In reinforced concrete structures, understanding the differences between clear cover, nominal cover, and effective cover is crucial for ensuring the durability and strength of the construction.
The concrete cover is provided in all structural members like footing, column, beam, slab, etc. It is provided for a long life of the concrete structure and to prevent the concrete structure from rust and corrosion.
This article provides an in-depth explanation of each term, their significance, and their impact on the structure’s overall performance. Gain insights into the importance of cover in RCC by reading this informative article.
Table of Contents
Difference Between Clear Cover, Nominal Cover, And Effective Cover
What is Clear Cover in Concrete?
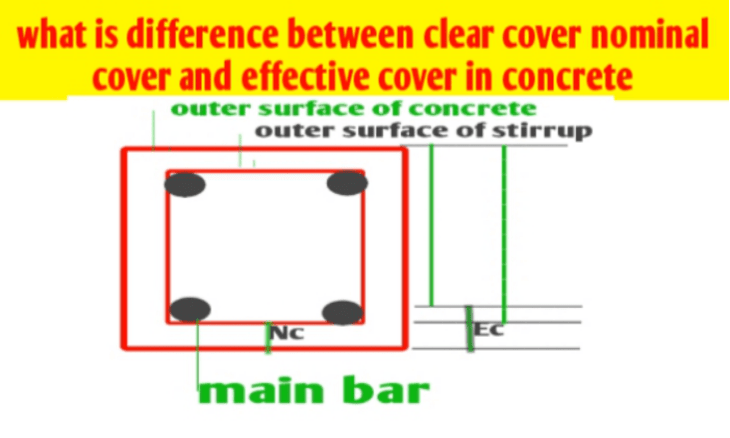
The clear cover is the least and minimal distance between the external face of concrete fiber and the external face of main reinforcement with link excluding the thickness of Plaster and finishing of concrete. Generally, At the construction site, a clear cover is called a concrete cover. So If anyone talking about the concrete cover that would be a clear cover.
What is a Nominal Concrete Cover?
The nominal concrete cover is the least and minimal distance between the outer face of concrete fiber to the main reinforcement inserted inside the construction structure. Nominal cover can be defined as is the design depth of concrete cover to all Steel including link/stirrups etc. As per IS 456 (Clause 26.4.1), the term clear cover is replaced by the nominal cover.
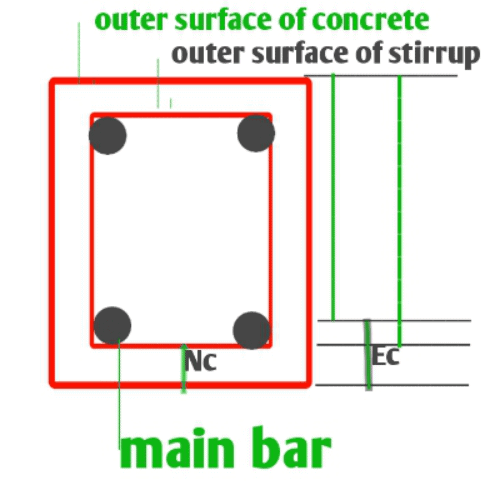
What is Effective Cover?
The effective concrete cover is the least and minimal distance between the outer face of concrete fiber to the half diameter of the main reinforcement which is inserted inside the construction structure.
Hence, the effective cover is the sum of clear concrete cover and half diameter of main reinforcement.
Effective cover = nominal cover + the half diameter of reinforcement
Role of Clear Concrete Cover:
- It is provided for the long life of the concrete.
- The clear cover is used to protect the reinforcement is surrounded by sufficient concrete cover to prevent the concrete from atmospheric conditions which make concrete corrode.
- The outermost face of concrete fiber works as a thermal insulator and prevent reinforcement to shield it.
- The clear cover provides sufficient embedding to the reinforcement bar to facilitate them to be stressed without losing grip.
- Clear cover of concrete protects the reinforcement from environmental conditions moisture and soil.
- The thickness of a clear concrete cover depends on the environmental circumstances and type of structural member.
Clear Cover for Different Structural Members
| Structural member | Normal Dry Climate | Wet Climate |
| Beam | 25-40 mm | 35-40 |
| Column | 40 mm | 50 mm |
| slab | 20-25 mm | 25-30 mm |
| footing | 50-60 mm | 60-75 mm |
Advantages Of Concrete Cover
1. Corrosion protection:
The primary function of the concrete cover is to protect the reinforcement steel bars from corrosion, which can occur due to exposure to harsh environmental conditions, such as water, humidity, and chemicals. A sufficient concrete cover helps to prevent corrosion, which can weaken the structure and reduce its service life.
2. Durability:
Concrete cover provides durability to reinforced concrete structures by protecting the embedded steel from external factors that may cause damage, such as abrasion, impact, or fire. This ensures that the structure can last for a long time without needing extensive repairs or replacements.
3. Fire resistance:
Concrete is a non-combustible material and provides good fire resistance to reinforced concrete structures. The concrete cover on the reinforcement steel bars helps to maintain the integrity of the structure during a fire, preventing it from collapsing.
4. Increased strength:
An adequate concrete cover helps to increase the strength of reinforced concrete structures by providing better bonding between the reinforcement steel bars and the surrounding concrete. This improves the load-carrying capacity of the structure and makes it more resilient to external forces.
5. Aesthetics:
Concrete cover can also enhance the aesthetic appeal of the structure by providing a smooth, finished surface. This can be particularly important in architectural applications where the appearance of the structure is important.
Faq
The footing is in direct contact with the soil. The water present in the soil can react with reinforcement. Due to the reaction between water and reinforcement, rust and corrosion can occur. Due to rust and corrosion footing can damage. So, to prevent rust and corrosion size of the footing is to provide more than another structural member like beam, column which is normally not in the direct contact of soil.
To prevent corrosion from attacking, covering is utilized. Reinforcement is susceptible to corrosion and fire due to environmental factors. In case the appropriate covering is not employed, the likelihood of corrosion and cracks in hardened reinforced concrete (RCC) increases.
Covering is essential for every component of the building (such as slabs, beams, and footings) that involves the use of reinforcement. The purpose is to ensure the proper placement of the reinforcement and to provide adequate covering using covering blocks.
