Today we will discuss about the difference between plastering and pointing.
In the below image I have shown major differences between plastering and pointing.
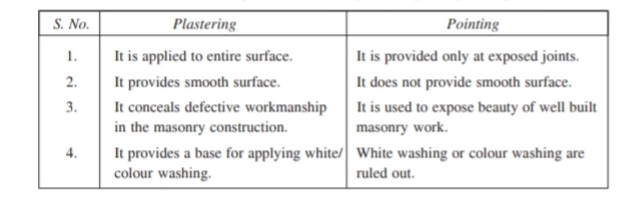
We will discuss difference between plastering and pointing in detail.
Table of Contents
Introduction
Plastering and pointing are two important techniques used in the construction industry to finish and protect the exterior and interior walls of a building.
While both techniques involve the application of a material onto a surface, they are used for different purposes and have different characteristics.
What is Plastering?
Plastering is the process of applying a thin layer of a mixture of cement, lime, and sand onto the walls of a building to provide a smooth and even surface. The plaster is applied in layers and is typically around 12mm thick.
The main purpose of plastering is to create a smooth and even surface that can be painted or wallpapered. It also helps to seal the walls and prevent dampness.
Plastering is usually done on both the exterior and interior walls of a building. Exterior plastering is known as rendering, and it is used to protect the walls from the elements and to improve the appearance of the building.
Interior plastering is used to smooth out uneven walls and to create a finish that can be painted or wallpapered.
What is Pointing?
Pointing is the process of filling in the gaps between bricks, stones, or other masonry units with a mixture of cement and sand. The pointing material is applied into the joints between the masonry units, and it is used to keep the wall weathertight and to improve the appearance of the building.
Unlike plastering, pointing is only done on the exterior of a building. It is used to repair or replace the original pointing that has been damaged by weathering or to improve the appearance of older buildings. Pointing is a specialist job and requires a skilled bricklayer to ensure that the pointing is done correctly.
Materials Used
Plastering and pointing both use a mixture of cement, lime, and sand as the base material. However, the proportions of these materials can vary depending on the type of plaster or pointing that is being used.
For plastering, a mix of 1:3 cement to lime and 3:1 sand to cement is commonly used. This creates a strong and durable plaster that can withstand the wear and tear of daily use.
For pointing, a mix of 1:3 cement to lime and 3:1 sand to cement is also commonly used. This creates a strong and durable pointing that can withstand the weathering.
Techniques
Plastering and pointing both require different techniques to be applied correctly.
For plastering, the plaster is mixed with water to create a thick, smooth consistency. It is then applied to the wall in thin layers using a trowel. Each layer is smoothed out to create a smooth surface, and the plaster is left to dry before the next layer is applied.
For pointing, the pointing material is mixed with water to create a stiff consistency. It is then forced into the joints between the masonry units using a pointing trowel. The pointing is then smoothed out to create a flush surface with the surrounding masonry.
Sum Up
Plastering and pointing are two important techniques used in the construction industry to finish and protect the exterior and interior walls of a building.
While both techniques involve the application of a material onto a surface, they are used for different purposes and have different characteristics.
Plastering is used to create a smooth and even surface on both the exterior and interior walls of a building, while pointing is used to fill in the gaps between bricks, stones, or other masonry units and to keep the wall weathertight.
Both techniques require different materials and techniques to be applied correctly and should be done by skilled professionals to ensure that the final result is of high quality.
Frequently Asked Questions
Plastering is the process of applying a thin layer of a mixture of cement, lime, and sand onto the walls of a building to provide a smooth and even surface, while pointing is the process of filling in the gaps between bricks, stones, or other masonry units with a mixture of cement and sand. The main purpose of plastering is to create a smooth and even surface that can be painted or wallpapered, while pointing is used to keep the wall weathertight and to improve the appearance of the building.
Plastering is usually done on both the exterior and interior walls of a building. Exterior plastering is known as rendering, and it is used to protect the walls from the elements and to improve the appearance of the building. Interior plastering is used to smooth out uneven walls and to create a finish that can be painted or wallpapered.
Pointing is only done on the exterior of a building. It is used to repair or replace the original pointing that has been damaged by weathering or to improve the appearance of older buildings.
For plastering, a mix of 1:3 cement to lime and 3:1 sand to cement is commonly used. This creates a strong and durable plaster that can withstand the wear and tear of daily use.
For pointing, a mix of 1:3 cement to lime and 3:1 sand to cement is also commonly used. This creates a strong and durable pointing that can withstand the weathering.
No, pointing is used to fill in the gaps between bricks, stones, or other masonry units and to keep the wall weathertight. Using pointing to smooth out a wall will not provide the same level of protection and finish as using plastering.
No, plastering is used to create a smooth and even surface on both the exterior and interior walls of a building. Using plastering to fill in the gaps between masonry units will not provide the same level of protection and finish as using pointing.
Both plastering and pointing require skilled professionals to ensure that the final result is of high quality. It is important to choose a skilled and experienced professional for your plastering or pointing project to ensure that the final result is of the highest quality.
