Various types of roads are used in road transportation system. Roads are necessary network for any country. This article discusses the classification of roads based on many factors, like materials, locations, and traffic.
Table of Contents
What Is Road?
The road is a paved way or a route or a thoroughfare which drives you to reach your destination by vehicle. Roads are classified depending on different criteria, each among them is further classified into different types of roads. In this article, we will describe each and every type and term which you frequently listen to when someone talks about roads.
Classification or Types of Roads:
The roads are classified based on many factors as given below.
- Materials.
- Location & function.
- Traffic volume.
- Width.
- Economy.
- Traffic type.
- Rigidity.
- Topography.
Classification of Roads Based on Materials:
- Earthen roads.
- Gravel roads.
- Murrum roads.
- Kankar roads.
- WBM roads.
- Bituminous roads.
- Concrete roads.
1. Earthen Roads:
Earthen roads are laid with soil. They are cheaper than all other types of roads. Earthen roads are provided for fewer traffic areas or countryside areas. A good drainage system should be provided, which reflects superior performance for a more extended period.

2. Gravel Roads:
Gravel roads are also low-quality roads, but they are better when we compared them with earthen roads. A compacted mixture of gravel and earth is utilized as pavement material in this case.

3. Murrum Roads:
Murrum is a matter acquired from the disintegration of igneous rocks by weathering agencies. This is utilized to make roads called murrum roads.

4. Kankar Roads:
Kankar is an impure form of limestone. Kankar roads are provided where lime is acquirable in a reasonable quantity. These types of roads are of low quality and performance.
Kankar is an impure form of limestone. Kankar roads are provided where lime is acquirable in a reasonable quantity. These types of roads are of low quality and performance.
5. WBM Roads:
Water Bound Macadam or WBM roads contain crushed stone aggregate in their base course. The aggregates are dispersed on the surface and rolled after sprinkling water. WBM roads provide better performance when we compared them to earthen, gravel, murrum, and kankar roads.
WBM roads are laid as layers of about 10 cm thickness of each layer. They are rough and may disintegrate instantly under traffic.

6. Bituminous Roads:
Bituminous roads are prevalent roads around the world. They are the most used roads in the world. These road types are low in cost and suitable for driving conditions. The thickness of bituminous roads depends upon the subgrade soil conditions.

7. Concrete Roads:
Cement concrete is utilized to construct the pavements in the case of concrete roads. These are very popular and costlier than other types of roads. They are rigid, so they need less maintenance.
Concrete roads are appropriate for high traffic areas. They are laid with joints and the time of construction is much.

Classification of Roads Based on Location and Function:
- National highways
- State highways
- District roads
- Rural roads or village roads
1. National Highways:
National highways are the primary roads that connect all major cities to the capital of the country. They run throughout the length and width of the country. At least a two-lane road is provided for national highways.

2. State Highways:
State highways are the second main roads that connect important parts of the state within it. State highway finally connects to the national highways.

3. District Roads:
District roads are provided within the cities and link markets and production places to state and national highways. Two kinds of district roads are there namely:
- Major district roads
- Minor district roads
Major district roads link headquarters of the neighboring district with important parts of the area while minor district roads are laid within the region.

4. Rural Roads or Village Roads:
Village roads connect the neighboring villages. They lead to nearby town or district roads. Normally, low-quality roads are provided as village roads because of low traffic.

Classification of Roads Based on Traffic Volume:
- Light traffic roads.
- Medium traffic roads.
- High traffic roads.
1. Light Traffic Roads:
The roads which are carrying 400 vehicles daily on average are known as light traffic roads.
2. Medium Traffic Roads:
The road which is carrying 400 to 1000 vehicles per day, is known as a medium traffic road.
3. High Traffic Roads:
If a road is carrying is more than 1000 vehicles per day then it is known as high traffic road.
Classification of Roads Based on Economy:
- Low-cost roads.
- Medium cost roads.
- High-cost roads.
The economy is based on the location and function of roads and also on the traffic analysis.
Classification of Roads Based on Traffic Type:
- Pedestrian ways.
- Cycle tracks.
- Motorways.
1. Pedestrian Ways:
Pedestrian ways are exclusively built for pedestrians, and no vehicles are authorized in this way.
2. Cycle Tracks:
Cycle tracks or bicycle tracks are provided on both sides of the pavement for cyclists; thus they can travel safely.
3. Motorways:
Motorways are also called expressways. Only a few vehicles are accessible to utilize this type of road. The cars which can move with high-speed acceleration are authorized in this way. Motorways make travel fast and provide comfort for high-speed vehicles.
Classification of Roads Based on Rigidity:
- Flexible roads.
- Rigid roads.
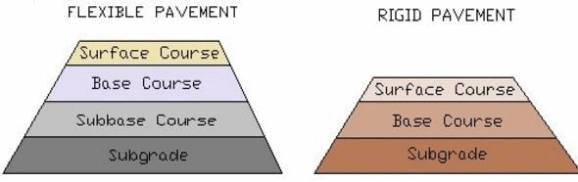
1. Flexible Roads:
Flexible roads consist of a flexible layer as a pavement surface, which needs proper maintenance; otherwise, it may be disintegrated easily with heavy traffic. All types of roads except concrete roads come under this category.
2. Rigid Roads:
Rigid pavements are non-flexible and cement concrete roads come under this category.
Classification of Roads Based on Topography:
- Plain area roads
- Hilly area roads
1. Plain Area Roads:
The roads constructed on the leveled surface are called plain area roads.
2. Hilly Area Roads:
Roads constructed in hilly regions are known as hill area roads or ghat roads. Mostly these are provided around the hill in a spiral shape.

Faqs
We classify roads based on their function into different categories, such as primary, secondary, and tertiary roads. Primary roads serve as the backbone of the transportation network, while secondary roads connect smaller towns and cities. Tertiary roads serve residential areas and rural communities.
Urban roads are wider and have more lanes than rural roads. They are located within or near densely populated areas like cities and suburbs. In contrast, rural roads are narrower and often windier, with fewer lanes and lower speed limits. They are located in sparsely populated areas.
A collector road collects traffic from local roads and connects them to arterial roads. These roads have more lanes than local roads and are designed to handle higher volumes of traffic. They often have traffic signals or roundabouts to control the flow of traffic.
We classify roads based on their design speed, which is the maximum safe speed that a road can accommodate. Rural, suburban, and urban design speeds differ. Highways have higher design speeds, while local roads have lower design speeds. The design speed of a road is important in determining its safety and capacity.
