Table of Contents
What is tacheometric surveying?
The definition of tacheometric surveying cab be given as:
In this type of surveying different measurements like vertical distance and horizontal distance are taken indirectly by taking only instrumental observation.
Typically, tacheometric survey is used when high observation accuracy is not required.
A survey is performed to create a contour map of the site. It can be used to determine the height of a road or railroad.
From this overview, we can calculate the RLs of various points based on our readings and some observations.
Principle of Tacheometry
The basic principle of Tacheometry is based on the basic principle of an isosceles triangle.
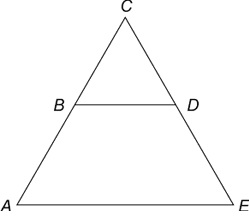
On any two sides equal triangle means an isosceles triangle, there is one property that is used in the Tacheometry.
Ratio of the perpendicular to vertex on their base and their base is always constant in isoceles triangle.
In other words, if the object is far from the top, it covers a large area, and if it is close, it covers a smaller area because the proportions are constant. This is how the tachometer works.
There is an object that is far away from the instrument, and when you look at the instrument, it appears at a small distance from the diaphragm.
Now let’s look at the advantages of using a Tacheometer survey compared to other survey methods.
Advantages of Tacheometric surveying
- You don’t have to do the chain work required by other surveying methods.
- Surveying is possible even in areas that are difficult to shoot in other ways, such as hills and mountains.
- If you don’t need very high standards and accuracy, this is the right way to go.
- It takes less time compared to other surveying methods.
- Because tachometrics is an indirect method, it does not require the tools required for vegetative or theodolite surveys.
Uses of Tacheometric survey
- Used for contour mapping when both horizontal and vertical distances are required. It is also very useful for triangulation.
- Sometimes geodetic operations are performed in hard-to-reach areas when direct methods such as Theodolite traversing or plane table are not available.
- Tacheometry is a reconnaissance survey of roads, roads, and railways.
- Can be used to set secondary control points.
Method of Tacheometric surveying
- Stadia Method
- Tangential Method
1. Stadia Method
The stadia method is a popular method for calculating horizontal distance and vertical height.
The horizontal distance between the pole and the instrument point and the height of the pole point along the line of sight of the instrument is calculated using this approach with only one instrument position observation.
This survey method can be divided into two types:
A. Fixed Hair Method:
In this type of survey, the device used to make observations is a telescope with two additional crosshairs.
So, the hair on the stage is the hair at the same distance from the center hair.
If you look through the telescope, you can see that the hair in the stadium is blocking a certain length of the rail.
This is the most commonly used tacheometric survey method.
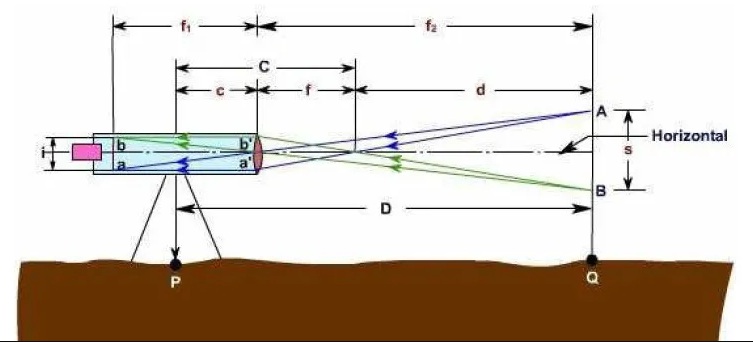
B. Movable Hair Method:
Unlike the stadium hairstyle, the moving hairstyle contains a moving crosshair in a telescope attached to the instrument. You can also use the central hair to secure the removable crosshairs.
Stadium spacing is adjusted in this way for different staff positions. Then the horizontal distance is calculated. The gadget is used with two targets at a fixed distance.
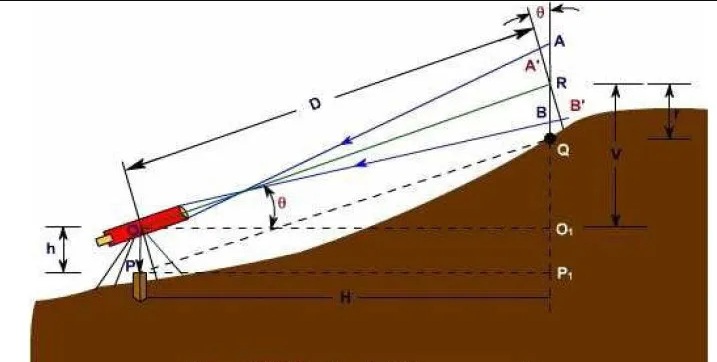
2. Tangential Method
A tangential tacheometric survey requires two observations between a regular column and an instrument column. It calculates the horizontal distance and height difference between the collimation line and the pole.
The most important advantage of this procedure is that it can be performed by standard means of transport. Obviously, because of the slower operating speed, this approach is less used compared to stadium systems.
