Table of Contents
Confined Space Entry (CSE)
Confined Space Entry (CSE) is when anyone puts any part of their body through the opening of the space.
Entry also includes all periods of time when the confined space is occupied.
For example, putting your head into a tank opening or manhole is a confined space entry.
When work tasks require you to enter into a confined space, you must follow CSE procedure and a confined space entry permit must be issued before work can start.
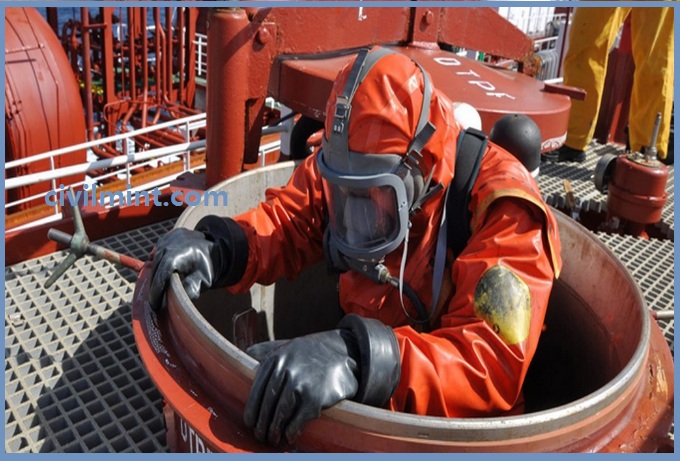

Confined Space
Confined space has limited entry and exit. A confined space can be open from one side or both sides. A confined space is not designed for human occupancy. A confined space can be open from one side or both sides.
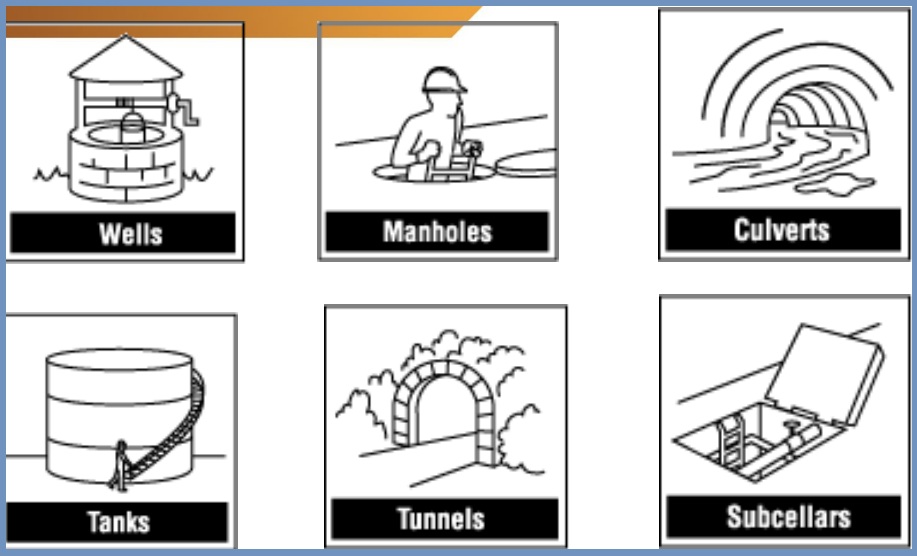
Some examples of confined spaces:
- Columns, vessels
- Storage tanks
- Pipelines
- Valve boxes
- Manholes
- Ventilation ducts
- Boilers, steam generators
- Heat exchangers
- Sewers, sumps, pits
- Barge compartments
- Excavations
Confined space may be designed for very limited entry.
Some examples of very limited entry confined spaces are:
- Manholes
- Sewer systems
- Cargo holds
- Barge compartments
- Shaft and tunnels
A confined space may not necessarily be enclosed on all sides and may have open tops.
Some examples are:
- Vats
- Storage towers
- Floating roofs of large tanks
- Trenches, excavations, pits, culverts, and sumps.
Space may become a confined space due to the work or due to a change in the conditions inside.
For example, spray painting in an enclosed room can create a hazardous atmosphere.
Also, asbestos work in an enclosed room and sealed with plastic drapes can create a hazardous atmosphere.
Unventilated or poorly ventilated spaces, storage areas, and voids may be oxygen-deficient or may develop a hazardous atmosphere.
Even a new tank can become a confined space during the late stages of assembly on location.
Confined Space Entry Permit:
In most organizations, a confined space entry permit is needed for all jobs where personnel enter into the confined space.
CSE activities in hydrocarbon processing areas can include vessel cleaning, inspecting the inside of tanks, working in sewers, sumps pits, or valve boxes, and working in excavation trenches.
