In this post, we will discuss all the major effects of earthquakes. A high intensity earthquake can be very dangerous to humans life.
Table of Contents
Various Effects of Earthquakes
1. Ground Movement
When an earthquake occurs, seismic waves propagate horizontally or vertically, shaking structures in all directions.
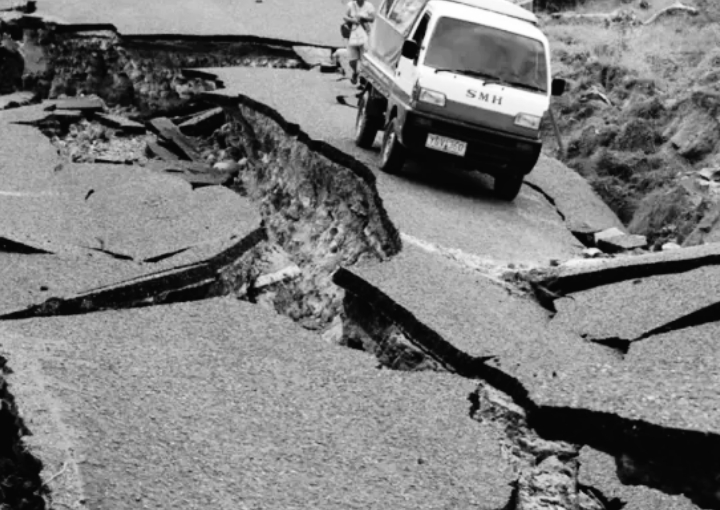

This can lead to loose joints and weakened structures, and in some cases to tilting and collapsing structures, leading to loss of life and property.
Ground vibration is measured with the help of a ground accelerator.
2. Soil Liquefaction
Ground liquefaction is one of the alternative effects of land deformation.
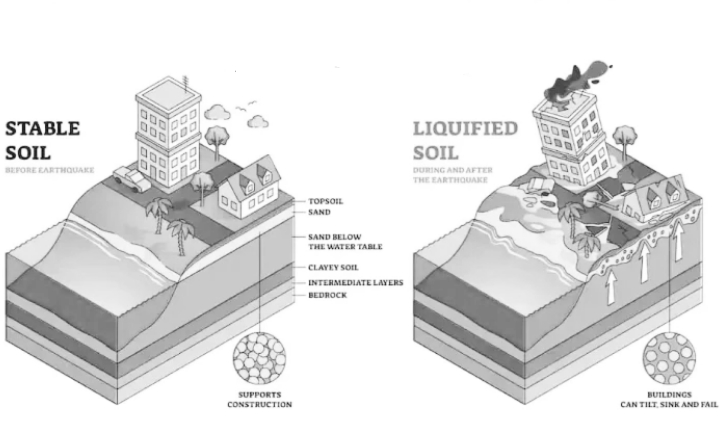
When grains such as sand containing moisture temporarily lose their strength, they change from solid to liquid and liquefy.
This commonly causes rigid structures such as buildings to sag or tilt.
3. Soil Settlement
Earthquake tremors act as natural oscillators, removing air bubbles and using natural pressure to move underground water from one place to another. This results in a high degree of land subsidence.
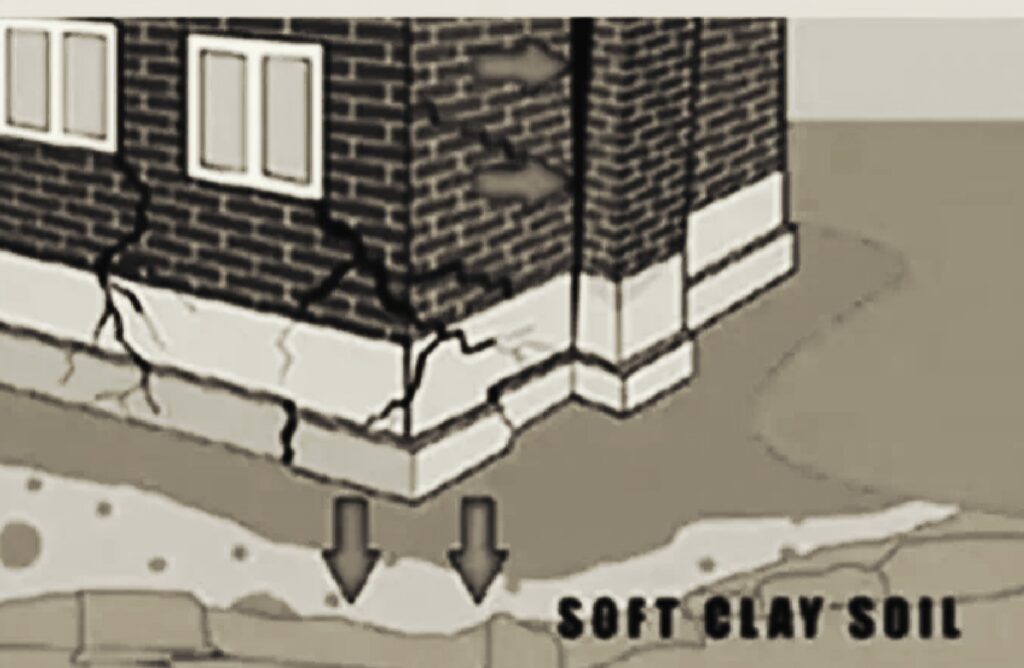
This can lead to the tilting of the settlement and sometimes to the complete collapse of the structure.
4. Broken Ground
A ground fault is a visible disruption and movement of the earth’s surface along a fault track, and it can be small or large.

