The flange pressure temperature rating or class refers to the maximum pressure that a flange withstands at the increasing temperatures. Flanges with a higher rating are stronger than the flanges with a lower rating, which means 600# flanges can bear more pressure than 150# flanges. But it totally depends upon the temperature range.
As the temperature of the system increases the pressure withstanding capacity of flange decreases. Also, the flanges of the same rating made with different materials show the different pressure bearing performance.
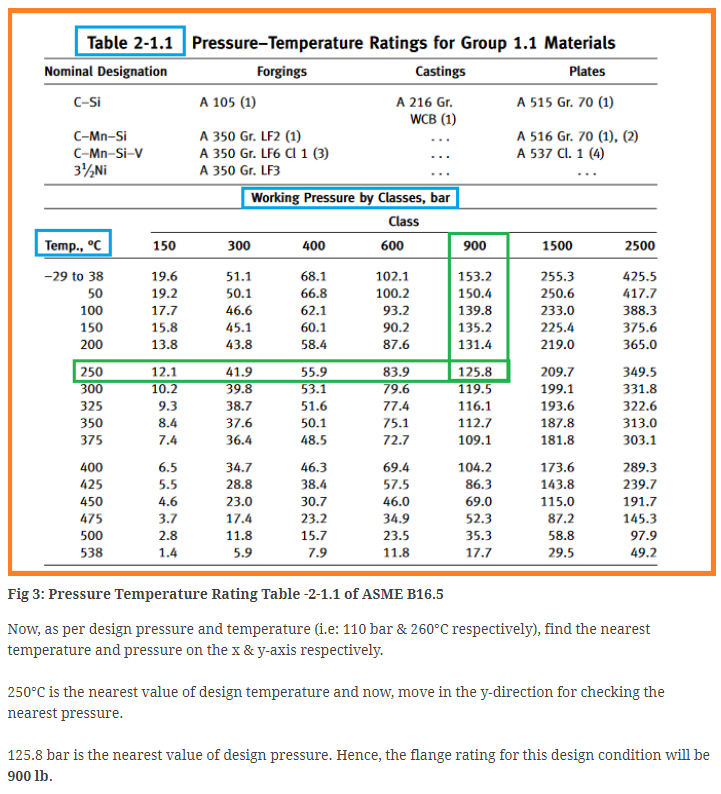
All Pipes and various pipe fittings are most commonly classified based on their pressure temperature rating or commonly known as P-T Rating. The most common way of specifying pipe pressure temperature rating is given by ASME 16.5, using pound ratings (or lb ratings) – #150, #300, #400, #600, #900, #1500 and #2500. The pressure rating or pound rating for a pipe is determined using the design pressure and design temperature for the pipe.
Among other methods of classification by using pressure temperature ratings is ‘Pression Nominal’ or ‘Pressure Nominal’ or PN number method. This PN number is a rough indicator of pressure rating in bar.
Pressure rating or pound rating of a pipe is dependent on the pipe material and design temperature. The pipe pressure rating for the same material changes at different temperatures. For the same material and constant design pressure, different pressure ratings are applicable over different ranges of design temperatures. As the design temperature increases the pressure rating requirement for the pipe also increases for the same design pressure.
It should be noted that the pound rating for the whole piping system is equal to the pound rating of the weakest part, having the lowest pressure rating in the system. The weakest part may be any piping component or fitting which contains the pressure in the system and has the lowest pound rating due to any possible reasons.
All the piping components are not designated by Pressure class, only flanges and items related to flanges like gaskets(not bolts) are designated as class. Also socket welded components are designated by Pressure class eg 3000, 6000 & 9000 AND SCREWED COMPONENTS Eg 2000, 3000 & 6000 based on the thickness as per ASME 16.11.Rest all components are designated by thickness(either sch or thickness).
So we can broadly divide the piping components in two groups
1- Flanges,Gaskets,Valves,Socket Welded fittings,Screwed fittings designated by CLASS.
2-Piping components designated by THICKNESS and SCHEDULE.
The basic principle of any design is to make the weakest component strong.A flange joint is the weakest in piping system. (Note: joint is weak not the flange.) this is the reason why we establish rating first for flanges(group-1). And then based on the corresponding pressure and temperature .Allowable stresses are noted down and pipe thickness are computed.
Rating of a piping component is designated by class followed by a dimensionless number(for example Class150 ). This is the very important term used to differentiate piping components in a specifications.
Understanding of pressure temperature rating is very essential and mandatory for the study of piping engineering.
Pressure temperature ratings are defined on the basis of definitions of design pressure,design temperature stated in code ASME B31.3 and & Material group (ref B16.5)
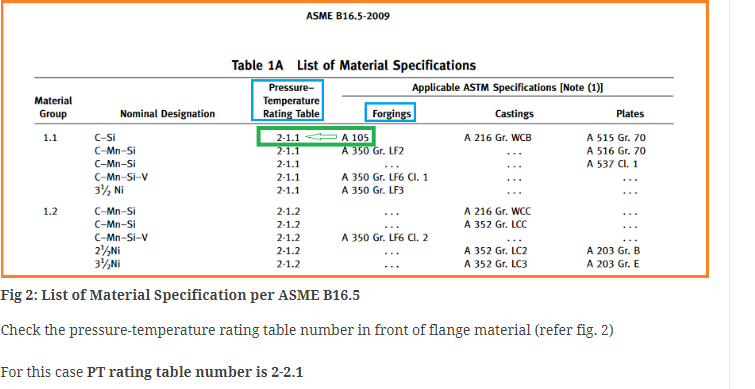
We get design condition from process and base material from metallurgist, we need to choose relevant material group based on base material. The material group in B16.5 is only flange material not pipe/fitting material.
Design Pressure as per code ASME B31.3-2008(Revision of ASME B31.3-2006)states that
as per para 301.2.1
(a)The design pressure of each component in a piping system shall be not less than the pressure at the most severe condition of coincident internal or external pressure and temperature (minimum or maximum) expected during service, except as provided in para. 302.2.4.
(b)The most severe condition is that which results in the greatest required component thickness and the highest component rating.
Table of Contents
Basic of selection of P-T rating.
Design pressure and operating temperature:-
If a fluid having 10 bar working temperature filled in a cylinder then vessel always should be design more then 10 bar pressure to withstand the fluid pressure. This pressure is called design pressure.

Temperature vs Strength:-
if the temperature of any mechanical components increase then tensile strength gets reduced because when we increase the temperature of any rod then it’s become melted at certain temperature. and load Bearing capacity of that components become reduced .
Pressure VS Strength:-
if the temperature of any cylindrical components increase then strength and rigidity gets reduces due to this result the pressure bearing capacity of the component is reduced so we can say tensile strength is directly proportional to pressure. Strength material can bear more pressure w.r.t to temperature.
from above points we can say that the rating of flanges is defined as the rating increase then strength also increase.
Selection of flange rating:-
Inputs Required for Deciding Flange Rating
The following are required input for selection of flange rating or class-
Code – ASME B16.5 (as per the application)
Flange Material – ASTM A105 (CS forged Flange)
Design Pressure – 110 bar
Design Temperature – 260°C
Flange Rating Selection Steps
Step 1:Now, using “Table 1A” of ASME B16.5, find out the PT (Pressure-Temperature) Table number according to the flange material (i.e; A105)
Step 2:Now, go to the PT rating table number 2-2.1 of ASME B16.5 (refer fig. 3)