Table of Contents
Definition
The flakiness index measures the proportion (by weight) of stones in an aggregate that possess an aspect ratio less than 0.6 times their mean size.
What Is Flaky Aggregate?
Flaky aggregate refers to an aggregate particle with a least dimension (thickness) that is less than 0.6 of the mean of the smallest sieve size through which the particle passes and the largest sieve size on which the particle is retained.
These types of aggregates tend to pack more tightly than cubical aggregates, leading to seals with fewer voids. Consequently, they require less binder.
Description Of Flakiness Index
The process to determine the flakiness index of aggregates involves first obtaining the weight of each fraction of the aggregates that pass through or are retained by a specific set of sieves. The aggregates are then prepared and weighed after passing through a gauge of a specific thickness.
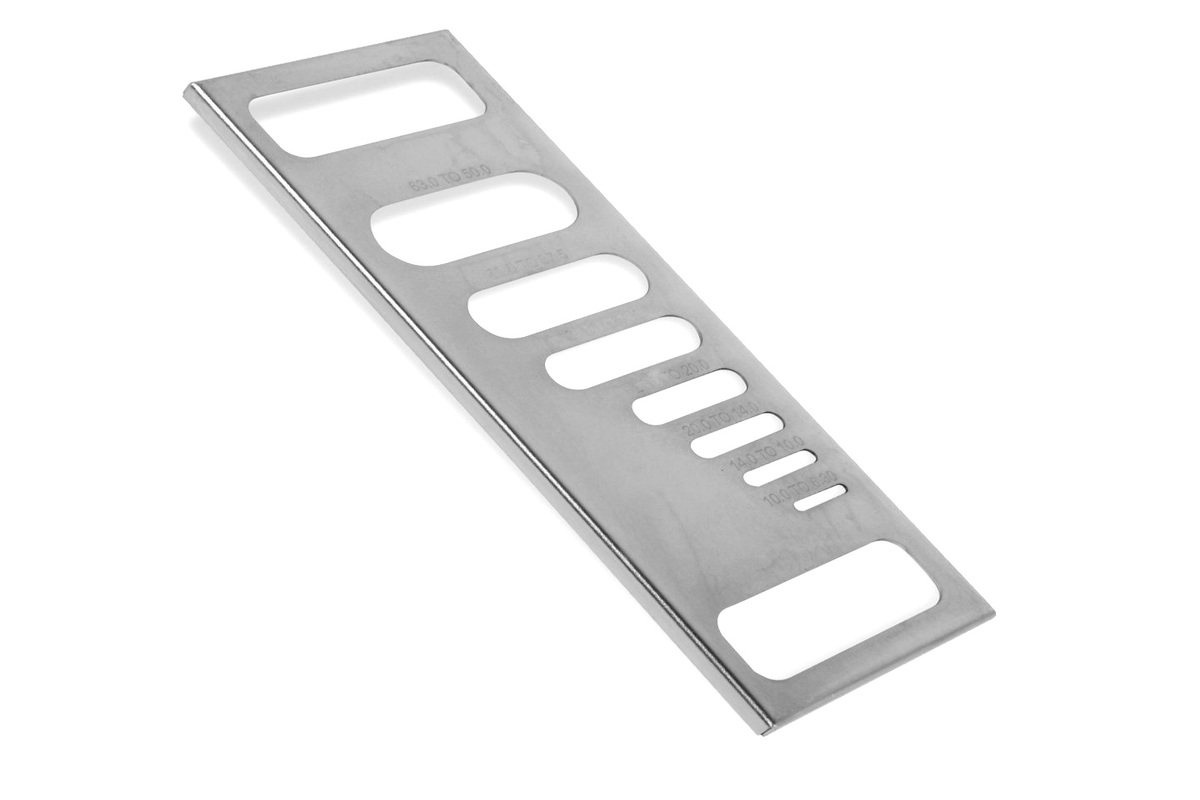
The flakiness index is calculated as the percentage of the total weight of the material that passes through various thickness gauges, with W2 representing the weight of material passing through a gauge of 0.6 times the mean size of the sample, and W1 representing the total weight of the aggregates.
It is recommended that the flakiness index of aggregates used in road construction should be less than 15% and typically not exceed 25%. Flaky particles should not be used in the construction of roads, especially in surface courses, as they can easily break down when subjected to loads along their thin axis.
Therefore, it is crucial to test the flakiness index of particles before employing them in road construction to ensure their suitability for the job. This is the primary reason for conducting the flakiness index test.
What is Elongation Index?
The elongation index refers to the percentage, by weight, of particles whose greatest dimension is more than 1.8 times the mean dimension of particles. The measurement of the elongation index involves the use of particles that pass through a mesh size of 63 mm and are retained on a mesh size of 6.3 mm. The determination of the elongation index is critical in identifying the presence of elongated aggregate particles in a mixture that can disrupt the packing of particles and create additional space.
Elongated particles possess a high ratio of surface area to volume, leading to a significant reduction in the workability of concrete. The use of elongated particles for constructing the pavement base course can lead to the easy breakdown of the pavement under heavy load or stress. Thus, it is imperative to comprehend the elongation index of a given aggregate mix.
Flakiness Index Vs Elongation Index
The flakiness index measures the percentage of stones whose average minimum dimension is less than 0.6 times the mean dimension of the stones. In contrast, the elongation index gives an estimate of the total weight of a material placed on various length gauges, expressed as a percentage of the total weight of the sample. The main difference between the two indices lies in the fact that the flakiness index determines the concentration of flaky particles in a sample, whereas the elongation index determines the concentration of elongated particles in a sample.
Faqs
The Flakiness Index measures the proportion of flat and elongated particles in an aggregate. It’s important in road construction because flaky particles can easily break down when subjected to loads along their thin axis, leading to pavement failure.
The Flakiness Index measures the concentration of flat and elongated particles in a sample, while the Elongation Index measures the concentration of elongated particles.
