Geotextiles are permeable fibrous materials used to increase soil stability, control erosion, and facilitate drainage. Depending on the manufacturing process, it can be geotextile woven or non-woven geotextile fabric depending on the type of application.
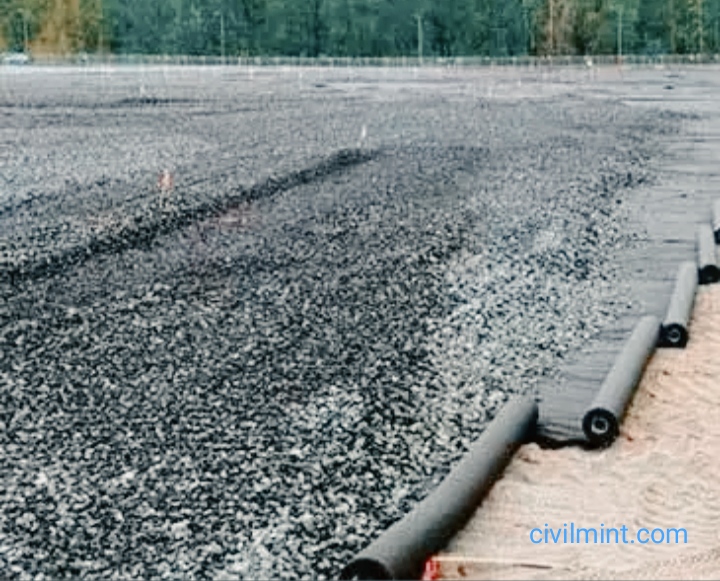

Woven fabrics and non-woven fabrics have different manufacturing processes. Geotextile non-wovens contain fibers, filaments, or other elements that are randomly connected, whereas in woven fabrics, these threads, fibers, or filaments are intertwined. This new post focuses on the application properties of woven geotextiles.
Table of Contents
Types of Geotextiles
Normally, there are three types of geotextile as listed below.
- Non-woven Geotextile Fabric
- Woven Geotextile Fabric
- Knitted Geotextile
Lets discuss about these three types of Geotextile.
1. Non-woven Geotextile Fabric
It resembles felt and ensures even water flow. They are commonly known as filter fabrics, but woven monofilament geotextiles are also sometimes called filter fabrics.
Non-wovens are arranged in rolls and despite their strength and toughness, they are light and easy to handle.
Offers greater flexibility and mobility than woven geotextiles. This makes them ideal for use in isolation. The thickness and perforation resistance of non-woven geotextiles provide geo membrane cushioning and protection in applications such as landfills, ponds, drains, dams, rivers, coastal construction, barriers and mining projects.
Non-woven geotextile is also used in applications where filtration and dewatering are required due to its small opening size and ability to filter small particle sizes that allow water to pass through. Perfect for parting applications on both asphalt and concrete pavements.
2. Woven Geotextile Fabric
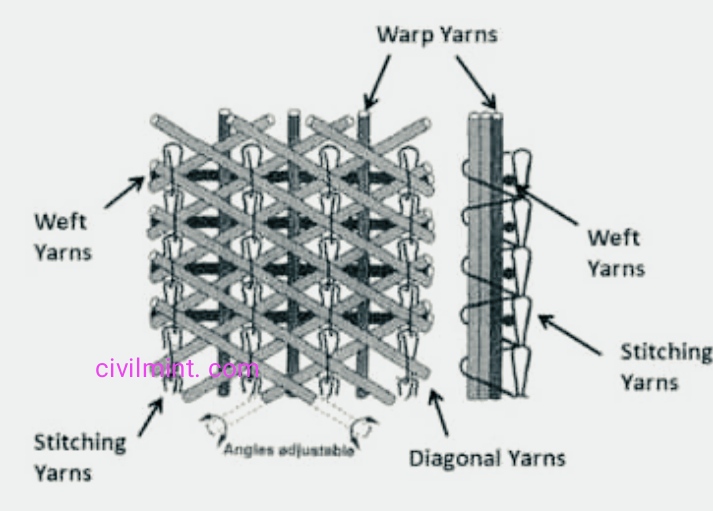
Woven geotextiles are produced by a textile process in which two or more threads, fibers, filaments, strips, or other elements are woven together, usually at right angles, i.e., both in the warp and weft directions. These substances are mainly used in the construction sector.
