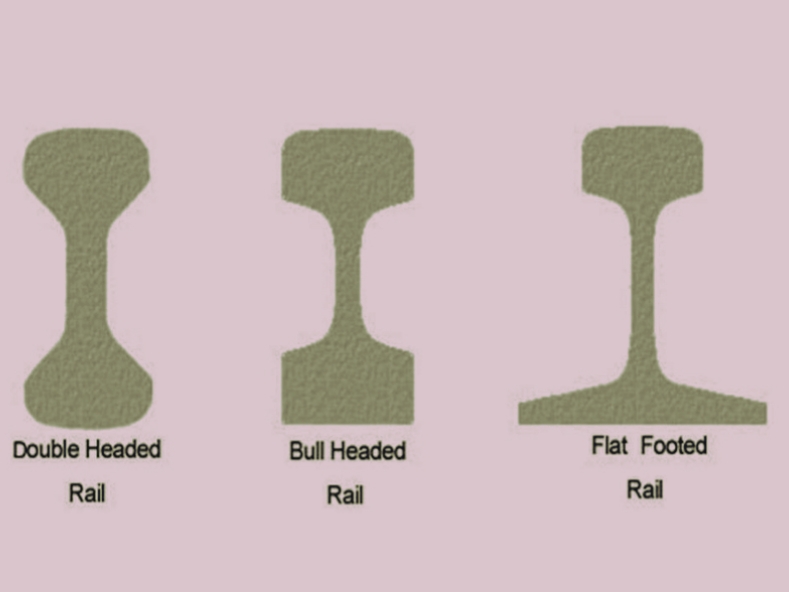
There are 3 types of rail sections used in the construction of railway track. These are double headed rails, bull headed rails and flat footed rails.
We will learn about these three types of rails in detail.
Let’s start!
Table of Contents
1. Flat Footed Rails ( F.F. Rails)
Flat-footed rails are the name given to the rail sections because of its flat foot. These rails are stronger and more rigid than double-headed and bull-headed rails. These types of rails are most popular in India and South Africa.
Flat Footed Rail Benefits
- These rails are stiffer and stronger.
- It is easier to fit rails with sleepers so they can be placed and re-laid with ease.
- There are no chairs or keys needed, unlike with B.H. rails.
- It is simple to maintain points and crossings built with these rails.
- They improve the track’s stability, extend its life, and lower maintenance costs.
- These rails are less expensive than other rail kinds.
- Fewer fastenings are needed for these rails.
Issues With Flat Footed Rails
- Frequent loosening of the fitting.
- It is challenging to straighten bent rails, replace rails, and de-hog battered rails.
- When there is a lot of train weight, these rails dig into the wooden sleepers. They therefore need a bearing plate to solve this issue.
- It is challenging to make points and cross these rails.
2. Bull Headed Rails (B.H. Rails)
Bull headed rails are rails that have a head that is a little bit thicker and stronger (Bull size) than the lower half. Compared to rails with flat feet, these rails are less strong and sturdy. Typically, bull headed rails are used to build points and crossings.
Bull Headed Rails Benefits
- They provide a more stable and smoother track while maintaining greater alignment.
- The rails are simply removed and rapidly replaced. Therefore, track renewal is simple.
- The hefty chair, which has a significant influence on the sleepers, increases the track’s stability and extends the life of the wooden sleepers.
- These rails make it simple to create points and crossings.
Negative Aspects Of Bull Headed Rails
- They demand pricey fastenings.
- They are less stiff and strong.
- They demand expensive maintenance.
3. Double Headed Rails
Rail sections with the same head and foot dimensions are known as double head or dumbbell rails. These rails are less strong and less rigid than flat foot rails. These rails are very rarely used nowadays.
FAQ
What Is A Rail?
A rail is a steel rod that extends horizontally between two supports and serves as a track trains.
