The gate valve is the most famous and common type of valve used in the plumbing system or pipeline system. This type of valve is also called a sluice valve. A valve raises (opens) or lowers (closes) a disk or valve or controls the flow of fluid. Sluice or gate valves include the most common types of valves used in various process plants. This is a linear motion valve used to stop or start the flow of a fluid. This type of valve is used for fully closed or fully open service. The valve must not be used to regulate liquids. They are mainly used in pipelines in various industries. The valve is therefore used as a shut-off valve to close and open the flow of fluid.
The sluice valve is a universal valve that operates according to the opening and closing of the disc. Because this valve disk is similar to a plug, the valve disk is positioned perpendicular to the fluid flow path. The valve should not be used for fluid regulation as the disc may be damaged if the disc is partially open. High-velocity fluid flow in partially open valves can erode the disc and seat surfaces and cause noise and vibration. This valve limits the pressure loss across the valve when the disc is fully open. In fully opened or closed conditions, the disk damage chances become very low.
Gate valves are used when the flow of a liquid or gas needs to be equalized with minimal restrictions. All gate valves feature a two-way seal, allowing installation in virtually any orientation. If the sluice valve has a pressure reducing function, it can only be installed in the direction of the arrow.
Gate valves are available in a variety of options such as bonnet and gate designs, materials, and sizes.
Table of Contents
Working Principle of Gate Valve:
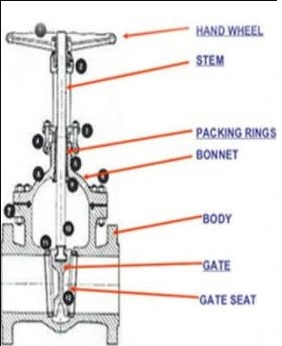
A sluice valve is a form of rising stem multi-turn valve. This stem rotates several times to fully close or open the valve. It is usually used either fully open or fully closed. Therefore, the flow control speed cannot be adjusted. Use of this valve in the semi-closed position may damage the disc. Turn the handwheel counterclockwise to open the valve and clockwise to close the valve. The disc acts as an opening element that attaches to the end of the threaded rod. The disc is attached to the wedge seat of the valve body. This disc blocks the flow through the valve.
When the valve is fully open, the valve disc moves up and opens. Allows fluid flow in all directions. When the valve is fully closed, a disk or valve fills the channel and completely shuts off flow through the valve. For handwheel valves, vapor mist from the handwheel indicates that the valve is closed or open. For gear control valves, the top of the stem is not visible and a separate indicator is provided if necessary.
Construction of Gate Valve:
Gate valves are made of alloy steel, steel, bronze, cast carbon, Aluminum, bronze, and cast-iron, e.tc. It has flanged ends. The valve bonnet is made of cast iron. So be careful when checking it out. The gate valve has a disk, like a gate that attaches with a spindle that acts on the nut. The valve bonnet is selected based on the installation requirements and the valve position. The valve bonnet can be union, bolted, or screwed-in type.
The screw cap ensures a permanent seal. Union Caps are used in applications that require proper cleaning and inspection. Bolt-on lids are used for high-pressure applications. A pressure cap is another type of valve cap that is also used in high-pressure applications.
Types of Gate Valve
- Rising and Non-rising stem gate valve
- Knife Valve
- Flexible Wedge Valve
- Wedge Gate Valve
- Parallel Slide Gate Valves
- Slab Gates
Let’s take a look at the above-mentioned gate valves.
1. Rising and Non-rising stem gate valve
Gate valves have either a rising or rising stem. Large valves usually have a non-rising stem. As the handwheel rotates, the valve stem is pulled from the bonnet by the handwheel. The disc position refers to the disc and also indicates whether the valve is closed or open. A small valve allows the valve stem and wheel to be lifted simultaneously. The stem of some valves does not rise. This is because the valve stem does not fit the valve body. This type of valve can be used when there is not enough room for the valve stem to protrude from the body.
