Various types of footings are used in construction. Footing is the most important part of the structure that transfers loads of a structure to the underlying soil.
In this blog article, I will describe the types of footing.
Selection of Footings depends upon the following factors:
- Depth of Soil at which safe bearing strength exists.
- Types and Condition of Soil.
- Types of Superstructure.
We have listed some common types of footing used in the field of construction.
- Strip or Wall Footing
- Spread Footing
- Isolated Footing
- Stepped Footing
- Combined Footing
- Strapped Footing
Let’s discuss these types of footing in brief.
Table of Contents
Types of Footing:
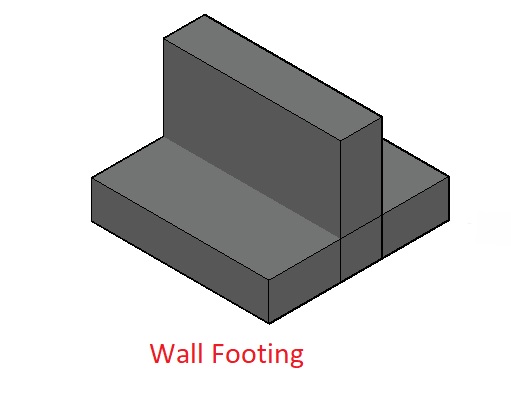
1. Strip or Wall Footing
The component of the Shallow foundation distributes the weight of the wall across the area of ground.
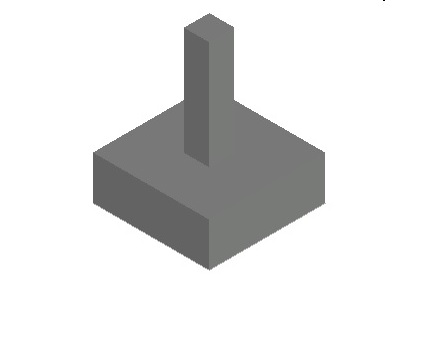
2. Spread Footing
Spread is given under the base of the foundation so that load of the structure is distributed on the wide area of soil.
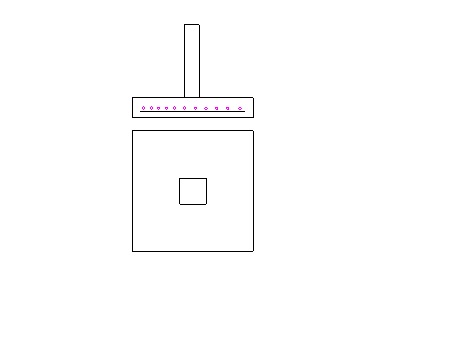
3. Isolated Footing
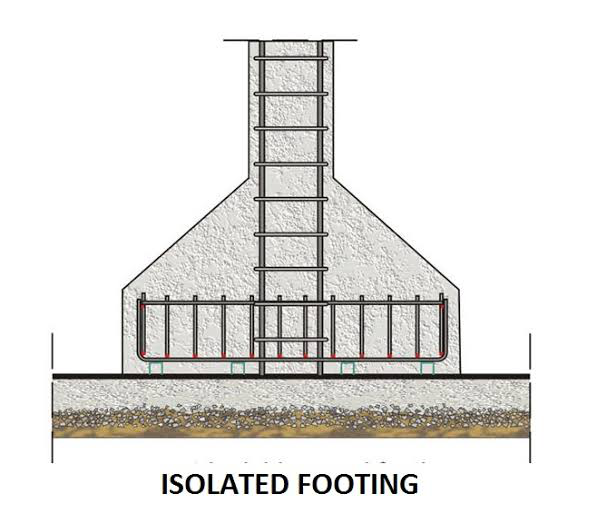
It is a sequence, circular, or individually rectangular slab of Uniform thickness provided under each column.
4. Stepped Footing
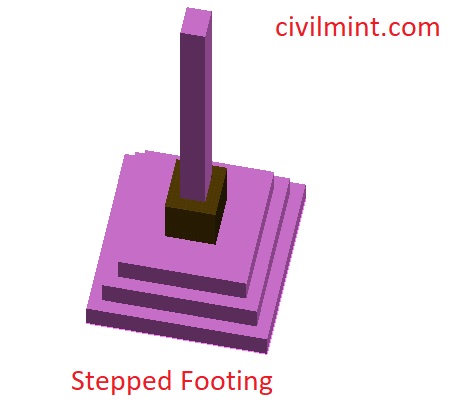

The primary purpose of using Stepped footing is to keep the metal columns away from direct contact with soil to save them from the corrosive effect.
