Table of Contents
What are the Waves?
Waves can be defined as the things which creates a disturbance in the various medium when it travels while carrying energy even though the net movement of particles remains zero. So, we can say that it transfers the energy which includes a periodic motion of waves without a net movement of the particles present in the medium (Mechanical Waves).
Wave Properties:
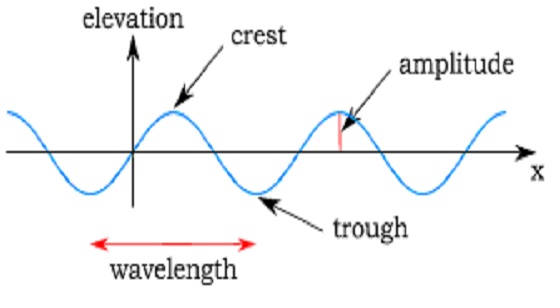
Amplitude:
We know that wave travels in a repetitive motion which is also called the periodic motion. So, the amplitude can be defined as the maximum height or displacement of the wave from the neutral axis. It is measured in meters. The higher amplitude carries higher energy and vice versa.
Wavelength:
The wavelength is also measured in meters. It is defined as the distance between two identical or repetitive parts of the wave. So, we can say the distance between two crests, or two troughs is known as the wavelength. It is denoted by λ.
Period:
The period of a wave is measured in the second or minute. It can be defined as the time taken by the wave while traveling in a medium to complete one full vibration or oscillation cycle. It is denoted by T.
Period = T = 1/frequency
T= 1/f
Frequency:
The frequency is denoted by f. So, the frequency can be defined as the number of waves that pass through a particular point in a second. It can be also defined as the number of repetitions of waves per second. It is measured in Hz.
Frequency = 1/Period
f = 1/T
Speed Of Waves:
The speed of the waves can be defined as the distance traveled by the waves from a given point at a particular time. It is denoted by V. The unit of the speed of the wave is m/s.
Speed = V = Distance Travelled /Time Taken
Different Types Of Waves:
1. Transverse Waves:
The transverse waves can be defined as the waves in which waves move at a right angle to the medium. So, the medium will be perpendicular to the direction of movement of the waves in the transverse waves. For example – water waves, light waves, s – earthquake waves, torsion waves, etc.
Crest:
The highest point in the transverse waves from the axis is called the crest.
Trough:
The lowest point in the transverse waves from the axis is called a trough.
2. Longitudinal Waves:
In longitudinal waves, the movements of the waves are in the same direction as the particles in the medium. That means in longitudinal waves the movements of the waves are parallel to the medium in which it is traveling. For example – sound waves, p – earthquake waves, compressive waves, etc.
There Are Two Types Of Longitudinal Waves.
⦁ Compressive Longitudinal Waves.
⦁ Rarefaction Longitudinal Waves.
Compressive Longitudinal Waves:
It is the longitudinal waves in which the particles are very close to each other.
Rarefaction Longitudinal Waves:
It is the longitudinal waves in which the particles are far away from each other.
3. Mechanical Waves:
Mechanical waves are the waves that required medium to travel from one point to another. Sound waves and water waves are good examples of mechanical waves.
4. Electromagnetic Waves:
Electromagnetic waves are the kinds of waves that do not require any medium to travel from one point to another. It can also travel in a vacuum. When electromagnetic waves travel in a medium the electric and magnetic field oscillates at a right angle. The magnetic and electric field is also at 90 degrees to each other in EM waves. Radio waves, light waves, X-rays, and cosmic rays are some good examples of electromagnetic waves.
