Table of Contents
What is Distributorless Ignition System?
A distributorless ignition system is an all solid state electronic system with no moving parts. No distributors means fewer problems. These types of systems are also called as direct ignition systems (DIS).
A distributorless ignition system is a type of ignition system that consists of multiple induction coils instead of having a distributor in an electronic ignition system.
I have shown the figure of distributorless ignition system.
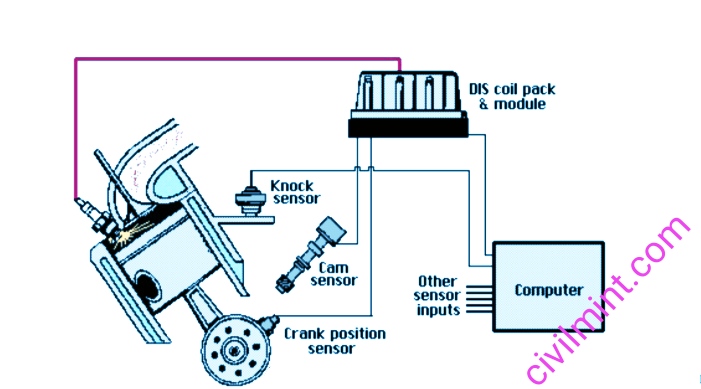
This is very different from traditional electronic ignition systems. The coil is above the spark plug. Additionally, the system has no spark plug wires and is electronic.
In this system, the spark plugs are ignited by a coil and the spark plug timing is controlled by the Ignition Control Unit (ICU) and Engine Control Unit (ECU), increasing the efficiency and reliability of the system.
Distributorless ignition systems typically consist of one coil per cylinder or one coil per pair of cylinders. Using multiple ignition coils, each spark plug in these cylinders ignites simultaneously.
Parts of Distributorless Ignition System
1. Battery:
Battery is used as a power pack for the ignition system.
2. Ignition Switch:
The ignition switch is the switch used to turn the ignition system on and off.
3. E.C.U.:
The Electronic Control Unit is a minicomputer that receives signals from various sensors and coordinates all other components by giving the correct signals to the ignition control unit.
4. I.C.U.:
ICU is an electronic control sub unit that contains multiple ignition coils. Receives signals from camshaft position sensor,
crankshaft position sensor and ECU. The ignition coil then creates a high voltage for each spark plug individually.
5. Magnetic Triggering Device:
This is a device consisting of gears and sensors. All but one of the teeth are evenly spaced. He has two types of trigger wheels. One is used to know the exact position of the crankshaft and the other is used to know the position of the camshaft.
6. Spark Plugs:
Spark plugs are typically used to produce one spark per cylinder.
How Does Distributorless Ignition System Work?
When the ignition switch is turned on, current begins to flow from the battery through the ignition switch to the vehicle’s ECU. The ECU processes various data from sensors and continuously calculates ignition timing.
At the same time, the trigger wheels attached to the camshafts and crankshafts have equally spaced teeth except for one that identifies the positions of the crankshafts and camshafts. Position sensors are equipped with magnetic coils that continuously generate a magnetic field. Signal fluctuations occur when the trigger wheel gap is ahead of the position sensor. These signals are sent to the intensive care unit. The ICU detects the signal and stops current flow to the primary winding of the coil.
When the gap leaves the sensor, an appropriate signal is again sent to the ICU, which causes current to flow through the primary winding of the coil.
This continuous process creates a magnetic field in the primary coil and induces an electromotive force in the secondary winding of the coil. This voltage can go up to 70,000 volts. This high voltage is sent to the spark plugs to produce a quality spark with precise timing.
Pros
- A distributorless ignition system eliminates wear and tear on moving distributor parts.
- These work via an engine computer that receives a top dead center signal from a sensor in the flywheel and can quickly adjust ignition timing for different driving conditions.
- One of the biggest advantages of the is that it is easily adaptable to the fuel you are using. For example, if you are using low octane fuel, the computer can detect engine knock and minimize the time it takes to process low octane fuel.
- The RPM reference signal is boosted directly from the crankshaft, so it doesn’t change with wear. This eliminates the need to adjust ignition timing from time to time.
- The distributorless ignition system is highly reliable and has low maintenance costs. The
has no distributor to drive, so the motor has less resistance.
Cons
- Distributorless ignition systems are more difficult to diagnose than solid state electronics.
- As with conventional systems, high voltage wiring is required from the coil to the spark plug.
- The main drawback of the distributorless ignition system is its sensitivity to heat loss.
- The distributorless ignition system is more sensor dependent. If one sensor fails, the whole system collapses.
Uses
Most of the 1.8L, 2.8L VR6 and 2.8L V-6 engine cars on the road have used this method for a century. This type of ignition system first used in the 2.8-liter VR6 engine in the Volkswagen Passat.In addition to the Ducati Supersport, this formula is also followed by some high-end bikes.
