Table of Contents
What Is Geofoam?
Geofoam is a lightweight fill material used in construction and engineering projects, composed of expanded polystyrene (EPS) beads. These beads are expanded through heating, creating a foam-like structure that is molded into large blocks, offering versatility and exceptional properties for various applications.

The material’s low density compared to traditional fill materials like soil or gravel makes it easier to transport and install, reducing construction time and cost. Despite its lightness, Geofoam is remarkably strong and capable of supporting heavy loads, making it suitable for roadways, embankments, foundations, and landscaping projects.
One of its key advantages is its ability to reduce lateral pressure, benefiting retaining walls and bridge abutments’ stability, especially in earthquake-prone regions. Geofoam’s resistance to moisture and chemicals ensures long-term stability, making it attractive for underground applications like tunneling or buried utilities.
The installation process is straightforward, requiring minimal equipment, and its lightweight nature reduces the need for heavy machinery, minimizing disturbance during installation.
In transportation projects, Geofoam creates lightweight embankments for roadways and bridges, reducing load on the underlying soil and enhancing safety during adverse conditions. It’s also widely used in retaining walls in urban areas with limited space, providing erosion control and slope stabilization.
Geofoam finds use in geotechnical engineering on weak or compressible soils to minimize settlement and prevent structural damage. Its environmental benefits include lower greenhouse gas emissions during production and being 100% recyclable.
However, Geofoam may not be suitable for applications requiring high thermal resistance, and in areas with rodent activity, protective measures might be necessary to prevent damage.
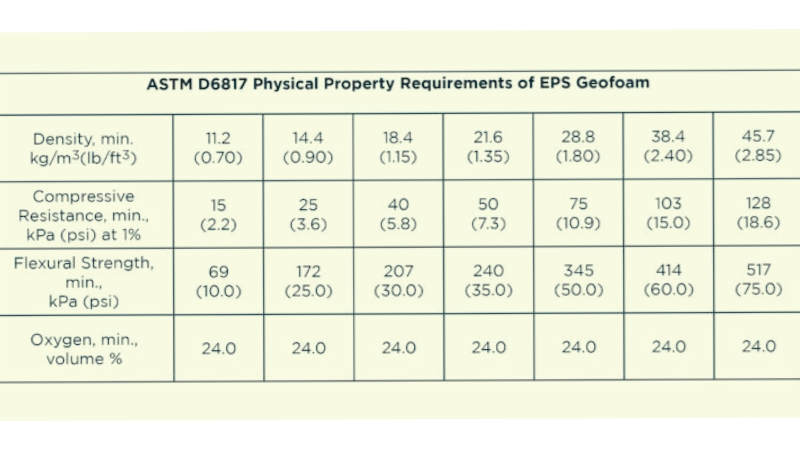
Properties Of Geofoam As Per ASTM D6817
Manufacturing Process
Geofoam manufacturing involves several steps. First, manufacturers carefully select raw materials, primarily expanded polystyrene (EPS) beads, based on specific density and size criteria.
Next, they pre-expand the EPS beads using steam, causing them to increase in size and decrease in density, making them suitable for geofoam production.
After pre-expansion, the pre-expanded EPS beads are placed into molds of desired shapes and sizes. These molds are custom-made to fit the requirements of the project.
Then, the filled molds undergo another round of steam treatment, further expanding the EPS beads to fill the mold cavity completely.
Once molded, the geofoam blocks are left to cool and cure, solidifying the material and stabilizing its dimensions.
Subsequently, the cured blocks are cut into specific sizes and shapes using hot wires or other cutting tools.
Throughout the process, manufacturers conduct rigorous quality control checks to ensure that the finished geofoam blocks meet the required specifications and standards.
Finally, the completed geofoam blocks are packaged and distributed to construction sites or suppliers for use in various geotechnical and construction applications.
It’s essential to acknowledge that variations may exist in the manufacturing process depending on the manufacturer and the intended application of the geofoam.
Uses Of Geofoam
- Geofoam is used to reduce soil settlement beneath roads and bridges, ensuring stable infrastructure.
- It provides insulation for building foundations, helping maintain a constant temperature indoors.
- Geofoam acts as a lightweight fill material in embankments, reducing overall construction costs.
- It is utilized in sports fields to enhance shock absorption and create safer playing surfaces.
- Geofoam is employed in landscaping projects to create raised garden beds and planters.
- It helps to control erosion and stabilize slopes in hilly areas.
- Geofoam is used as a buoyancy material in floating docks and pontoons.
- It serves as a lightweight fill in underground utility trenches, simplifying installation.
- Geofoam is used in sound walls and barriers to reduce noise pollution along highways and railways.
- It acts as a protective layer for buried pipelines, preventing damage from external loads.
- Geofoam is utilized in geotechnical engineering to reduce lateral pressures on retaining walls.
- It is used in lightweight fill applications for underground tunnels and cavities.
- Geofoam is employed in creating green roofs to promote energy efficiency and urban biodiversity.
- It acts as a thermal insulator for refrigeration units and cold storage facilities.
- Geofoam is used in creating lightweight, earthquake-resistant structures.
- It serves as a lightweight backfill material for voids in building foundations.
- Geofoam is used in coastal protection projects to create artificial dunes and beaches.
- It is employed in levee construction to reduce overall weight and settlement.
- Geofoam is used in the installation of underground stormwater management systems.
- It acts as a fill material for underground utility trenches in airport runways and taxiways.
Advantages Of Geofoam
- Geofoam exhibits low density and high strength, providing an efficient lightweight fill option with equal strength to soil.
- Its predictable behavior allows engineers to specify precise design criteria, ensuring reliable and consistent performance.
- Being inert, Geofoam does not degrade or pollute surrounding soils, making it environmentally friendly and sustainable.
- The installation of Geofoam is quick and can be carried out during any weather conditions, leading to reduced construction time.
- It can be easily dug up and reused, making it a cost-effective and flexible material for various construction projects.
- Geofoam’s thermal insulation properties make it an excellent choice for insulating buildings and infrastructure.
- The material’s resistance to insect damage can be enhanced through appropriate treatments, ensuring long-term stability.
- Geofoam’s low weight reduces the load on foundations, minimizing the need for extensive reinforcement in construction.
- It provides excellent buoyancy control, preventing issues caused by uplift forces in certain applications.
- Geofoam’s consistent composition ensures a uniform and reliable structural performance in different projects.
Disadvantages Of Geofoam
- Untreated Geofoam poses a fire hazard, requiring appropriate fireproofing measures in specific applications.
- Contact with petroleum solvents can render Geofoam unable to support any load, making proper handling crucial in such scenarios.
- Buoyancy forces can lead to dangerous uplift forces, necessitating proper engineering and anchoring solutions in certain situations.
- Geofoam may be vulnerable to insect damage, particularly in buildings where wood is present, requiring preventive treatments.
- The material’s vulnerability to certain factors may limit its application in specific construction contexts.
