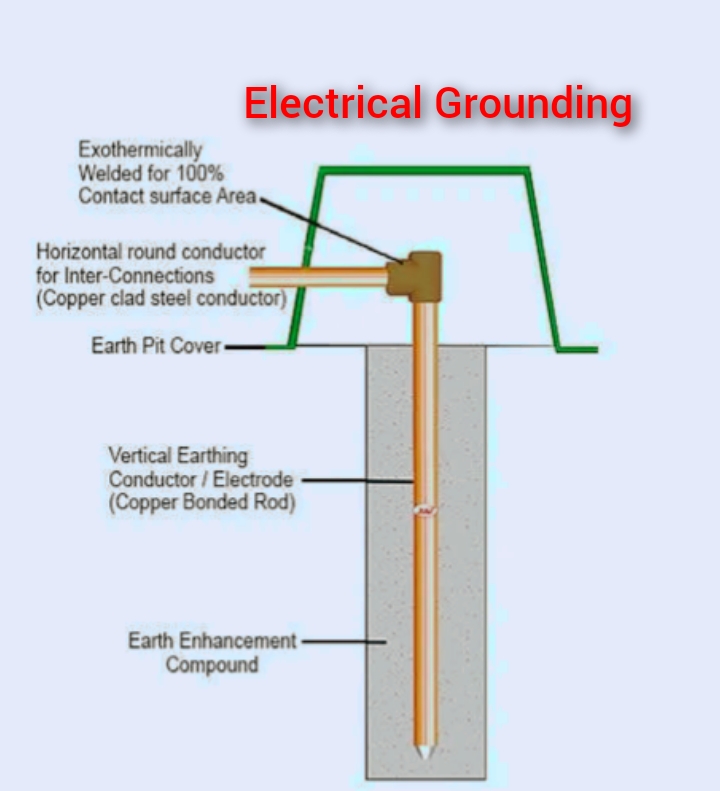
Various types of grounding are used to connect metal parts of electrical equipment or installations to ground to prevent or reduce the risk of electric shock.
Various forms of electrical grounding include plate grounding systems, tape or wire grounding, rod grounding systems, and pipe grounding systems to grounds including cables in buildings, homes, machines, and electrical equipment.
Electrical Grounding Procedure
Grounding is done to ensure safety by connecting electrical equipment to a grounding system or electrode near or below the ground.
Flat riser electrodes or ground mats are installed below the surface of the earth. Used to connect all non-current-carrying metal parts of the device.
If an overload current is transmitted through the device, or if the current causes a system fault, the fault current from the device will flow through the ground system. The conductor of the ground mat raises the voltage by the resistance of the ground mat multiplied by the ground fault. This protects the device from overloads or fault currents.
Buildings have three different cable types Live, Neutral and Earth cables. The ground is connected to a buried metal plate and conducts the current from the power station live and neutral. All electrical appliances such as Led screens, irons, washing machine, etc. are connected to the ground wire. This protects these devices from shocks and power failures. Local grounding is done near the home electricity meter.
Types of Electrical Grounding
Various types of electrical grounding are used in construction.
1. Pipe Grounding
Pipe grounding is a common method of connecting to the earth’s electrical conductors using steel pipes. For pipe grounding, a galvanized steel pipe with a diameter of 38mm and a length of 2m is laid vertically in the ground and used as a grounding electrode.
