There are four methods of levelling used in the field of construction. Levelling methods are used to calculate the height difference at different ground levels.
The following methods are used to determine the difference in elevation of various points:
- Barometric levelling
- Hypsometric levelling
- Direct levelling
- Indirect levelling.
Let’s learn about these methods of leveling.
Table of Contents
1. Barometric Levelling
This method depends on the principle that atmospheric pressure depends upon the elevation of place.
Barometer is used to measure the atmospheric pressure and hence elevation is computed.
However it is not accurate method since the atmospheric pressure depends upon season and temperature also. It may
be used in exploratory surveys.
2. Hypsometric Levelling
This is based on the principle that boiling point of water decreases with the elevation of the place.
Hence the elevation difference between two points may be found by noting the difference in boiling
point of water in the two places. This method is also useful only for exploratory survey.
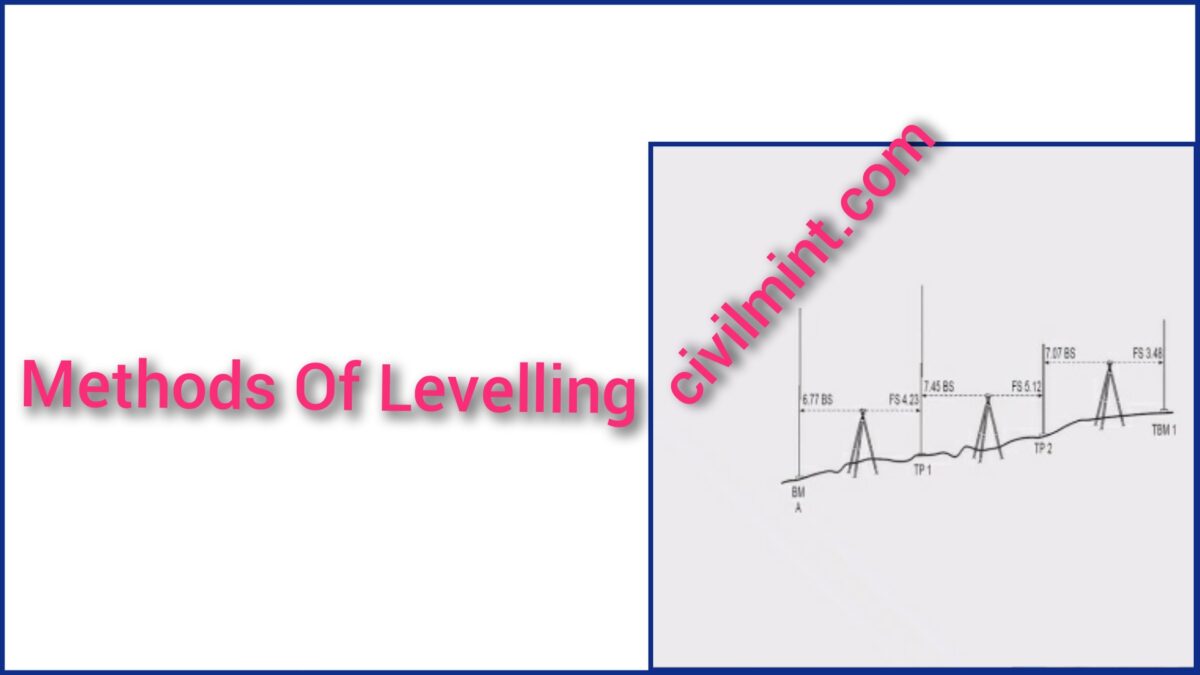
3. Direct Levelling
It is common form of levelling in all engineering projects. In this method horizontal sight is taken on a
graduated staff and the difference in the elevation of line of sight and ground at which staff is held are
found. Knowing the height of line of sight from the instrument station the difference in the elevations of
instrument station and the ground on which staff is held can be found. This method is thoroughly
explained in next article.
4. Indirect Methods
In this method instruments are used to measure the vertical angles. Distance between the instrument
and staff is measured by various methods. Then using trigonometric relations, the difference in elevation
can be computed. This is considered beyond the scope of this book. One can find details of such methods
in books on surveying and levelling.
Faqs
Trigonometric, barometric, and differential leveling.
Several types, including trigonometric, barometric, differential, and digital leveling.
Differential, trigonometric, and barometric leveling.
Techniques used to measure elevations and determine height differences between points.
