Table of Contents
What Is A Rail Gauge?
Rail gauge is the distance between the inner faces of the two rail tracks.
In United States Of America, rail gauge is known as track gauge.
See the image of rail gauge as shown below.
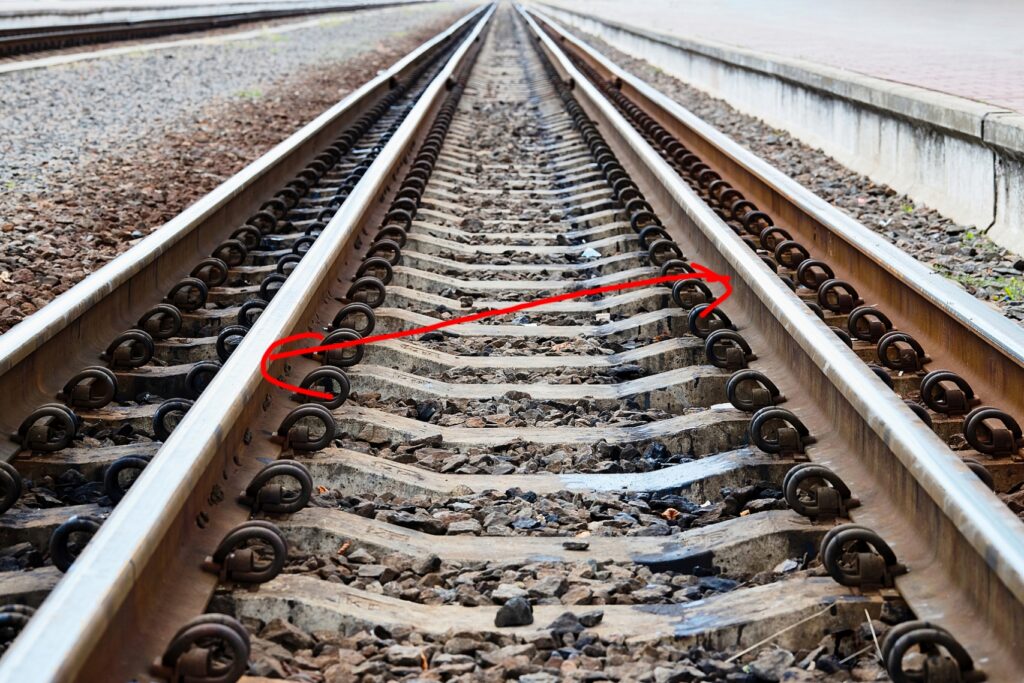

The term gauge refers to the metal bar used to check that the rails are at the correct distance. Two additional gauges are also used by the railroad to meet a required standard.
A rail network requires that all vehicles have wheels that fit the track gauge. Gauge discrepancies often hinder extensive functioning on railway networks as many different track gauges are used around the world.
Types of Rail Gauges
- Standard Gauge or Broad Gauge
- Meter Gauge
- Narrow Gauge
- Feeder Track Gauge or Light Gauge
1. Standard Gauge or Broad Gauge
Broad Gauge is the term used to describe a gauge where the open space between the inner sides of the two tracks is 1.676 meters. The Standard Gauge is another name for this.
2. Meter Gauge
The gauge is known as Meter Gauge if the horizontal distance between the inner faces of two rails is 1.0 meter.
3. Narrow Gauge
The gauge is referred to as narrow gauge when the clear space between the inner sides of the two rails is 0.762 meter. These gauges are primarily utilized in hilly and sparsely populated areas.
4. Feeder Track Gauge or Light Gauge
In this type of rail gauge, the clear space between the inner sides of the two rails is 0.61 meters. Light gauge is used in India and South Africa.
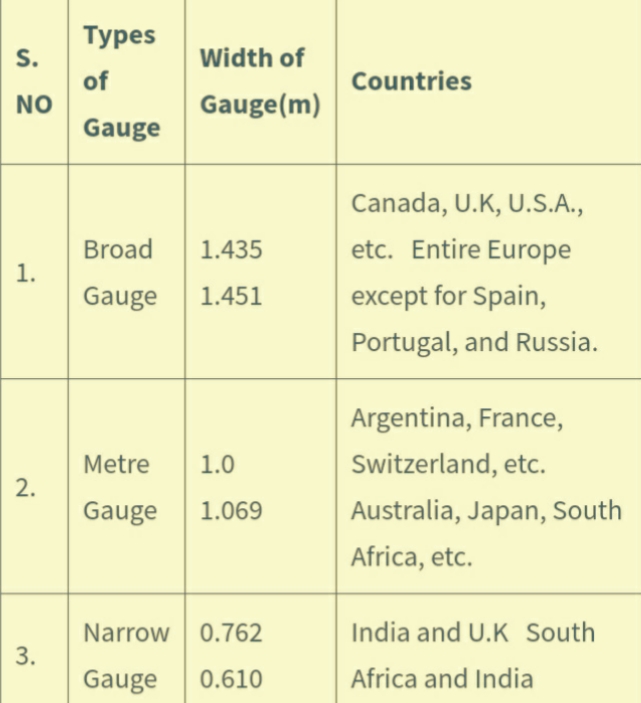
Types Of Rail Gauges In Different Countries
In the below picture, I have shown types of gauges used in different countries.
Factors Influencing The Adoption Of A Specific Gauge
The following variables influence the selection of various gauges:
- Construction costs and available funding for the railroad project.
- the quantity and type of traffic.
- how densely people are living.
- Commercial and industrial growth in the area.
- future development possibilities for the area.
- geographical and geological characteristics of the nation.
- Movement must be swift.
Advantages Of Uniform Gauge
- It is prevented from being expensive and difficult to change cargo and passengers from one gauge of vehicle to another.
- Moving labor costs are reduced.
- Shifting-related product damage is avoided.
- Elimination of the possibility of theft and loss during the relocation process.
- There is no need for large sheds to store products.
- Train service and operation are unaffected by labor strikes and other such events.
- If the gauge is consistent, wagons can be operated effectively on all of the rails.
- A consistent gauge can be used to properly operate locomotives on all of the lines.
- If the gauge is uniform, there is no time spent when moving soldiers and equipment during military operations.
- Avoiding the need for additional platforms, sanitary facilities, etc.
FAQ
What Is The Spacing Of Standard Gauge?
The spacing of standard gauge between two inner rail track is 1.676 meters.
What Is The Spacing Of Narrow Gauge?
The spacing of narrow gauge between two inner rail track is 0.762 meter.
