Table of Contents
What Is Groundwater Contamination?
Pollution in the groundwater due to such as impurities oil and salts is known as groundwater contamination. These contaminants pollutes groundwater. High contaminated water can not use for drinking.
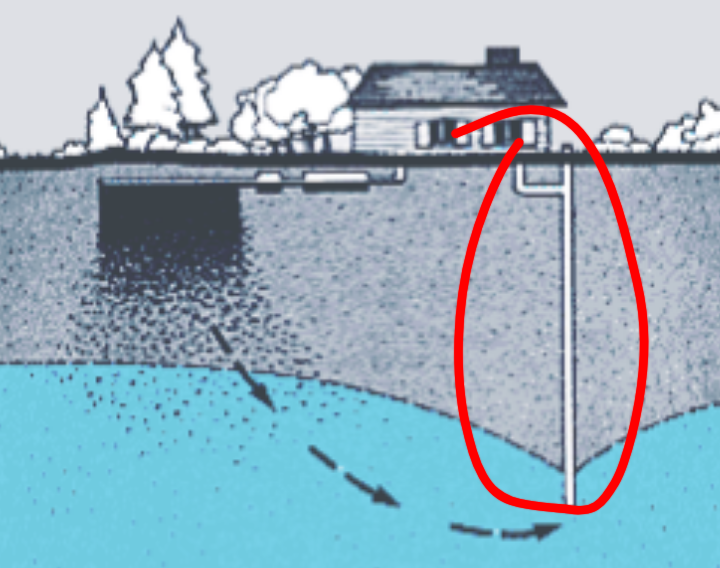
Groundwater Contamination Process
Materials from the land’s surface can travel through the soil and end up in the groundwater. For example, chemicals and fertilizers can find their way into groundwater supplies over time. Used motor oil, hazardous materials from mining sites, and road salt may also leak into the groundwater. Additionally, harmful compounds from underground storage tanks, leaking landfills, and untreated septic tank waste have the potential to contaminate groundwater.
Major Groundwater Contaminants
- Road salts.
- Grease, oily materials recovered from parking lots and other paved surfaces.
- Fuel, chemical leaks and spills.
- Mine garbage dump.
- Agricultural fertilizers, herbicides, and pesticides.
- Landfill.
- Leakage from septic tank.
- Oil leakage from pipelines.
- Uncontrolled hazardous waste.
Impacts Of Groundwater Contamination
Drinking tainted groundwater can have detrimental impacts on one’s health. Contamination from septic tank waste can result in illnesses including hepatitis and diarrhea. Toxins that have seeped into well water supplies may result in poisoning. Contaminated groundwater can potentially impact wildlife. Exposure to dirty water may potentially have other long-term impacts, such as some types of cancer.
FAQ
How Can Groundwater Be Contaminated?
When contaminants are dispersed into the earth and then find their way into groundwater, groundwater can become contaminated.
