Global Information System is very innovative technology in the field of surveying. It is also called as geographical information system.
Table of Contents
What Is Global Information System (GIS)?
Global Information System or GIS is a computer-based info system that carries out the activities of capturing, storing, manipulating, analyzing, and displaying both spatial and non-spatial data in order to solve complex research, planning, and management difficulty. It is a system of hardware and software that executes the above-mentioned activities on the information about the areas of the earth.

Purpose of the Global Information System (GIS):
There are four important purposes of the GIS modern survey as given below.
- Assistance for general research.
- Collection, manipulation, and utilization of spatial data in database management systems.
- Standardization and customization of cartographic production.
- Supports the decision-making process depend on spatial data.
4th purpose of GIS can be described by an example, where the engineering geologist evaluates the slope stability conditions of the area through GIS in order to decide the new and best possible routes.
Subsystems of GIS:
There are five main elements of a Global Information System (GIS) as follows:
- Computer Hardware.
- Computer Software.
- Data.
- People.
- Methods.
1. Hardware:
The GIS operation and GIS software run in Computer Hardware. Therefore, the computer forms the backbone of the GIS hardware. Other than the computer, it incorporates input and output devices.
Digitizer boards and scanners are the input devices. The printers and the plotters are the output devices for a GIS hardware setup.
2. Software:
The GIS software stipulates the functions and the tools for the following works:
- To Store the graphic information.
- To Analyze the graphic information.
- To Display the graphic information.
The essential and significant programming segments of a GIS are:
- Data input and data verification.
- Data storage and database management.
- Data transformation.
- Data output and presentation.
- Interaction with the user.
3. Data:
The most essential component of a GIS system is Data.
There are two types of data in GIS:
(a) Spatial Data:
The data objects and elements that exist in the geographical space from the spatial data. spatial data enables the global finding and location of the individuals or devices anywhere on the earth. The spatial data is also called geographic data or geospatial data.
(b) Attribute Data:
These are information that is appended in the tabular form mentioned regarding spatial features. All the features of the spatial data are provided by the attribute data.
4. People:
Usually, two classes of people are employed in a GIS operation. They are:
- GIS Operators.
- GIS Engineers.
GIS operators work to vectorize the map objects. GIS engineers or GIS users use this vectorized data to execute the queries and analysis to solve problems.
5. Methods:
A well-designed plan and business rules are very crucial for successful GIS Operations. The methods are the models and the operational practices that are unique to each organization.
Components of GIS Subsystem:
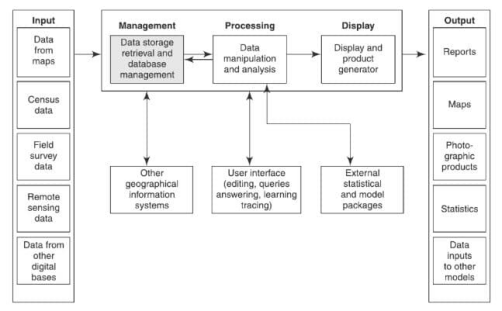
The GIS is intended to have 5 major component subsystems. They are:
- Input.
- Management.
- Processing.
- Display.
- Output.
Let us discuss these components in brief.
1. Input:
An input system deals with creating a picture-based GIS from the datasets.
2. Management:
This system serves the purpose of storing, retrieving, and managing the database with efficiency.
3. Processing:
This stage involves data manipulation, characteristic enhancement, classification, etc.
4. Display:
It involves the display and the generation of the product.
5. Output:
This gives the thematic maps, images, etc. for the application.
How It Works
Watch the video to learn how global information system works.
Applications of GIS:
The essential applications of GIS are:
- Widely used in business, government, and research which performs environmental analysis, land use planning, tax appraisal, utility, location analysis, utility, and infrastructure planning.
- GIS is utilized for real estate analysis, marketing, and demographic analysis, with wide application in habitat and archaeological analysis.
- Applied in remote sensing, surveying, geodesy, civil engineering, artificial intelligence (AI), operation research.
- Employed in natural resource management for locating the underground pipes and cables, planning facility maintenance, tracking energy utilization, and balancing the loads in electrical networks.
- Modern GIS applications include address matching, location analysis or site selection, and development of evacuation plans, landscape, etc.
- GIS also used in data capture for utility mapping as well as interpreting and digitizing information on many types of utility lines, e.g. water mains, sewage systems, telephone lines, power lines, gas mains, oil pipelines, railway/signals mapping.
