A gyroscope is a device used to measure or maintain direction and angular rate. This is a spinning wheel or disc whose axis of rotation is free to orient itself. When rotating, according to angular momentum conservation, the orientation of this axis is unaffected by tilting or rotating the mount.
Table of Contents
What is Gyroscopic Effect?
When the device rotates around any axis it will continue to rotate around the same axis, and if you disturb or try to change the axis of rotation, it will resist the change and try to return to its original state by applying a reactive power.
Detailed Description
A gyroscope is a device consisting of two or three gimbal-mounted wheels that provide a pivot mount that allows the wheels to rotate about a single axis. One uses a set of three gimbals mounted with orthogonal pivot axes so that the wheel attached to the innermost gimbal can have an orientation independent of the spatial orientation of its mount.
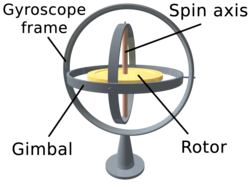
Spinning wheel axis defines the axis of rotation. The rotor is constrained to rotate about an axis that is always perpendicular to the inner gimbal axis. So the rotor has 3 rotational degrees of freedom and on its axis he has 2 rotational degrees of freedom. The rotor responds to the force applied to the input shaft by the reaction force on the output shaft.
The easiest way to check the behavior of the top is to look at the front wheel of the bicycle. If the wheel is tilted from vertical so that the top of the wheel moves to the left, the front edge of the wheel will also rotate to the left. In other words, rotation of the rotating wheel about her one axis produces rotation about the third axis.
The gyroscope flywheel rotates or resists around the output axis depending on whether the output gimbal is in free or fixed configuration. An example of a free output gimbal is an attitude control gyroscope used to sense or measure the pitch, roll, and yaw attitude angles of a spacecraft or aircraft.
Animation of spinning wheel in action. The center of gravity of the rotor can be in a fixed position. The rotor simultaneously he rotates around one axis and the other he can oscillate around two axes and is free to rotate around a fixed point in any direction. Some gyroscopes have mechanical equivalents that replace one or more elements. For example, a rotating rotor can be suspended in a fluid instead of being attached to a gimbal. A control moment gyroscope (CMG) is an example of a fixed output gimbal used in spacecraft to hold or maintain a desired attitude angle or orientation using gyro drag.
The rotor’s center of gravity may be off the vibration axis, so the rotor’s center of gravity and the rotor’s mounting point should not coincide.
Working Principal of Gyroscope
Its principle is based on conservation of angular momentum and inertia. Gyroscopes can be very confusing objects because they move in unusual ways and seem to defy gravity, but there are physics concepts behind them.
Gyroscope precession is caused by torque. It is written as the rate of change of angular momentum and angular velocity produced by the same applied torque. This physical phenomenon leads to seemingly impossible dynamic events.
Some Important Uses of Gyroscope
- This is used for smartphone sensors that help automatically rotate the screen view when needed. Gyroscopes use the earth’s gravity to determine direction.
- Gyro compasses have been in use on ships for a long time, and the gyro is a very important part of it. Used to know the exact geographic position of a ship.
- Used in automobiles, satellites, airplanes and many other devices. Today it is widely used in toys.
Closing Words
A gyroscope is not a specific device. This is an effect seen in mechanical devices called the gyroscopic effect. Any mechanical device that exhibits this spinning effect are called gyroscopes.
