Table of Contents
What Is Scan To BIM?
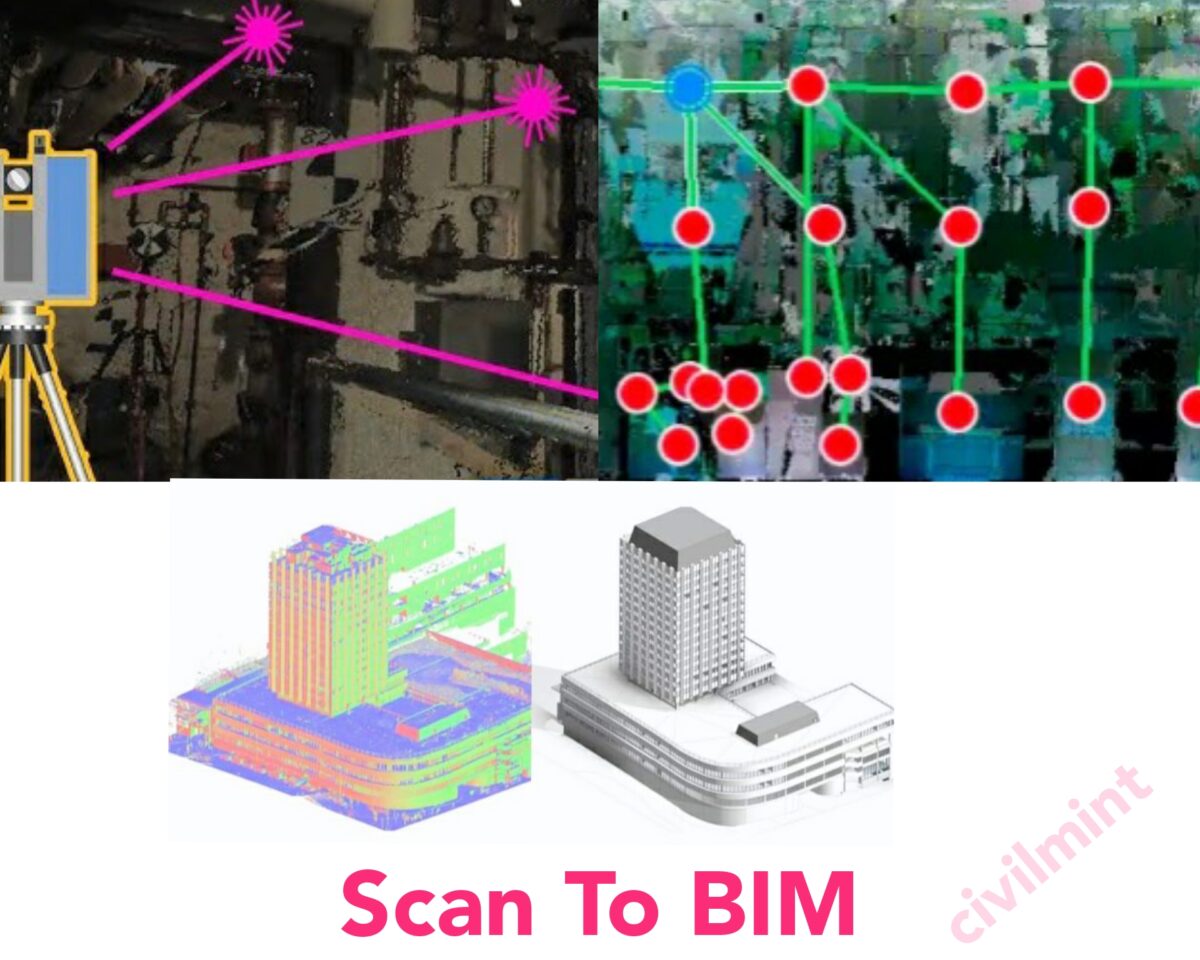
“Scan to BIM” represents a transformational process in the field of architecture, engineering and construction (AEC). It involves the use of a 3D laser scanner to digitally capture site data, which can then be converted into a detailed BIM (building information modeling) is employed to create models. This innovative technology has redefined the way AEC industry professionals create documents and work with existing structures. Laser scanning technology provides an unparalleled level of accuracy. BIM, which enables all aspects of a building to be comprehensively captured, from its architectural complexities to its structural elements. This wealth of data is then carefully translated into accurate BIM models, which effectively Creates a digital twin of the location.
