A pipe support or pipe hanger is a designed element that transfers the load from a pipe to the supporting structures then civil structure. The load includes the weight of the empty pipe, fluid (medium) that pipe carries, all the pipe fittings attached to pipe, weight of valve and special item, and the pipe covering such as insulation.
The four main functions of a pipe support are to anchor, guide, absorb shock, and support a specified load. Pipe supports used in high or low temperature applications may contain insulation materials. The overall design configuration of a pipe support assembly is dependent on the loading and operating conditions.
The selection of pipe support depends upon the various parameters like fluid density, movement, displacement, load acting on the piping system, operating temperature of pipe, weight of valve and fittings etc. The proper selection is done by the pipe stress engineer.
Table of Contents
There are many factors which affect the pipe support span.
Pipe support span is basically the distance between two pipe support.it also called pipe support spacing .there are so many factor which affect the pipe support span. today we will only discuss about the pipe support span factor during design the piping system. and our next topic will describe the type of support used in oil and gas industry/power industry and what type of material used for pipe support for different type of pipe.
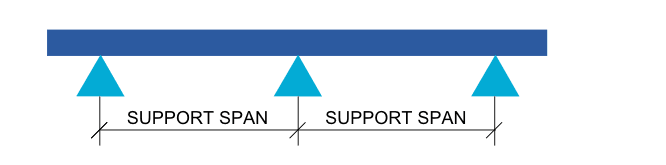
Factor:-
1.Type of Mechanical Equipment:-
There is two type of mechanical equipment’s ( static equipment’s ,rotating equipment’s),for static equipment’s there is no vibration so the supports selection is less critical but in rotating equipment’s (pumps, compressor, turbine) we have to minimize the vibration in all x,y,z direction so support selection is too critical .in rotatory equipment’s generally we provide hangers, axial stop considering the project cost and also decided by stress engineer.
2.Pipe Material:
pipe support spacing varies with pipe material .pipe support span will be different w.r.t pipe material .pipe support span of non-metallic pipe lesser then metallic pipe of the same size and for same fluid for exp. (ss pipe has lower pipe support span as compared to carbon steel). Support span is also depends upon the pipe material density and density of fluid which flow inside the piping system.
3.Nominal Diameter of pipe & schedule:-
with the increase in pipe diameter (NPS ,DN,NB) and Schedule( pipe thickness) ,pipe support span increase. In easy way we can say that for large diameter pipe have minimum number of support w.r.t small bore pipe because the load bearing capacity of large bore pipe is high as compared to small bore pipe and small bore pipe is easily sagging* when the fluid flow inside the pipe having pressure and temperature.
Exp.-4’’ pipe is leaser pipe support span as compare 36’’ pipe.
4.Type of Fluid Service:–
Piping support span varies with fluid service; Pipes carrying liquid service have less support span as compared to pipes carrying gaseous fluids. This means with an increase in density of the flow medium pipe support spacing decreases.
5.Type and Thickness of Insulation Material:-
With an increase in thickness and density of the insulation material, pipe support spacing reduces. An increase in insulation density and thickness imposes more load on the parent pipe which needs to be supported by increasing the number of supports which means pipe support span reduces.
6.Piping Configuration (Straight pipe and Pipe with elbows):–
Pipe support spacing is dependent on the piping routing or geometry. A straight pipe has more support span as compared to pipes with directional changes. Because of this reason, to find out the span for piping including elbows, the straight pipe span is multiplied by a factor as shown in Fig.1
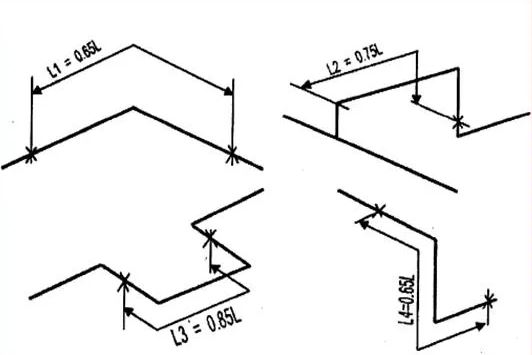
where L is normal pipe support span.
by multiplying by the factor new support span is decrease
7.Locations of Valves and Rigid Bodies:–
The presence of rigid bodies in a piping or pipeline system reduces the pipe support span. It is a general engineering practice is to provide at least one support near to the rigid-bodies like valves (Preferable to provide support on both sides of the valve).

