Introduction:
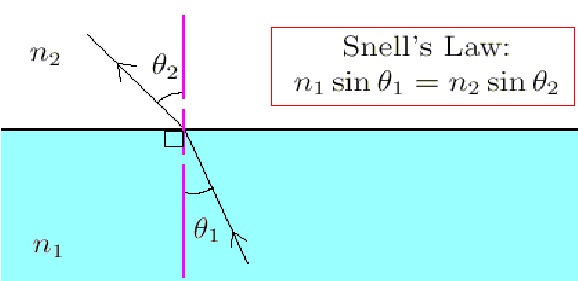
Snell’s Law is also called the Law Of Refraction. Snell’s law tells us about how much a refracted ray will bend when it passes from one medium to another medium. So, let’s say a light ray is passing from a denser medium to a rare medium then Snell’s law will give us the value that how much the refracted ray will bend away from the normal when it will enter rarer medium and vice versa.
So, in simple words, we can say that Snell’s law provides a degree of refraction. It also gives a relation between the incident angle, refraction angle, and the refractive index of the two mediums in which rays are traveling.
Snell’s Law:
Snell’s Law can be defined as the ratio between the sine of the angle of the incident to the sine of the angle of refraction which is constant.
So according to Snell’s Law, it’s for formula can be written as –
Sini/Sinr = Constant = μ
i = Incident angle.
r = Refraction angle.
μ = Constant = This represents the refractive index of the second medium with respect to the first medium.
So, This Can Be Written As –
Sini/Sinr = nr/nd
Sini X nd = Sinr X nr
nr = Refractive index of the rare medium
nd = Refractive index of the denser medium
So, when the angle of the incident becomes equal to the critical angle then the refraction angle becomes ninety degrees.
That means –
Sini = Sinic
Sinr = Sin90°
Sin90° = 1
Sinic = Critical angle
So,
Sinic / Sin90° = nr/nd
Sinic/1 = nr/nd
Sinic = nr/nd
So, If Light Rays Travel From Water To Air Then –
Sinic = 1/nw
1 = Refractive index of air
nw = Refractive index of water
