There are two theories accepted which define the characteristics of light.
The first is electromagnetic waves theory and the second one is corpuscular theory.
In this blog post, we will learn about the corpuscular theory and the rectilinear motion Of light.
Table of Contents
Introduction:
Because of light, the objects are visible in this world. If there is no light in this world, we can’t be able to see a thing. Whether it is a natural solar light or electric bulb light it helps in seeing things by removing the darkness. So, light can be defined as the form of energy that moves or travel in the form of electromagnetic waves and is made up of small energy particles called photons. The light shows two natures. Both natures of light are accepted today that’s why it is called dual nature. The electromagnetic waves theory explains the wave nature of light and how it propagates while the corpuscular theory has explained its particle nature and its other phenomena like emissions and absorption.
So let us get some idea about corpuscular theory and rectilinear motion of light.
Corpuscular Theory:
The corpuscular theory of light is given by Newton. According to the corpuscular theory, the light is made up of microparticles or corpuscular which travels in a straight line after getting emitted from its source. The microparticles of light can pass through the transparent objects and if it finds any non-transparent objects in the way then it reflects after striking the object and when these reflected rays reach our eyes, we can see the objects. For being visible the light must incident on the object for at least 1/6th second and then reflect. The speed of light concerning the refractive index of a medium varies. The speed of light is c = 3×108 m/s. But this speed is only in a vacuum. As the refractive index of a medium increases the speed of the light decreases. So, we can say that the light speed is indirectly proportional to the refractive index of a medium. White light is made up of all the seven lights which we can see in a rainbow. The sunlight takes 8 minutes and 19 seconds to reach the earth while moonlight takes 1.3 seconds to reach the earth.
Refractive Index = Speed In The Vacuum Of Light / Speed In A Medium Of Light
Rectilinear Motion Of Light:
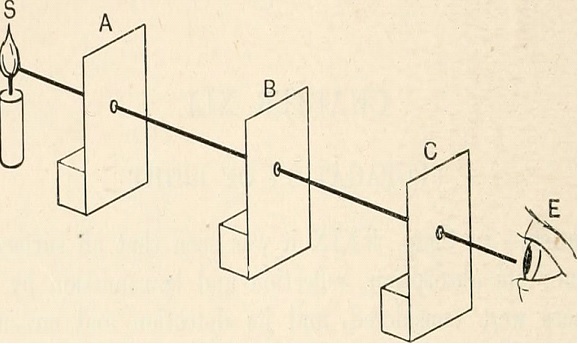
The light moves in a straight line in a medium that has constant or same density throughout called isotropic medium. This is what the rectilinear motion of light states. For example – Shadow formation, an image formed in a pinhole camera, and eclipse are some good examples of the rectilinear motion of the light. Now we will discuss both solar as well as a lunar eclipse to understand the rectilinear motion of light.
Solar Eclipse:
Solar Eclipse occurs when the moon comes in between the sun and earth. As we know according to rectilinear motion the light travels in a straight line. A big shadow of the moon directly comes on the earth and because of that shadow, we can’t be able to see the sun from the earth. That’s why this position is called a solar eclipse.
Lunar Eclipse:
In a lunar eclipse, the earth comes in between the sun and the moon. Since light travels in a straight line according to rectilinear motion. A shadow of the earth directly comes on the moon and due to which the moon is not visible from the earth. That’s why this position is called the lunar eclipse.
These eclipses can be full or partial depending on the position of the sun, moon, and earth. So, these phenomena correctly explain the rectilinear motion of the light.