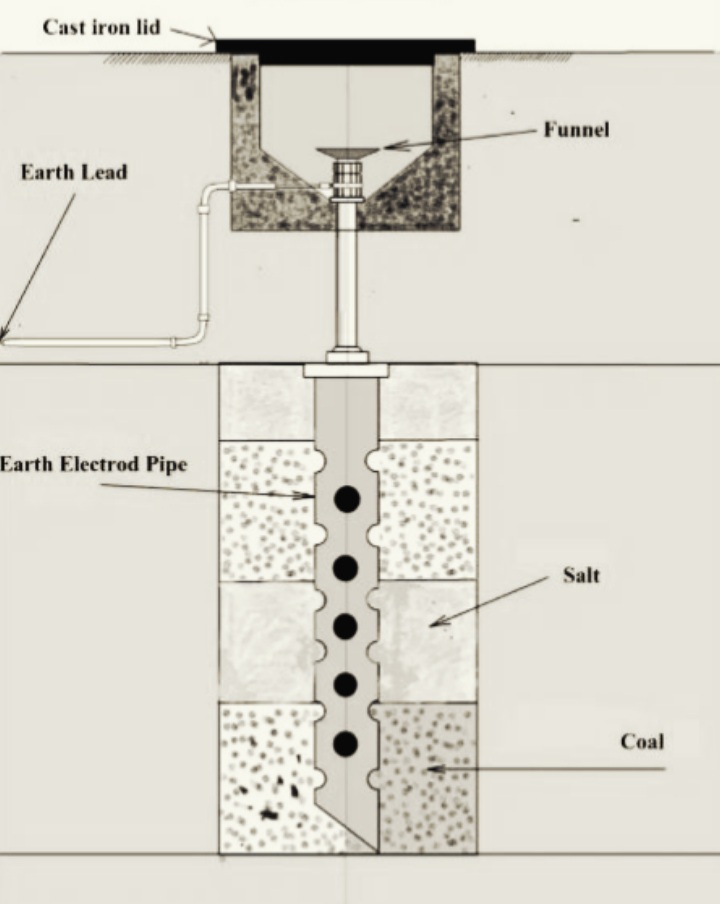
The size of the iron pipe to be used depends on the moisture in the ground and the strength of the current. Soil moisture determines the maximum depth to which steel pipes can be installed.
The best and most effective method of grounding is pipe grounding, which is also easily affordable.
2. Plate Ground
In this form of grounding, copper or galvanized steel plates are placed vertically in a pit less than 10 feet from the ground. To achieve a more effective electrical grounding system, it is necessary to maintain the soil moisture condition around the plate grounding system. This plate is attached to electrical wires and redirects electrical charges within the earth.
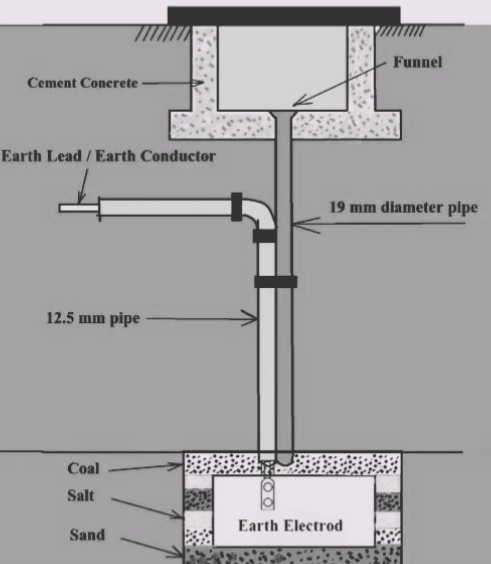
3. Strip Ground
In this form of grounding, strip electrodes with a minimum cross-section of 6.0 mm2 and a minimum depth of 0.5 m are placed in horizontal trenches. If the electrode is made of galvanized iron or steel, its cross-sectional area should be at least 25 mm x 1.6 mm.

A conductor at least 50 feet (15 m) long, buried in the ground, provides sufficient resistance to earth.
4. Ground Rod
In this grounding method, a copper rod with galvanized steel pipe is driven vertically into the ground by hand or with a hammer to the desired value. Embedded electrode length reduces ground resistance.

The rods used for this are buried at a certain depth in the ground and safely discharge the short circuit current into the ground.
This grounding technique works well on sandy surfaces and is very budget friendly.
Final Thought
Electrical grounding is done for the purpose of safety. Capacity of earth is infinite, that is why electrical current dishcharge to earth.
