A laser beam machining is a non-ordinary machining technique in which the activity is performed by laser light. The laser light has high-temperature strikes on the workpiece, because of the high temperature the workpiece gets softens. The process utilized nuclear power to eliminate material from a metallic surface.
The high frequency of monochromatic light will fall on a superficial level at that point heating, melting, and disintegrating of the material occur because of impinging of photons. Laser bar machining is most appropriate for weak materials with low conductivity yet can be utilized on most materials.
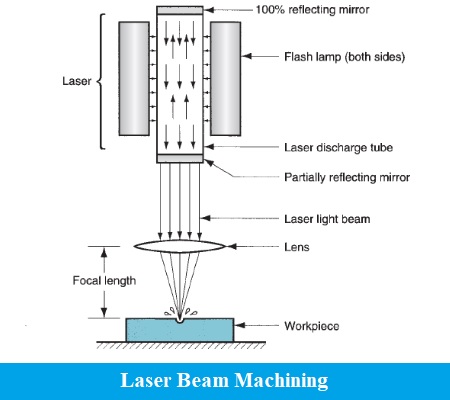
Table of Contents
Working Principle of Laser Beam Machining (LBM)
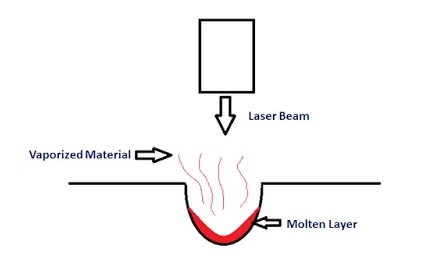
LBM works on the principle that when a high-energy laser beam strikes the outer layer of the workpiece. The heat energy contained by the laser beam gets moved to the surface of the workpiece. This heat energy consumed by the surface heat melts and vaporizes the material from the workpiece. In this manner, the machining of material happens by the utilization of a laser beam.
Process to Produced Laser Beam
As we know that light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation is called laser.
Before understanding how laser beams are produced, we must need to learn about what is stimulated emission is.
Prior to seeing how laser beams are created, we should have to find out with regards to what is stimulated emission is.
In-Depth Study of Stimulated Emission
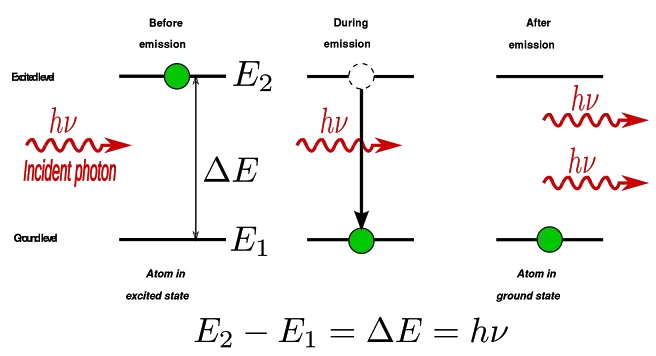
In typical circumstances, the electrons present in molecules lie in the ground state (most minimal energy level). Whenever some source of energy is given to the atoms as radiation, the electrons of the particles retain energy and are eager to a higher energy level. After a brief term, these electrons naturally bounce back to the ground state, and keeping in mind that doing as such they produce photons of light. This outflow of photons by the electrons is called spontaneous emission.
At the point when the electrons in the energized state don’t bounce back to the ground state all alone. The present circumstance is known as a metastable state. At the point when a photon is terminated to the meta-stable condition of particles, this stimulates an electron at an energized state and it bounces back to its ground state giving two photons (one photon that we terminated and the other delivered by the electron). These two photons animate other atoms’ electrons and produce more photons-a chain response begins and the quantity of photons increments. This interaction is called stimulated emission as we are stimulating different electrons to get photons. Here we are getting two light photons from a solitary photon for example intensifying the light.
Henceforth the light beams created by this technique are called laser (light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation).
Diffrent Types of Laser
1. Gas Lasers
In these kinds of lasers, gases are utilized as the medium to create lasers. The ordinarily utilized gases are He-Ne, argon, and Co2.
2. Solid State Lasers:
The media of the solid-state lasers are created by doping an uncommon component into a host material.
Ruby laser is an illustration of a solid-state laser in which ruby crystal is utilized as a medium for the generation of the laser beam.
Main Componants
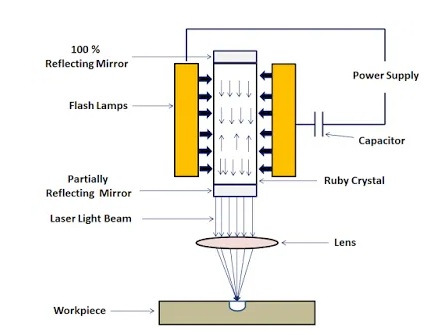
Different parts of the laser beam machining are described below.
1. Flash Lamp
The flash tube or flash lamp is utilized to give vital energy to the molecules to excite their electrons.
2. A Pumping Medium
A medium is required that contains a huge number of atoms. The atoms of the media are utilized to create lasers.
3. Power Supply
A high voltage power source is utilized to deliver light in electric lamp tubes.
4. Capacitor
The capacitor is utilized to work the laser beam machine at beat mode.
5. Reflecting Mirror
Two sorts of mirrors are utilized, the initial one is 100 % reflecting and the other is partially extent reflecting. 100 % reflecting mirror is kept toward one side and somewhat reflecting mirror is at the opposite end. The laser radiates emerges from that side where to some extent reflecting mirror is kept.
Process to Produce Lase Beam
A high voltage power supply is applied across the flash tube. A capacitor is utilized to work the flash tube at beat mode.
As the flash is created by the flash tube, it transmits light photons that contain energy. These light photons radiated by the flash tube are consumed by the ruby precious stone. The photons consumed by the particles of the ruby precious stones invigorate the electrons to the high energy level and populace reversal (circumstance when the quantity of left electrons is more noteworthy than the ground state electrons) is accomplished. After the brief term, these energized electrons hop back to their ground state and discharge a light photon. This outflow of the photon is called unconstrained discharge.
The produced photon invigorates the energized electrons and they begin to get back to the ground state by radiating two photons. In this manner, two light photons are delivered by using a solitary photon. Here the intensification (increment) of light happens by the invigorated emanation of radiation. Grouping of the light photon increments and it frames a laser shaft. 100 % reflecting mirror skips back the photons into the precious stone. To some extent reflecting mirror mirrors a portion of the photons back to the gem and some of it escapes out and shapes an exceptionally thought laser beam. A focal point is utilized to concentrate the laser beam to an ideal location.
Working Procedure of Laser Beam Machining
An exceptionally high-energy laser shaft is delivered by the laser machines. This laser bar delivered is centered around the workpiece to be machined.
At the point when the laser shaft strikes the outer layer of the workpiece, the nuclear power of the laser pillar is moved to the outer layer of the workpiece. This warms, liquefies, disintegrates lastly eliminates the material from the workpiece. In this manner laser beam machining works.
Advantages:
- The laser beam focuses on a small area and produces high power.
- The laser beam can cut all types of materials.
- Different types of lasers have different uses.
- The maintenance cost of laser machines is low.
- It provides high precision.
- It works with all types of gases.
Disadvantages:
- The initial cost to purchase a laser beam is very high.
- It required skilled workers to maintain laser beams.
- It is not suitable for mass metal processes.
- It consumes lots of energy.
