Table of Contents
What Is Arch Foundation?
Arch foundation is a type of footing used to support heavy structures or when ground conditions are not stable enough to support conventional footings.
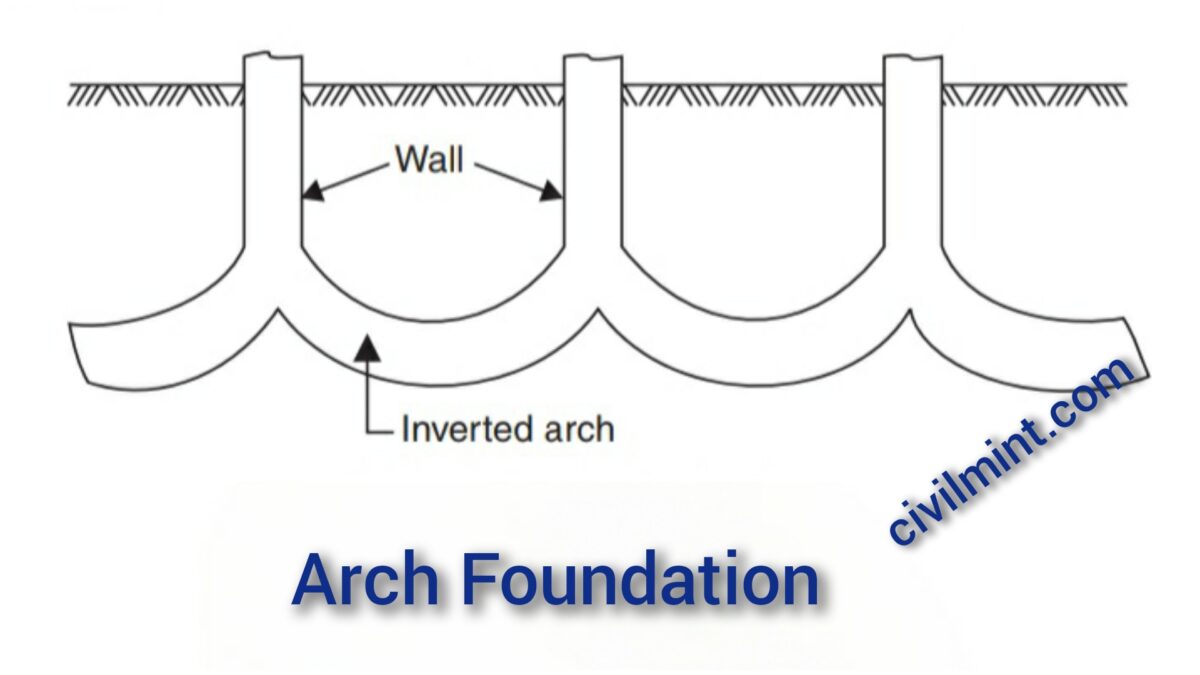
A foundation consists of a series of arches, usually made of brick or stone, that are built underground and distribute the weight of the structure over a large area.
This provides greater stability and reduces the risk of settling or sinking.
Arch foundations are commonly used in situations where there are multiple load-bearing walls that need to be supported or when it is necessary to span a large area.
However, their design and construction require careful planning and expertise, which makes them more expensive than other types of footers. Despite this, arch foundations are known for their durability and stability over a long period of time.
What Is Inverted Arch Foundation?
An inverted arch foundation is a type of foundation that is designed to transfer the load of a structure to the soil beneath it. This type of foundation is commonly used in areas where the soil bearing capacity (SBC) is poor and the load of the structure is carried by walls.
In these cases, inverted arches are built between the walls to provide stability and prevent settling or shifting over time.
However, it’s crucial to note that end walls must be thick and strong enough to withstand the outward horizontal thrust caused by the arch action.
To further strengthen the outer walls, buttress walls may be added. Although constructing an inverted arch foundation can be more complex and expensive than traditional foundations, it is a good option for buildings that require a strong and stable foundation in areas with poor soil conditions.
Faqs
Inverted arch foundations distribute weight evenly between load-bearing walls where soil bearing capacity is poor.
End walls should be thick and strong to withstand horizontal thrust, while outer walls may have buttress walls to resist lateral forces.
