Branches of surveying are Geodetic surveys, Topographic surveys, Hydrographic surveys, Cadastral surveys, Engineering surveys, etc.
The work of the land surveyor can be categorized into three main areas of responsibility.
- Firstly, he is concerned with the recording of measurements that permit the size and shape of the earth to be determined.
- Secondly, he is active in the collection, processing, and presentation of the information necessary to produce maps and plans.
- Thirdly, he may be required to locate on the surface of the Earth the exact positions to be taken up by new roads, dams, or other civil construction works.
As a result of the diverse nature of the land surveyor’s work, various distinct branches of surveying have emerged.
Table of Contents
Branches Of Surveying:
Following are the primary branches of surveying.
- Geodetic surveys.
- Topographic surveys.
- Hydrographic surveys.
- Cadastral surveys.
- Engineering surveys.
Let us discuss each type of survey.
1. Geodetic Surveys

Geodetic surveys are executed on a national or international basis in order to locate points large distances apart. This type of survey work as a framework for ‘lower order’ surveys. In order to assure high accuracy, the effect of factors like the curvature of the earth on observations must be considered and the necessary corrections applied.
2. Topographic Surveys

Topographic surveys are concerned with the small-scale representation of the physical characteristic of the earth’s surface. Most Often, the data necessary for such an operation will be provided by the use of aerial photography. The science of fetching measurements from photography in order to produce maps is known as photogrammetry. Topographic surveys are frequently the responsibility of a national organization. such as, for example, the Ordnance Survey in the UK, American Congress on Surveying and Mapping, in the USA.
3. Hydrographic Surveys
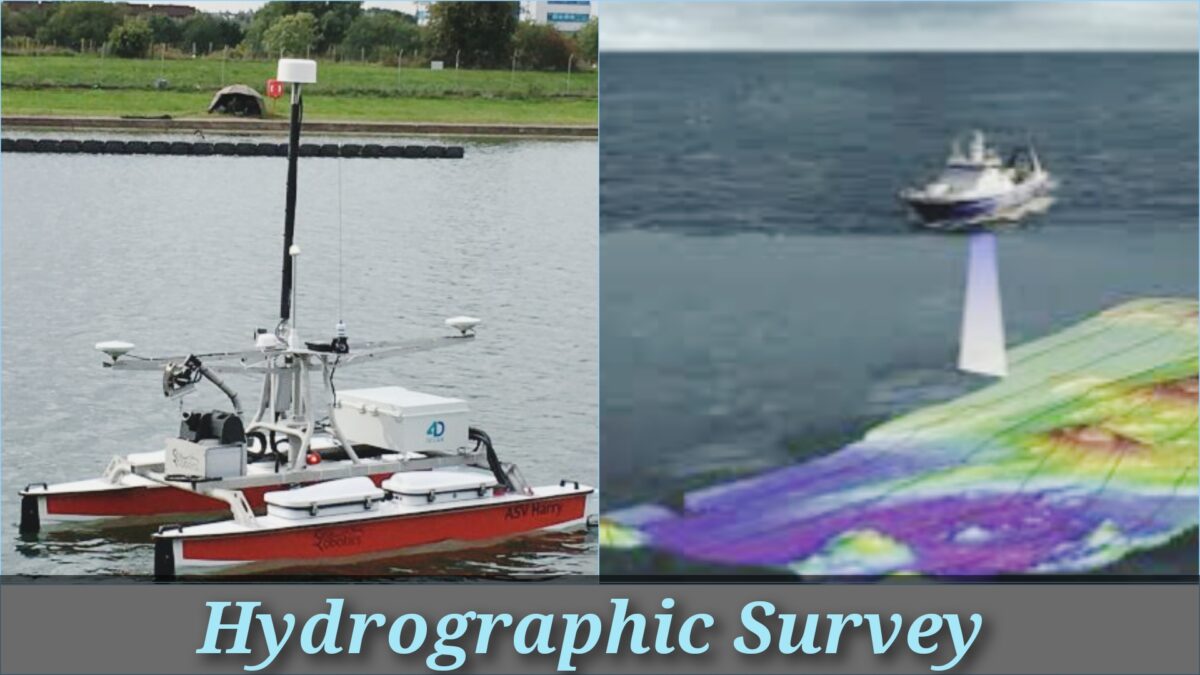
Hydrographic surveys involve the representation of the surface of the ocean floor. The final product is normally a navigational chart. In past years this branch has become increasingly essential with the development of the offshore oil industry. In this case, in addition to the production of charts, the surveyor may be needed to position large structures such as oil production platforms. This type of operation would usually necessitate the utilization of ground and satellite electronic Position-fixing equipment.
4. Cadastral Surveys

Cadastral surveys are associated with the location and fixing of land boundaries. In many countries in the world, like America, the information rendered by the cadastral surveyor may be a constitutional part of a land registration system.
5. Engineering Surveys

Engineering surveys are mandatory for the preparation of design drawings relating to construction works such as roads, dams, or airports. The surveys are normally at a large scale, with scales of 1:500 and 1:1000 being most popular.
Sum Up
These are the 5 important branches of surveying. These branches of surveying are used in various engineering fields like construction, oil and gas exploration, mining and geotechnical engineering.