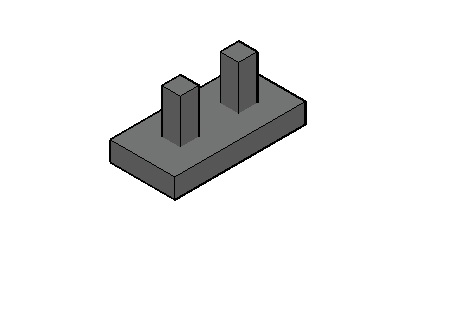
5. Combined Footing
At least two columns are supported by a footing. This footing may be rectangular or trapezoidal in plan.
Combined footings are provided under the following situations:
- Columns are close to each other and their individual footings overlap
- Soil having a low bearing capacity and requires more area under individual footings
- The column end is situated near the property line and the footing cannot Extended.
6. Strapped Footing
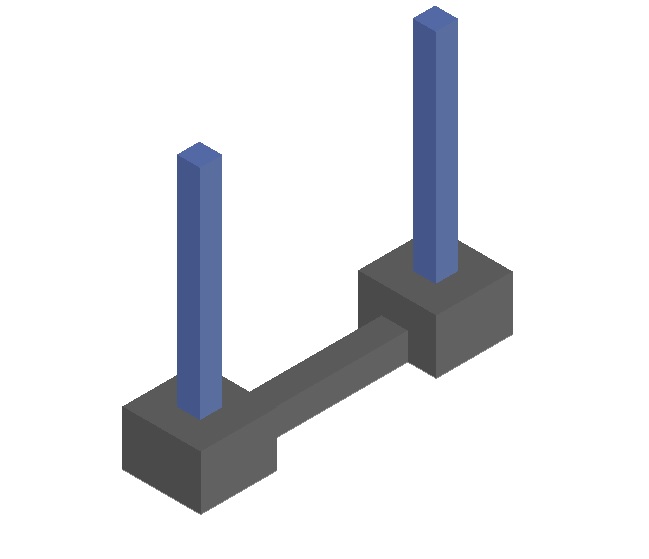
The outer and inner column is connected by the strap beam, The main purpose of the strap beam is to distribute and transfer the weight of eccentrically loaded column footings to adjacent footings as shown above.
Conclusion:
This article was all about types of footing. I have described important types of footings such as strip footing, spread footing, isolated footing, stepped footing, combined footing, and strapped footing.
These footing commonly used in the field of construction. Civil engineering students and professionals must have knowledge of these footings.
FAQS
Some common types include spread footings, shallow foundations, deep foundations, pile foundations, crawlspace foundations, and slab foundations.
The type of footing that is best suited will depend on various factors such as the soil conditions, load-bearing requirements, and local building codes.
Shallow foundations are commonly used among builders as they are relatively easy to construct and provide adequate support for most buildings.
A simple footing is a type of shallow foundation that is used to support a single load-bearing point, such as a column or a wall.
Four types of footings are commonly used, including spread footings, shallow foundations, deep foundations, and pile foundations.
The standard size for a footing can vary depending on local building codes and the load-bearing requirements of the specific construction project.
The maximum depth of a footing will depend on factors such as soil conditions and local building codes.
The minimum depth of a footing will depend on factors such as soil conditions and local building codes.
The thickness of a footing will depend on factors such as soil conditions, local building codes, and load-bearing requirements of the specific construction project.
The size of a footing can be determined by considering factors such as soil conditions, local building codes, and the load-bearing requirements of the specific construction project.
A minimum grade of M20 concrete is recommended for constructing footings to ensure adequate strength and durability.
A minimum grade of M20 concrete is recommended as it ensures adequate strength and durability of the footing.

At first I congratulate you on this nicely presented article. It is quite informative.
Would you please elaborate the difference between FOOTING and FOUNDATIONS.
Generally, the footing is a sort of shallow foundation. Foundation can be shallow or profound. Footing incorporates section, rebar which are manufactured of brickwork, stonework, or cement. Foundation incorporates piles, caissons, footings, docks, the horizontal backings, and anchors.