2. Knife Valve
This type of gate valve is the most common type of industrial valve. The design of these valves minimizes contact between the various valve components. Therefore, the design of the knife valve reduces the wear between the various parts. Knife valves have certain functions. For example, by preventing sliding contact between the valve plug and the body, the medium is ejected into the valve, resulting in an anti-skid movement. If there are solid particles at the bottom of the knife valve body, they can be separated through the bottom of the valve. This type of gate valve is a one-way valve with the function of shutting off the flowing fluid. Any material in the knife valve seat area will drain and close. Knife valves can withstand high abrasive slurries and temperatures. Knife valves are used in chemical, power, and mining applications.
3. Flexible Wedge Valve
These valves have a single-piece disc with truncated edges. These incisions vary in depth, shape, and size. A narrow, flat cut along the edge of the wedge reduces flexibility but retains strength. Wider and deeper teeth around the cast groove or wedge provide more flexibility but reduce strength.
This model improves the firmness and alignment of the seat. It also improves thermal bonding performance. Flexible wedge valves are used in steam systems.
Thermal expansion in the steam line can deform the valve body and cause thermal blindness. The flexible closure prevents thermal blindness by allowing the closure to flex when the valve seat is compressed by the thermal expansion of the steam pipe.
The downside of these sprues is that the fluid in the line will collect on the disc. This process can cause corrosion and eventually damage the disk.
4. Wedge Gate Valve
In this type of valve, the valve is closed by pushing a wedge against the equivalent cone of the valve body. Perfect sealing is possible by combining the wedge shape of the valve body and the seat ring. When the valve is fully open, the back seat of the valve stem retracts into the bonnet sleeve. For actuated valves, the valve stem cannot be fully seated in the rear seat to avoid damage. The valve is fully open below the travel limit and fully closed below the torque limit.
5. Parallel Slide Gate Valves
No wedges are required for a proper fit. The valve is closed via two separate discs connected by a disc holder and the spring is lowered in parallel to close the valve. Because the valve body port is sealed, the valve stem plug prevents further movement. When the valve opens, the disc rises, and the valve stem returns to its original position. This type of gate valve usually opens fully and closes with limited movement.
6. Slab Gates
These gate valves (also called straight gate valves) are integral gate valves with bore diameters. When opened, the hole aligns with the two rings of the seat. This direction provides uniform fluid flow with minimal turbulence. This unique design minimizes system pressure loss. Gate valves are best suited for transporting liquefied natural gas (NGL) and crude oil. The valve seat remains clean. However, the disc cavity can trap foreign objects. Therefore, the hole usually has a built-in plug and is used to remove accumulated debris for maintenance purposes.
Applications/Uses of Gate Valve:
- These valves are used in the pipeline industry.
- It is used for salt work pipelines. Used in chemical plants.
- Gate valves are used to transport liquefied natural gas (NGL) and crude oil.
- Used for corrosive liquids, vapors, slurries, and gases.
- This type of valve is used on ships for steam circuit purposes.
- Sluice or gate valves are used for high temperature and high pressure.
- These valves are used for almost all liquids such as hydrocarbons, steam, feedwater, fuel gas, and air.
Advantages of Gate Valve:
- The pressure loss during operation is very low.
- Basically, it can be used as a two-way valve.
- Best suited for high temperature and high pressure.
Disadvantages of Gate Valve:
- They do not close or open as quickly as globe valves.
- These valves require a large area for maintenance, operation, and installation.
- High torque is required due to the high-pressure drop across the seat.
- This valve is slow. When the sluice valve is partially open, a lot of noise and vibration are generated.
- This valve is not suitable for regulation.
- These valves are difficult to repair by lapping and grinding.
Difference between Gate Valve and Globe Valve:
| Globe Valve | Gate Valve |
|---|---|
| It uses to regulate, start or close the flow of the different fluids. A globe valve is used to start, close or regulate the flow. | It can only open and close. There is no option to regulate the fluid flow. |
| This type of valve can not install in different directions. | Gate valves can be installed in various directions. |
| Globe valve is expensive. | It is cheaper compared to the globe valve. |
| Globe valves have a high-pressure drop. | Low pressure compared to the globe valve. |
| They provide a good seal. | It cannot provide a better seal than a globe valve. |
| It has a fast opertaion. | Normally slow operation. |
| Globe valves have a shorter stroke. | Gate valves have a longer stroke. |
