The combustion chamber is the part of the internal combustion engine where the air-fuel mixture is burned. This is a closed cylinder. The combustion chamber is also called a combustor.
There is a piston in the combustion chamber of the reciprocating engine. This piston reciprocates in the chamber, compressing the air-fuel mixture.
When the air-fuel mixture is compressed, the spark plug (of the spark ignition engine) produces sparks and ignites the compressed air-fuel mixture. The ignition process of the air-fuel mixture in the combustion chamber significantly increases the internal temperature and pressure in the combustion chamber.
After the ignition process, the piston pushes the burned air-fuel mixture out of the chamber. The combustion cylinder of an
internal combustion engine contains many parts such as fuel pumps, fuel nozzles, spark plugs, and pistons.
The combustor is most commonly used in the engines of automobiles, ships, planes, buses, trucks, and many other vehicles. If you have a car or car, you can easily find it there.
How Does the Combustion Chamber Work?
The combustion chamber is one of the maximum essential elements of the engine. The fundamental feature of the combustion chamber is to burn the air-gas aggregate to provide high-pressure, high-temperature gas.
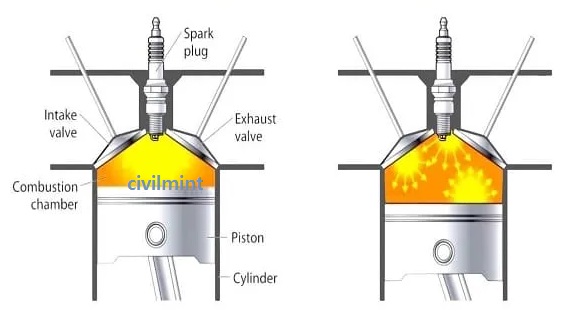
A combustion chamber works withinside the following way:
- Firstly, the carburetor sucks air from the environment, mixes it with gas, and gives you this aggregate to the engine combustion chamber.
- The chamber has a reciprocating piston.
- As the air-gas aggregate enters the chamber, the piston compresses it.
- At the give up of the compression manner, a spark plug ignites the aggregate.
- The combusted air-gas aggregate generates high-stress and high-temperature gases within the chamber.
- As the combustion manner completes, the piston expels the high-stress aggregate out of the chamber and introduces it into a growth valve wherein it expands.
- When the high-stress aggregate expands, it exerts pressure at the pinnacle of the piston and reciprocates it.
- As the piston gets stress strength from the combusted aggregate, it converts this strength into mechanical strength (reciprocating movement). A connecting rod connects to the piston. As the piston transfers its movement to the connecting rod, the rod covers reciprocating movement into rotary movement.
- The connecting rod gives you its rotary movement to the crankshaft.
- When the crankshaft gets movement, it turns the flywheel, similarly turning the car tire.
