The pre-engineered building is also called PEB in short form. In this type of system, building components are fabricated in factories and installed at the construction site.
These buildings, when built with high efficiency, are up to 30% lighter than conventional steel buildings.

PEB is designed as per clients’ requirements and actual design calculations using tapered sections.
Pre-engineered buildings are a combination of the built-up section, cold-formed elements, and profiled sheets.
Designing and casting are done in the factory. Building components are brought to the site and then fixed/jointed at the site. All connections are bolted.
Table of Contents
Applications
- Industrial buildings
- Warehouses
- Commercial complexes
- Showrooms
- Offices
- Schools
- Indoor Stadiums
- Outdoor stadiums with canopies
- Gas stations
- Metro stations, bus terminals, parking lots
- Primary health centers and many more.

Advantages
- Aesthetic appeal
- Faster completion
- Economical
- Seismic resistance
- Ease of expansion
- Maintenance-free
- Large clear spans
- Controlled quality
- Hassle-free
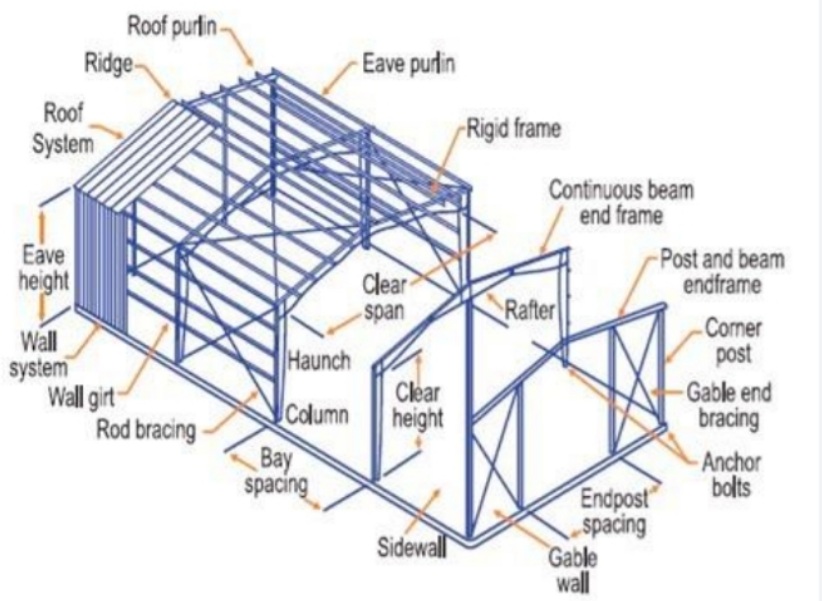
Components of Pre-engineered Building (PEB)
Main Frame:
- Primary Members: Columns and rafters.
Secondary Members:
- Purlins, Girts.
Sheeting:
- Roof, wall, fascias, etc.
Accessories:
- Ventilators, skylights, etc.
Guidelines for PEB Design
- All designs shall be as per MBMA (Metal Building Manufacturer Association) and the client specifies the code.
- Live load as per America Code = 0.57 KN/M2.
- Horizontal Deflection as per America Code = L/180.
- Vertical Deflection as per America Code = eh/100 for the mainframe.
- The wind terrain category should be selected as 3 unless more data is available.
- In American design, the wind coefficient is to be followed as given in MBMA.
- Normally buildings are to be designed as Pinned except for building span> 30m or Crane capacity of more than 5 tones or height greater than 9m.
- Standard purlin laps should be 385 mm.
Design Codes:
- AISC: The American Institute of Steel Construction
- AISI: American Iron and Steel Institute
- MBMA: Metal Building Manufacture’s Code
- ANSI: American National Standards Institute
- ASCE: American Society of Civil Engineers
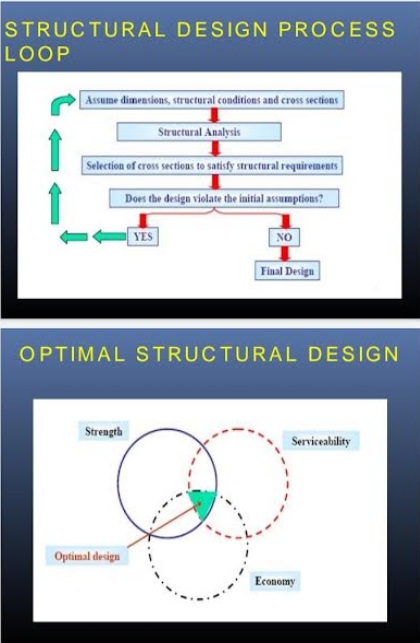
Structural Design Process Loop
In the below image I have shown the structural design process loop for Pre-engineered buildings. This can help you a lot while designing a PEB structure.