Table of Contents
What is Cam?
The cam can be defined as the machine parts which rotate to provide reciprocating or oscillating movements to the other machinery element called a follower. The cam and follower work together when they are in contact with each other. It can either be a point contact or a line contact. The follower reciprocates according to the shape of the cam on which it is in contact. The cam rotates at a uniform speed with the help of the shaft and follower movements are predetermined.
Cams and followers are used everywhere in this modern machinery world. The inlet and outlet valves in an Internal combustion engine is prime example of the cam and follower mechanism.
Types of Cam:
In this article, we will describe the two most common types of cam.
- Radial Or Disc Cam.
- Cylindrical Cam.
1. Radial Or Disc Cam:
The radial or disc cam can be defined as when the cam rotates at a uniform speed then the follower reciprocates or oscillates at a right angle to the direction of the axis of the cam. That means in radial or disc cam the follower rotates at the perpendicular direction to the axis of the cam to which it has contact. The radial or disc cams are the most used cams in the industries to perform various operations. Radial or disc cam has its nomenclature which includes its base circle, tracepoint, pressure angle, pitch point, pitch circle, pitch curve, prime circle, strokes, etc.

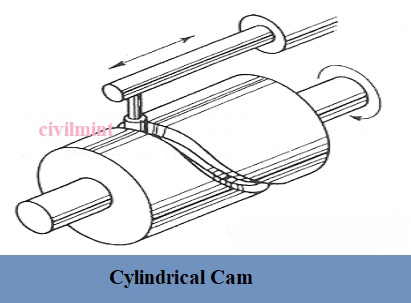
2. Cylindrical Cam:
The cylindrical cam can be defined as when the cam rotates at a uniform speed with the help of the shaft then the follower reciprocates or oscillates parallel to the direction of the axis of the cam. That means in a cylindrical cam the axis of motion of the follower is parallel to the direction of the axis of the cam. The cylindrical cam usually has a groove on its surface where the follower rides. The cylindrical cams are not used very often like radial or disc cam. So, in comparison to the cylindrical cam, the radial can is more compatible.