Table of Contents
Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG)
Liquefied Natural Gas also known as LNG. It is a natural gas consist of methane (CH4) and ethane (C2H6). It contains more than 90 % methane gas. This mixture if ethane gas and methane gas is known as natural gas.
Natural gas cooled down to liquid form for ease and safety of non-pressurized storage or transport.
Volume of LNG in liquid form = Volume of LNG in gaseous form/600.
So we can say, It takes up approximately 1/600th the volume of natural gas in the gaseous state.
You can not feel this gas because it is odorless, colorless, non-toxic and non-corrosive. Some serious hazards related to LNG are flammability after vaporization into a gaseous state, freezing and asphyxia.
Various components are removed in the liquefaction process such as dust, acid gases, helium, water, and heavy hydrocarbons, which could cause difficulty downstream. After that, natural gas is condensed in the liquid form. In the condensation process natural gas cooled down at −162 °C temperature. Transport pressure of this gas is kept at around 25 kPa (4 psi) (gauge pressure), which is about one-fourth times atmospheric pressure at sea level.
Natural liquefied gas is extracted from underground hydrocarbon sources. These hydrocarbon contains various gases such as methane, ethane, butane and propane. CO2 also found in the natural gas.
Gas streams are used to separate various other gases such as butane and propane. These gases can be stored in liquid form at relatively low pressure. Butane and propane further liquefied to make up the bulk of LNG that is shipped.
Recent Developments
As the technology grew in the oil and gas sector, liquefied natural gas picks demand. Before, there was no technology to transport and handle safely. Most of the known gas fields were located at offshore location. It was very difficult to transport the gas from the offshore locations. The natural gas market was limited to the local market.
Recent developments in the sector of oil and gas boost the production and utilisation of the liquified natural gas. Nowadays, it is competing conventional oil products such as diesel and petrol. Superior storage techniques has been developed to store the LNG for months. This make uninterrupted supply of LNG.
Lets see typical LNG process.
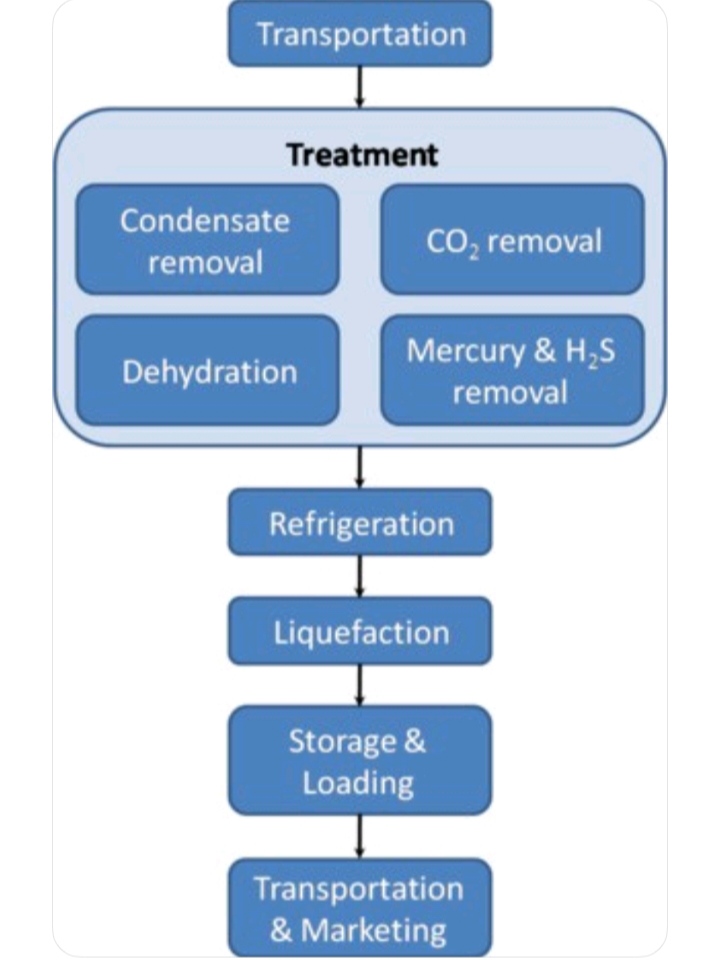
Production, Storage and Distribution
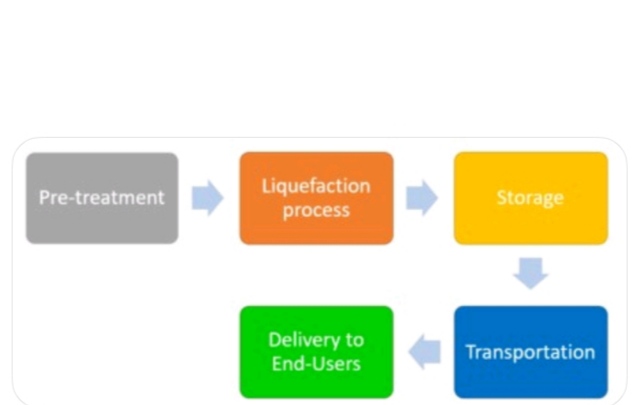
First pre-treatment is done. In this process various impurities removed. These are such as H2S, CO2, H2O and higher-chained hydrocarbons.
After pre-treatment, Feedstock gas then enters the liquefaction unit where it is cooled to between -145 °C and -163 °C. Natural gas is send into aluminum tube coil where gases comes into the contact of refrigerant. Refrigerant is vaporized and gas cooled down.
After liquefaction, LNG is then stored in a specialized double-walled insulated tank at atmospheric pressure ready to be transported to its final destination.
Liquefied natural gas is transported by truck/trailer. These trucks are designed for cryogenic temperatures. LNG is transported from one country to another country via tanker ships. These tanks have advance technology to prevent heat transfer.
When ready for distribution, the LNG enters a regasification facility where it is pumped into a vaporizer and heated back into gaseous form. After regasification, this gas is transported to end users via pipelines
Uses
As we knows that LNG is in early stage of development. It is normally used in vehicles and cooking foods. But in future more applications will come out. It can be used in trains, trucks and marine applications.
