Table of Contents
Precipitation Definition:
The condensed water that comes back to the surface of the earth due to gravitational forces is known as precipitation.
What Is Precipitation?
Any form of water that falls from the atmosphere and reaches the Earth is called precipitation. Water reaches to the earth in various forms such as rain, snow, ice, snow, and other frozen or liquid particles.
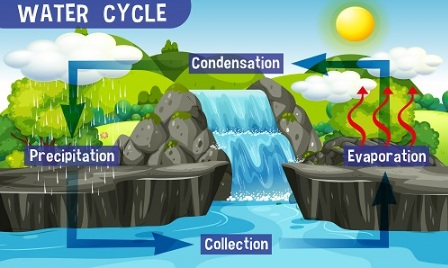
Precipitation occurs when moisture in the air condenses into tiny ice cubes or ice heavy enough to fall to the ground under the influence of gravity. Precipitation is an integral part of the Earth’s water cycle and plays a vital role in the survival of life and ecosystems. The amount and type of precipitation in an area can vary depending on a variety of factors, including temperature, humidity, wind conditions, and topography.
How Precipitation Takes Place?
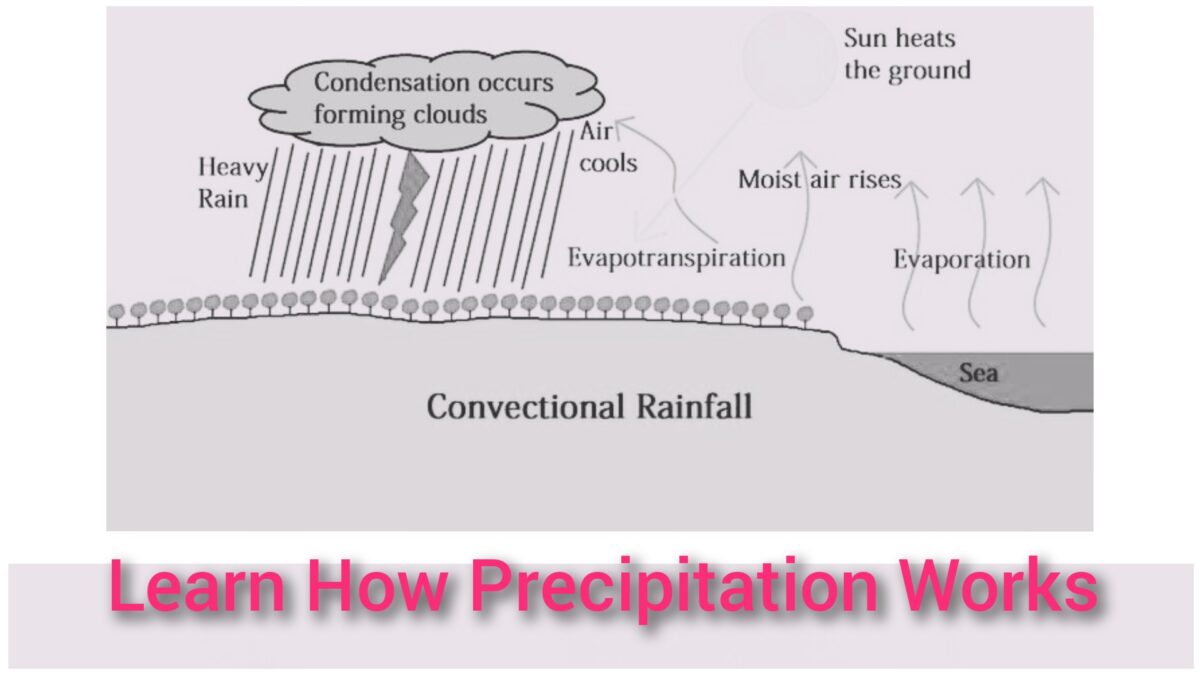
Water evaporates from the exposed water surfaces like streams, rivers, oceans, ponds, and the lands and plants, in the form of water vapour. These water vapours get collected in the atmosphere like a gas. As the evaporation continues, the atmospheric vapour goes on increasing and finally reached a state where any further addition of vapour will get condensed to the surface of the earth in the form of precipitation.
Different Forms of Precipitation:
There are many different forms of precipitation. A major part occurs in the form of rain and a minor part occurs in the form of snow.
1. Rain:
Rain is described as water droplets of 0.5 mm or larger that drop from the clouds in the atmosphere to the surface of the earth. In the atmosphere the small cloud particles strike and bind together and; as this process continues, the drops get bigger and bigger to an extent where they become too heavy to suspend in the air. As a result, gravity pulls them down to the earth which falls as rain.
| Rainfall category | Rates |
| Light Rain | 0.01-0.1 inches/hour |
| Moderate Rain | 0.1-0.3 inches/ hour |
| Heavy Rain | Above 0.3 inches/hour |
2. Snow:
Snow is defined as solid precipitation which is formed when the temperature is low and there is moisture in the atmosphere in the form of tiny ice crystals. Once these tiny ice crystals stick together to form snowflakes in the clouds, gravity pulls them down to the earth’s surface which falls as snow. It is nearly 20,000-footfall.
3. Sleet:
Frozen rain liquifies in light warm air, then refreezes into sleet before reaching the surface of the earth. Sleet is also known as ice pellets.
4. Hail:
Hail is formed when drops of water solidify together in the cold higher regions of thunderstorm clouds. Hail falls as a solid which is known as Hailstone.
5. Drizzle:
Any drop which has a diameter of 0.5 mm or less, is generally considered to be drizzle, falling much slower than rain.
6. Snow Grains:
Snow grain is a frozen drizzle. It is very small, white, and opaque grains of ice.
7. Ice Crystals:
Ice crystal forms where the temperature is very cold. They are falling crystals of ice in the form of needles, columns, or plates. Ice crystals are also known as diamond dust.
They seem like fog with individual water particles making ice by combining themselves.
Importance Of Precipitation:
Precipitation is important because it helps to maintain the atmospheric balance. It is an important input to hydrology. Floods and droughts are directly related to precipitation without precipitation, all the land on the planet would be desert. Precipitation helps farmers grow crops and provides a fresh water supply for us to drink. Precipitation is always fresh water, even if the water originated from the ocean.
However, in some cases, pollutants in the atmosphere can contaminate water droplets before they fall on the earth in the form of acid rain. Acid rain does not harm humans directly, but it can make lakes and streams more acidic. This harms aquatic ecosystems as plants and animals often cannot adapt to acidity.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Mist is small droplets of water hanging in the air. These droplets form when warmer water in the air is rapidly chilled, causing it to change from invisible gas to tiny visible water droplets. Mist often forms when warmer air over water suddenly encounters the cooler surface of the land. However, the mist can also form when warm air from land suddenly encounters cooler air over the ocean.
No. Fog and mist are not actually considered forms of precipitation because they stay suspended in the air.
Read More Articles:
