Table of Contents
What Is Hydrographic Survey?
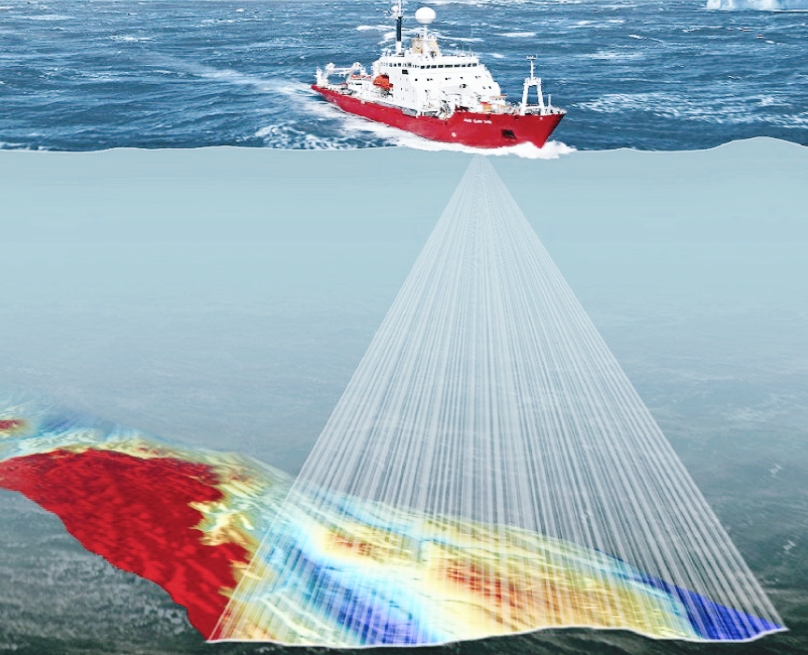
Survey of underwater objects is known as hydrographic survey. All the underwater natural objects are studied by using hydrographic survey.
There is a huge importance hydrographic survey in the field of oil and gas. Onshore and offshore drilling are conducted by using hydrographic survey.
The measurement of all submerged elements that influence all maritime activities, such as dredging, marine and construction are done by hydrographic survey.
The majority of hydrographic surveying is done for official purposes. For shallow water, it is mostly done out via sensors, sounding equipment, or electronic sensor systems.
How To Perform Hydrographic Survey?
There are 3 important steps in hydrographic survey.
- Reconnaissance
- Find Horizontal Control
- Detect Vertical Control
- Sounding
Let’s know more about these 3 steps of hydrographic survey.
1. Reconnaissance
Scouting is required because every project requires a start-up plan in order to be completed efficiently and successfully. To determine the best surveying method, a thorough reconnaissance of the entire survey area is carried out. This would make it easier to complete the survey while adhering to the guidelines and regulations that apply to such a job. Aerial photography would be useful in this study.
2. Find Horizontal Control
All land and marine features must be located in their true relative positions, which necessitates the use of horizontal control. As a result, there will be a series of lines with lengths and azimuths determined by triangulation or any other method. To prepare for rough work, tachometric and plane table surveys can be performed. There are no rules for establishing horizontal control because topography, vegetation, topography type, and topography size all have an impact on the rules.
3. Detect Vertical Control
It is critical to establish vertical control prior to sounding. Numerous benchmarks are placed to provide vertical control. Benchmarks are used to set and check the levels of gauges.
4. Sounding
Sounding is the process of determining depth beneath the water’s surface. Before proceeding with the sounding, the mean sea level must be determined. It is analogous to levelling if the reduced level of any point of a water body is determined by subtracting the sounding from mean sea level.
Applications Of Hydrographic Survey
The primary goal of hydrographic surveying is to estimate water depth, which is accomplished through bathymetric surveys. Waterway planning, dredging analysis, and wreck location are some of the other most common applications of hydrographic surveying.
Surveying is also used in the design and construction of docks, harbors, and dams. It is critical to ensure that the water depth in and around ports is sufficient to allow ships to enter and berth safely. Furthermore, the area of the seabed that supports floating structures must have a solid foundation. Dams also necessitate a thorough understanding of the surrounding terrain to ensure structural strength.
Underwater surveying can also be used to determine shorelines that extend around a coast. Preparing shore line charts is useful for conducting studies on the effects of water bodies on land and determining a country’s actual maritime border. Surveying also determines the mean sea level, which is crucial in almost every aspect of life. They influence the launch of space shuttles and rockets as well as assisting the government in charting coastlines.
FAQ
What Is Sounding In Hydrographic Survey?
Calculation of the water depth is known as sounding.