Adopting “Scan to BIM” offers several benefits. First, it streamlines the initial data collection process, reducing the time and effort required compared to traditional manual measurement techniques. Secondly, the resulting BIM model serves as a strong foundation for design and renovation projects, promoting better decision making and collaboration among project stakeholders. Additionally, it facilitates conflict detection by identifying potential design conflicts within the digital model before construction begins, saving significant time and resources. In short, “Scan to BIM” stands as a groundbreaking innovation in the industry, promoting efficiency, accuracy and better project outcomes.
What Is Laser Scanning?
Laser scanning represents a rapid and precise approach for gathering as-built site data and generating three-dimensional imagery. Utilizing LiDAR technology, 3D laser scanners efficiently measure and document exact locations and distances, resulting in the creation of a point cloud file. This technology empowers users to swiftly and effortlessly generate highly precise digital measurements and images, which find valuable application in construction and engineering projects.
Working Concept
1. Laser Scanning Of Physical Structure:
Advanced laser scanning or photogrammetry technologies are employed to capture intricate 3D data from existing buildings or construction sites. This data encompasses precise measurements, geometric details, textures, and other pertinent information.
2. Data Processing and Point Cloud Generation:
The collected scan data undergoes specialized software processing to generate a point cloud or mesh representation of the physical space. This point cloud comprises millions of data points, forming an exceedingly precise digital replica of the building.
3. BIM Model Conversion:
Subsequently, the point cloud data is transformed into a Building Information Model (BIM). BIM serves as a digital representation of both the physical and functional aspects of a building, encompassing comprehensive information about the structure, materials, systems, and more.
4. Visualization And Simulation:
The resultant BIM model attains an exceptional level of accuracy and proves invaluable for various applications, including architectural design, structural analysis, facility management, and renovation projects. Furthermore, it facilitates 3D visualization and simulations, enhancing our ability to interact with and understand real-world structures.
Benefits Of Scan To BIM
1. Improved Planning Accuracy
Adopting a scan-to-BIM workflow significantly enhances the accuracy of renovation and extension planning for buildings lacking digital documentation. This technology streamlines the acquisition of reliable, modern floorplans in standardized formats, reducing errors in project design.
2. Enhanced Quality Assurance
Scan-to-BIM offers a robust quality assurance mechanism by facilitating continuous progress comparison throughout a project’s stages. This allows for more frequent off-site inspections, reducing the necessity for on-site visits while ensuring assessment quality remains uncompromised.
3. Valuable in Complex Construction Environments
In challenging construction settings near existing structures, the scan-to-BIM workflow proves invaluable. It shields neighboring buildings from potential damage by providing real-time schematics of utility works, preemptively identifying and addressing potential problems before they escalate.
4 Efficiency Gains for Older Properties
Asset and facility managers overseeing older properties can leverage scan-to-BIM for efficiency improvements. By precisely identifying areas where enhanced insulation can be applied, these managers can reduce carbon footprints and improve fault reporting accuracy, mirroring the efficiency gains seen in modern buildings.
Closing Thought
Scanning to BIM forms a key element of the wider BIM (building information modeling) framework, and its growth is directly aligned with the extent of BIM adoption in the construction and building maintenance sectors. This interconnectedness underscores its profound importance in shaping the future of the AEC (architecture, engineering and construction) industry.
An important catalyst for the increasing importance of photogrammetry to BIM is the increasing accessibility and ease of use of point cloud technology. This technological advance significantly lowers the barriers to entry for AEC professionals considering incorporating scanning to BIM into their workflow. The simplified adoption process opens the door to more widespread use.
Scan-to-BIM facilitates seamless collaboration between stakeholders across the entire project scope, including surveyors, project managers, construction teams and engineers, as well as interior designers and architects. This comprehensiveness reflects the collaborative benefits inherent in BIM, which promotes a holistic approach to project implementation.
You Might Also Like: CAD To BIM
Scanning to BIM not only complements but also drives the widespread adoption of BIM methods in construction and building maintenance. Technological advances and increased accessibility are fueling its progress, promising better collaboration and efficiency in all aspects of the AEC industry. As the industry evolves, scanning to BIM will continue to play a major role in reshaping the way structures are designed, built and maintained, pushing the industry into a more collaborative, data-driven future.