During vibration, stresses are generated in the ground, leading to ground failure.
Structures such as dams, nuclear power plants, bridges, tunnels, pipelines and roads are at high risk of ground failure.
5. Landslide
Earthquakes shake slopes in all directions, destabilizing them. This causes landslides and the loss of thousands of lives and property.
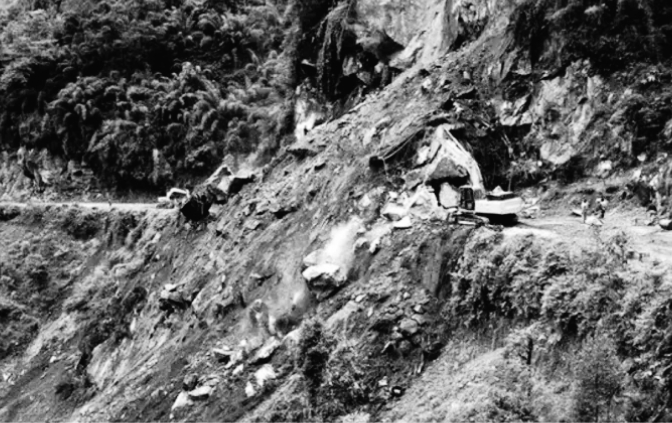

Mudslides can be so large that the mound is almost completely destroyed.
Rockfall is also a kind of dry landslide caused by an earthquake.
6. Flood
These are the indirect effects of earthquakes, such as landslides and dam failures.
Collapse of glaciers due to earthquakes is also a big problem.
7. Effects on Human
As we know, earthquakes cause ground motion along with various forms of seismic waves (horizontal or vertical). If the quake is prolonged and large, it can lead to health problems such as heart disease, panic attacks, and depression in survivors.
Thousands of people die in earthquakes every year.
The buildings we live in are hard, and the impact of earthquakes is greater on such structures.
It’s so sudden that most people don’t have a chance to escape.
8. Tsunami
Tsunami comes from the Japanese word for “minato wave”. Also called tsunami.

A tsunami is a series of large waves caused by the movement of large amounts of water, such as earthquakes in oceans and lakes, volcanic eruptions in oceans and oceans.
80% of tsunamis originate in the Pacific Ocean. Most countries such as Japan, USA and Hawaii are at high tsunami risk.
Landlocked countries such as Nepal, Mali, Hungary, Bhutan and Ethiopia are not at risk.
The main cause of tsunamis is earthquakes of magnitude 7.5 or higher.
9. Fire
It is also another secondary effect of earthquakes. Power supplies and gas pipes may collapse due to an earthquake, resulting in a fire. Once a fire starts, it is very difficult to control its spread.
10. Effects on Agriculture
Earthquakes badly impacts agricultural land. There are cracks in the land. Workers can not enter to the land due to high risk of landslides. Irrigation can not done due to unstable soil.
