Mutual interaction between antigen and antibody is known as antigen antibody interaction. In this blog post, we will learn about antigen antibody interaction in detail.
Table of Contents
Antigen (Ag)
In immunology, an antigen(Ag) is a molecule or molecular structure or any foreign particulate matter or a pollen grain that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune response. The term antigen originally referred to a substance that is an antibody generator.acid Antigens can be proteins, peptides (amino acid chains), polysaccharides (chains of monosaccharides/simple sugars), lipids, or nucleic acids.
Antigens are large molecules of proteins, present on the surface of the pathogen- such as bacteria, fungi viruses, and other foreign particles. When these harmful agents enter the body, it induces an immune response in the body for the production of antibodies.
Antibody (Ab)
An antibody (Ab)also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig),is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognised a unique molecule of the pathogen, called an antigen.Each tip of the “Y” of an antibody contains a para tope (analogous to a lock) that is specific for one particular epitope (analogous to a key) on an antigen, allowing these two structures to bind together with precision. Using this binding mechanism, an antibody can tag a microbe or an infected cell for attack by other parts of the immune system, or can neutralize it directly (for example, by blocking a part of a virus that is essential for its invasion).
An antibody is a component that the immune system produces in response to antigens. Thus, antigens result in the production of antibodies. They act together to exhibit an immunological response. The general characteristics of an antibody are as follows:
- An antibody is also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig)
- They are Y-shaped
- Glycoproteins
- Generated by plasma B-cells.
- Paratope is the name of the antigen binding site.
- Five types: IgG, IgA, IgM, IgE, and IgD.
Antigen-Antibody Interection

Antigen-antibody interaction, or antigen-antibody reaction, is a specific chemical interaction between antibodies produced by B cells of the white blood cells and antigens during immune reaction. The antigens and antibodies combine by a process called agglutination.
It is the fundamental reaction in the body by which the body is protected from complex foreign molecules, such as pathogens and their chemical toxins. In the blood, the antigens are specifically and with high affinity bound by antibodies to form an antigen-antibody complex. The immune complex is then transported to cellular systems where it can be destroyed or deactivated.
The principles of specificity and cross-reactivity of the antigen-antibody interaction are useful in clinical laboratory for diagnostic purposes. One basic application is determination of ABO blood group. It is also used as a molecular technique for infection with different pathogens, such as HIV, microbes, and helminth parasites.
Structure of Antigen-Antibody
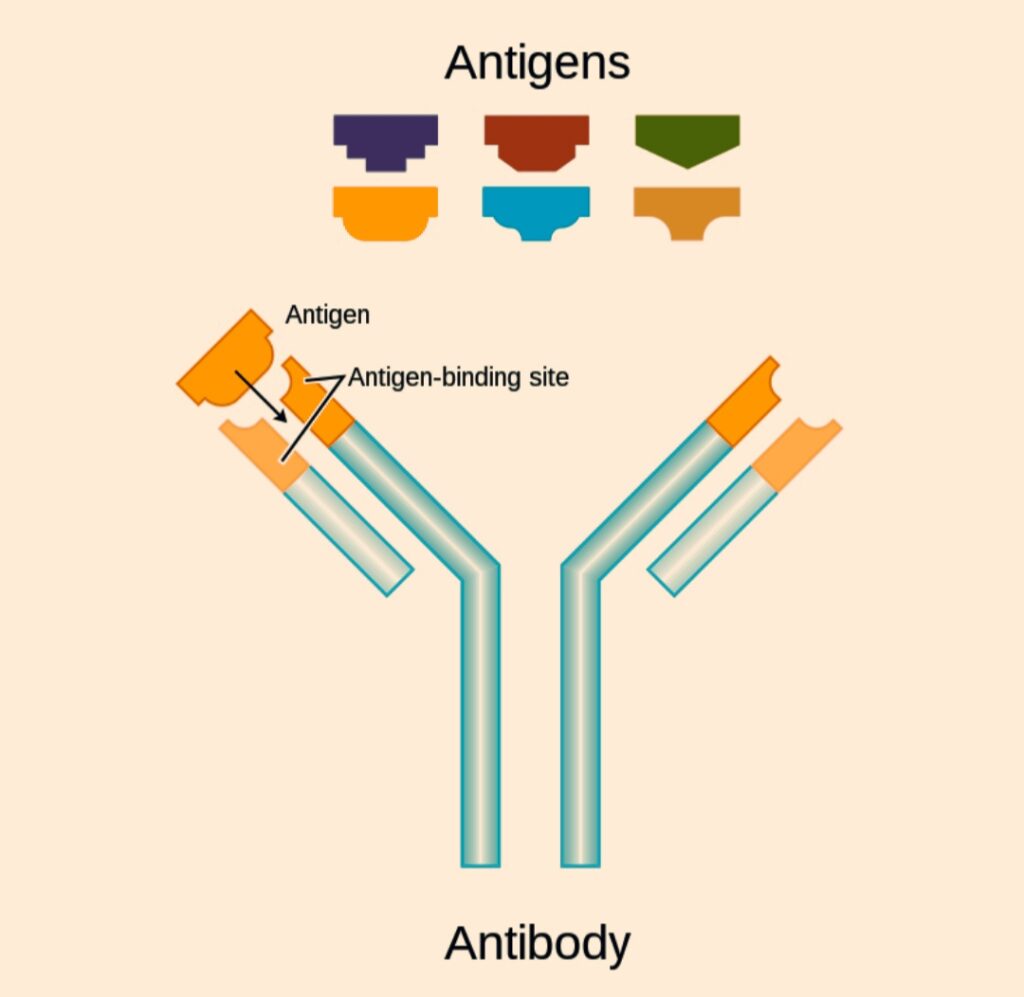
An antibody has a Y-shaped structure, made up of four polypeptide subunits. Each subunit has two identical light and heavy chains. The N-terminus of each heavy chain forms an antigen-binding domain with a light chain. There are two antigen-binding domains forming the arms of the “Y” shape.
The C-terminus of the heavy chains forms ‘fragment crystallization’ (Fc) domain, which helps in the interaction with the effector cells.
All four polypeptide subunits are held together by disulfide and non-covalent bonds.
The heavy chains of the antibodies contain a variable region and three constant regions. Each antibody has two identical antigen-binding sites and they differ in the antibodies.
Types of antigen-Antibody
The types of antigen-antibody interaction are as follows:
- Precipitation Reaction
- Agglutination Reaction
- Complement Fixation
- Immunofluorescence
- ELISA
Difference Between Antigen and Antibody
In the below image, I have shown difference between antigen and antibody.

There are some other differences between antigen and antibody. They are:
- Antigen also called Immunogens, antibody also called immunoglobulins.
- Antigens are usually lipids. However, they can also be proteins, carbohydrates and nucleic acids, all antibodies are proteins.
- Antigens have origins outside the body, Antibodies always originate within the body.