8.Structural Availability for support:
Available structures are normally used for supporting the pipe. So pipe span chart may be reduced in those places. Also, an increase in the number of supports distributes the piping loads on supports and increases the piping stiffness. So, if a structure is available, pipe supports are usually taken from those structures.
If structure not available then piping department should plan for supporting structure, T-Support from 0.00.this is the input for civil department.
9.Vibrating or Pulsating lines:–
For vibrating or pulsating lines pipe support span is reduced to avoid vibration tendency and to increase the natural frequency of the piping system. A reduction in pipe support spacing increases the system rigidity which reduces the tendency of pipe vibration.
10.Fluid Temperature:–
With an increase in fluid temperature as allowable stress value reduces, the pipe is supported nearby position and thus reducing the pipe support spacing.
Deciding Pipe Support Span:-
- Bending Stress
- Deflection
- Indentation
- Allowable Loads
- Vibration Possibility and Natural Frequency of the piping system.
1.Bending Stress: –
Bending is caused mainly due to two reasons:
- Uniform Weight Load
- Concentrated Weight Load
1a.Uniform Weight Load:-
- Own Weight Of Pipe
- Insulation Weight
- Weight of Fluid During operation
- Weight of hydrostatic fluid During Hydro Test.
1b.Concentrated Load
- Weight Of Valve, Flanges,
- Strainer, specialty items, inline items, etc.
2.Deflection:-
Deflection (Δ) is defined as a relative displacement of the point from its original position.
- The basic piping practice to limit pipe deflection between supports to 1” or 1/2 the nominal pipe diameter, whichever is the smaller.
- The most important reason for limiting deflection is to make the pipe stiff enough, that is , of high enough natural frequency, to avoid large amplitude response under any slight perturbing force. As a rough rule, for average piping, a natural frequency of 4 cycles per second will be found satisfactory. The natural frequency can be calculated by
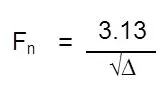
3.Indentation:-
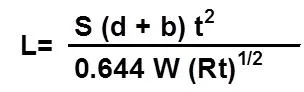
t=corroded Thickness of pipe Wall(mm)
S=0.67Sh(N/mm^2)
R=Radius of pipe (mm)
d=Bearing Length(mm)
b=Bearing width(mm)
4.Allowable Load at Support:-

t=effective local thickness (pipe wall +Reinforced Pad If Any)
R=outer radius of Pipe
b=Bearing length of pipe (along the axis) on the support structure.
IF THE ACTUAL LOAD AT SUPPORT IS GREATER THAN THE ALLOWABLE LOAD GIVEN BY THE ABOVE FORMULA, A REINFORCEMENT PAD WILL BE REQUIRED.
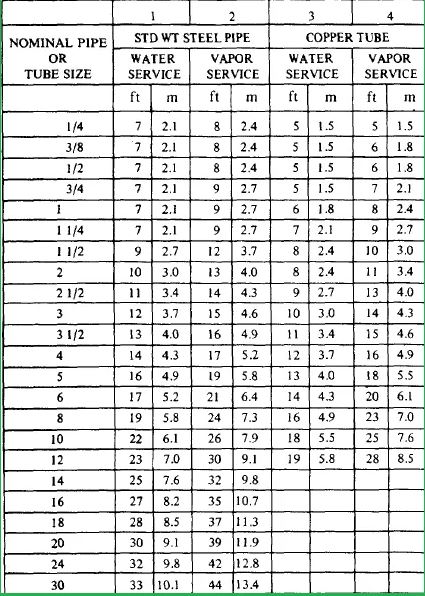
Pipe support span/pipe support spacing table:-
The selection of pipe support span by an layout engineer/support engineer/stress engineer/piping engineer varies from project to project by considering the project cost and process parameter. In the following image (Fig. 3) pipe support span chart from MSS SP-69 is reproduced as a sample.
**IN Our next two topic i will discuss about the type of pipe support ,how they work and support material.
