Metal–oxide–semiconductor Field-effect Transistor Or Metal–oxide–silicon Field-effect Transistor is called MOSFET.
MOSFET is a field-effect transistor with an electrically insulated gate where the voltage determines the conductivity of the device. The main purposes of MOSFET are to switch or amplify signals.
There are two types of MOSFET.
- P-Channel MOSFET
- N-Channel MOSFET
Table of Contents
1. P-Channel MOSFET
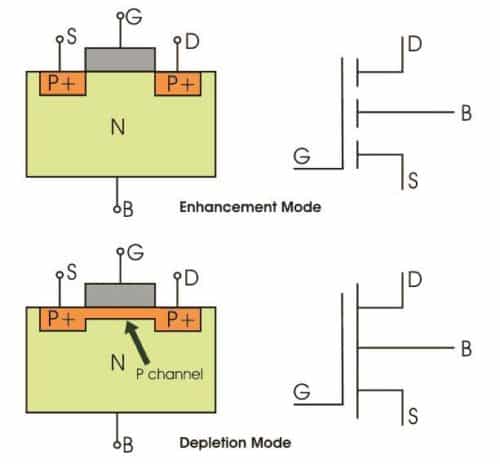
The drain and source are heavily doped P+ region and the substrate is in N-type impurities. The current flows because of the flow of positively charged holes also called P-channel MOSFET. When we apply negative gate voltage, the electrons present beneath the oxide layer experience repulsive force and they have pushed downward direction into the substrate, the depletion region is populated by the bound positive charges which are associated with the donor atoms. The negative gate voltage also attracts holes from the P+ source and drain region into the channel region.
2. N-Channel MOSFET
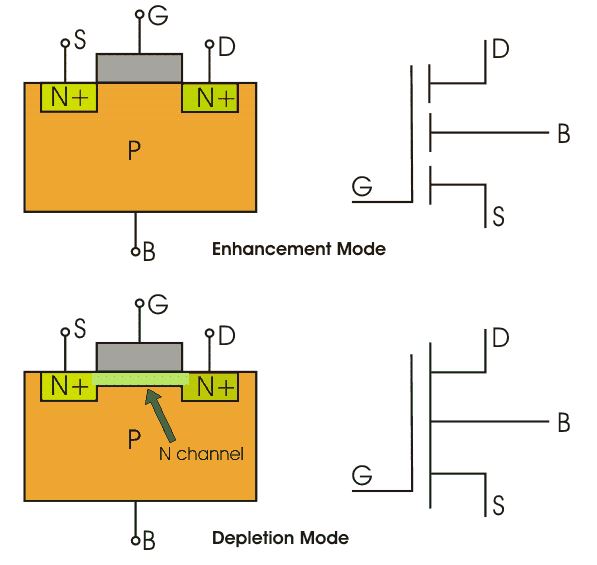
The drain and source are heavily doped N+ region and the substrate is P-type. The current flows because of the flow of negatively charged electrons, also known as N-channel MOSFET. When we apply the positive gate voltage the holes present beneath the oxide layer experience repulsive force and the holes are pushed downwards into the bound negative charges which are associated with the acceptor atoms. The positive gate voltage also attracts electrons from the N+ source and drains the region into the channel hence an electron reach channel is formed.
Applications of MOSFET
- MOSFET is used in modern days calculators.
- It is used in microprocessors.
- It is used in integrated circuits.
- It is used in electronic chip cards or electronic memories.
- It is used in logic CMOS gates.
- MOSFET is used in analog switches.
- It works as an amplifier.
- MOSFETs work as an oscillator.
- It is used in automobile sound systems.
