Table of Contents
What Is Artificial Rain?
Artificial rainfall is done using cloud seeding technique. Artificial rain is also known as man-made rain. Various chemicals like silver iodide, potassium iodide and dry ice are used to produce artificial rain. Following promising research, the use of hygroscopic ingredients such as table salt is becoming more popular.
Cloud seeding involves modifying weather by releasing substances into the air to influence cloud properties. These substances encourage cloud droplets or ice crystals to form, affecting how precipitation develops. Experts debate its effectiveness, as some studies find it challenging to conclusively prove significant impacts. The main goal is typically to enhance rainfall or snowfall, either directly or to inhibit subsequent precipitation.
The process of rain formation is well understood, starting with the evaporation of water from oceans or other water bodies. As the moisture-laden air rises into the troposphere, the droplets condense, gradually increasing in size until they become too heavy to stay aloft, resulting in precipitation.
However, the challenge of drought arises when clouds form without rain. One solution to this is artificial precipitation, which involves cloud seeding. This process intervenes when clouds near freezing temperatures contain ice crystals, which prevent water vapor from condensing into liquid. Through cloud seeding, rainfall can be induced, thereby providing a solution to water scarcity.
Chemicals For Artificial Rain
I have listed all the popular chemicals used in the process of artificial rain.
| Chemical | Purpose | Effects/Method |
|---|---|---|
| Silver Iodide | Nucleating agent | Promotes ice crystal formation in supercooled clouds |
| Potassium Iodide | Nucleating agent | Encourages ice crystal growth in clouds |
| Calcium Chloride | Hygroscopic agent | Attracts moisture to form larger cloud droplets |
| Sodium Chloride | Hygroscopic agent | Aids in increasing cloud droplet size |
| Propane | Carrier for silver iodide | Helps disperse seeding agents into clouds |
| Acetone | Carrier for silver iodide | Facilitates even distribution of seeding agents |
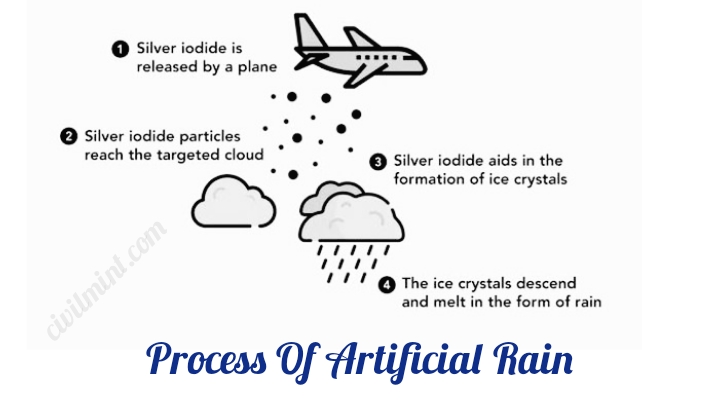
Various Steps Of Artificial Rain
1. Cloud Selection:
Meteorologists meticulously analyze atmospheric conditions to identify clouds that are conducive to producing precipitation. Typically, cumulus or cumulonimbus clouds are chosen due to their potential for significant vertical development. These clouds are likely to respond to seeding agents and result in enhanced precipitation.
2. Seeding Agents:
Seeding agents, often silver iodide crystals or other appropriate materials, are chosen. These substances serve as nuclei around which water vapor in the cloud can condense. Silver iodide, for instance, has a crystalline structure that mimics the structure of ice, facilitating the process of water vapor condensation.
3. Aircraft or Ground Generators:
To introduce seeding agents into the cloud, aircraft equipped with specialized flares or rockets are employed. These flares contain the seeding agents and are released into the atmosphere at predetermined altitudes. Alternatively, ground-based generators release seeding agents into the atmosphere, allowing them to be transported by prevailing winds to the target clouds.
4. Dispersion and Transport:
After release, the seeding agents disperse in the atmosphere and mix with the cloud’s moisture.
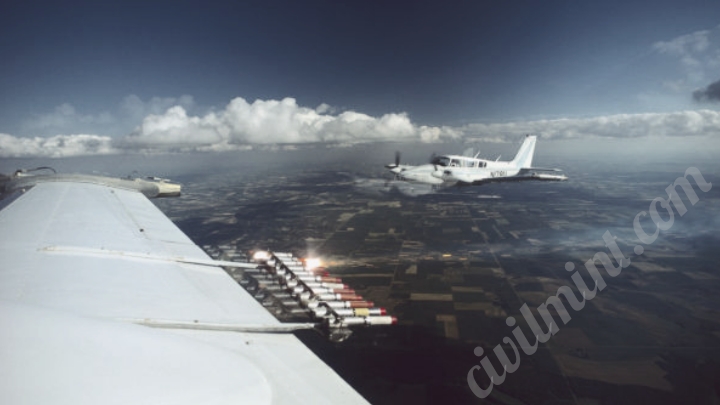

Natural updrafts within the cloud and prevailing air currents help evenly distribute the seeding agents throughout the cloud. This dispersion increases the chances of effective interaction between the seeding agents and water vapor.
5. Condensation:
As the seeding agents disperse within the cloud, they provide a surface for water vapor to condense around. Water molecules begin to adhere to the seeding agent particles, gradually forming water droplets. These droplets continue to grow in size as more water vapor condenses onto them.
6. Precipitation:
The now-enlarged water droplets become too heavy to remain suspended in the cloud’s updrafts. Gravity takes over, causing the droplets to fall from the cloud as precipitation. Depending on factors such as the temperature and altitude of the cloud, the precipitation can take the form of rain, snow, or other types of precipitation.
Effectiveness Of Artificial Rain
Artificial rain relies on cloud seeding, a technique that modifies the weather to boost rainfall in areas facing drought or water scarcity. Its success depends on factors such as weather conditions, its target location and the method used for cloud seeding.
The effectiveness of cloud seeding depends on the atmospheric conditions. All it takes is the right clouds and supercooled water droplets. Cloud seeding involves adding particles such as silver iodide or potassium iodide to the clouds. These particles help form ice crystals, which attract water vapor and potentially cause more precipitation.
However, cloud seeding doesn’t always work as expected due to natural processes in clouds. It is affected by such things as wind, temperature differences and the availability of moisture. Sometimes, seed clouds may not result in much precipitation, while other times they may produce more precipitation than anticipated.
Another important aspect is where the cloud seeding is done. Location, landscape and local climate patterns all affect the results. While some places may see better rainfall, other places may see minimal improvement or no significant change.
Advadvantages Of Cloud Seeding
- Artificial rain enhances water availability for agriculture.
- Artificial rain replenishes water reservoirs.
- Artificial rain helps mitigate drought conditions.
- Artificial rain assists in managing forest fires by increasing humidity.
- Artificial rain improves air quality by reducing airborne pollutants and dust particles.
Conclusion
Artificial rain is not a guaranteed solution but a supplement to natural rain. It cannot completely replace the complex processes that create natural rain. Even when cloud seeding appears to be successful, it is still a short-term measure to reduce water scarcity, not a sustainable long-term solution.