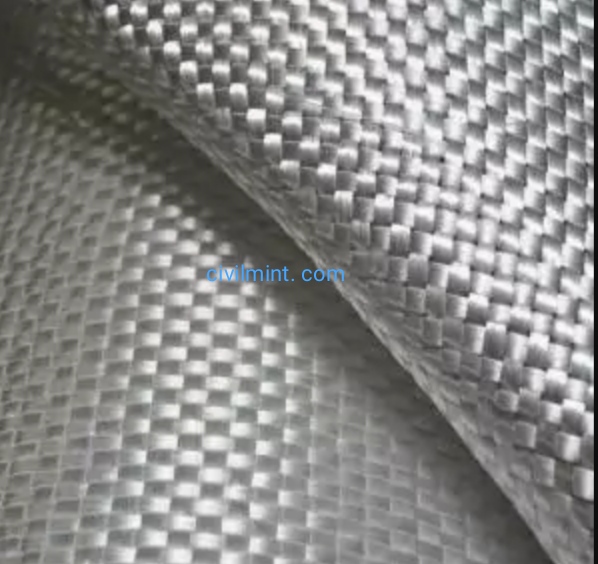

Woven geotextile provides biaxial resistance. H. In the same direction they were made. Due to the structure and properties of the tapes used in their manufacture, they are usually strong and less deformable, making them suitable for reinforcing roads, embankments, walls and foundations. Strand comes in his two varieties: flat slit foil and round monofilament.
Woven Slotted Sheet Geotextile is generally suitable for applications where high strength properties are required and filtration requirements are less critical. These fabrics reduce localised shear failure in weak ground conditions and aid construction in soft ground.
3. Knitted Geotextile
Knitted geotextiles are made by interlacing a series of yarn loops. All knitted geosynthetic are manufactured using knitting techniques in combination with another geosynthetics manufacturing process such as knitting, a weave is formed.
Apart from these three geotextiles, geo synthetics such as geo nets, geo grids, geo cells, geo membrane and geo composites are used, each with its own characteristics and applications.
What are the Functions of Geotextiles?
Six separate functions that define how geotextiles work in any application:
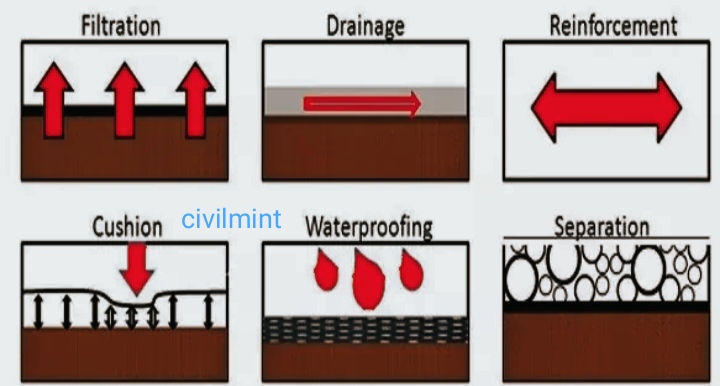
1. Separation
Geotextile separation function is mainly used for road construction. Geotextiles prevent mixing of two adjacent soils. For example, by separating the fine subgrade from the base course aggregate, geotextiles retain the drainage and strength properties of the aggregate material.
2. Filtration
The geotextile-to-soil system balance allows for adequate fluid flow and limits soil loss across the geotextile surface. Porosity and permeability are the most important properties of geotextiles with permeation effects.
A common application that illustrates the filtration function is the use of geotextiles in rim drains, as shown in the diagram above.
3. Reinforcement
Placing geotextile on the ground increases the tensile strength of the ground by the same amount that steel does with concrete. Strength gained in the ground with the introduction of geotextiles.
4. Sealing
A geotextile fleece layer is impregnated between the existing and new asphalt layers. Geotextiles absorb asphalt and become a waterproofing membrane that minimizes vertical water flow into the pavement structure.
Uses of Geotextile Fabric
- Railway
- Roads
- Agriculture
- Drainage
- Coastal work
