The engine cooling system is a collection of different components that allow coolant to pass through passages in the engine block and cylinder head to absorb combustion heat.
As the coolant absorbs heat, its temperature rises. This hot coolant is returned to the radiator through a rubber hose for cooling. As the molten coolant flows into the radiator through a thin tube, it is cooled by the flow of air.
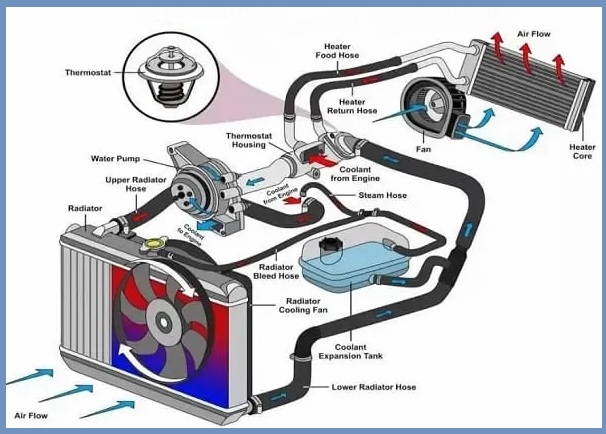
This is an important part of an internal combustion engine that prevents the engine from overheating. The cooling system cools the engine and stabilizes the temperature to meet the engine’s operating requirements.
The main function of the engine cooling system is to maintain a normal engine temperature and prevent it from overheating.
The engine cooling system cools the engine by circulating coolant through the engine vents. Some vehicles use air circulation to cool the engine. In this method, the air is circulated through a cylindrical shell with fins.
Overheating the motor can damage or stop the motor completely. This heat is generated by the combustion of the air-fuel mixture inside the combustion chamber. When combustion is over, the engine temperature becomes very high. This engine extracts the cooling system by heat transfer method.
The cooling system works efficiently by removing excess heat from the internal combustion engine and helping to keep the engine at normal operating temperature.
Table of Contents
How Does Engine Cooling System Work?
When the engine is running, it generates a tremendous amount of heat. This heat is generated by the combustion of the air-fuel mixture inside the combustion chamber of a heat engine. The cooling system is used to control engine heat.
There are several drain holes in the engine block with the engine cylinders. These vents circulate coolant through the engine’s cylinder head, dissipating engine heat and allowing the coolant to flow out of the engine optimally. The rubber hose connects the inlet and outlet of the water pump to the motor.
A step by step procedure for an engine cooling system is as follows:
- When the engine warms up, the cooling system kicks in. The water pump pumps coolant through the engine vents. As coolant begins to flow through the vents, it absorbs heat from the engine and cools it down to normal operating temperature.
- When the coolant temperature reaches between 160 and 190 Fahrenheit, the paraffin wax in the thermostat expands and opens. The thermostat acts as an on/off valve for the coolant.
- When the paraffin wax in the thermostat opens, the coolant passes through the hoses and into the radiator. The radiator acts as a heat exchanger.
- When the coolant reaches the heatsink, the heatsink fan blows cold air through the fins, reducing the coolant temperature rapidly. When the coolant cools, it returns to the water pump. The water pump will pump it back through the drain holes and the whole process repeats.
- The ability of the cooling system to absorb heat varies by engine type.
Key Components of Engine Cooling System
- Water pump
- Radiator
- Radiator overflow tank
- Thermostat
- Hoses
- Coolant temperature sensor
- Radiator cooling fan
- Freeze plugs
- Manifold gasket and head gasket
- Heater core
See the below image to know better.
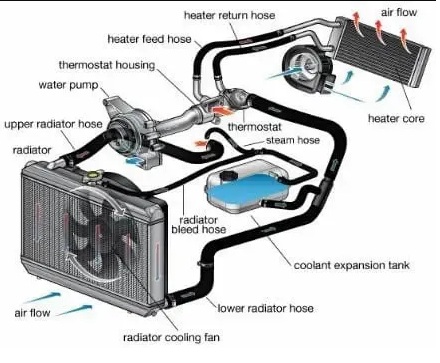
Types of Engine Cooling Systems
- Air-cooling system
- Liquid-cooling system
Let us have a look at these two types of engine cooling systems.
1. Air Cooling System
In an air-cooled engine, the cooling system blows cold air instead of coolant to cool the engine. These types of cooling systems are commonly found in old vehicles and conventional cars.
In air-cooled engines, aluminum fins cover the engine block. These fins also extract heat from the engine cylinders. Powerful fans pump air through these fins, transferring heat from the engine to circulating air to cool the engine.
The cylinders of these engines are highly efficient compared to water-cooled engines. They are more resistant to high temperatures than water-cooled cylinders.
Air-cooled systems offer the significant benefit of preventing corrosion from damaging the cooling system and preventing the coolant from freezing and boiling at extreme temperatures.
The temperature control of air-cooled engines is a complicated process and high-temperature ceramic components are required when the fixed operating temperature rises significantly.
In an air-cooled system, the amount of heat extracted by the engine varies depending on the coolant temperature, fin temperature, cooling airspeed/amount, and total blade surface area.
These types of engine cooling systems are mainly used in low horsepower engines such as small air-powered car engines, small cars, scooters, and motorcycles where the reciprocating motion of The machine provides enough speed to cool the engine. They are also used in compact industrial motors.
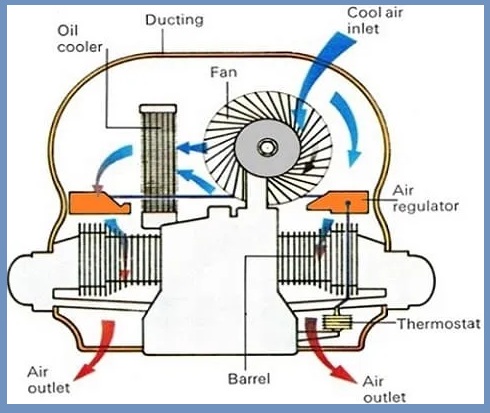
2. Liquid Cooling System
Liquid cooling systems are also known as indirect cooling systems. This system uses liquid coolant instead of air to cool the engine.
In this cooling system, the actual cooling material does not cool the system directly. The air cools the water and water cool the engine.
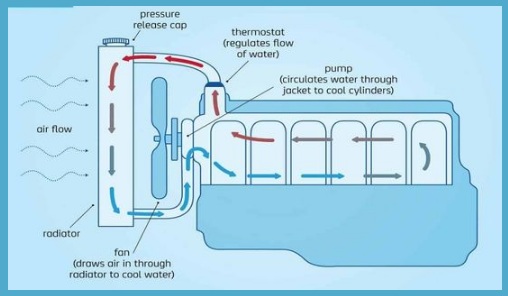
This system uses a water jacket to enclose the engine. Water pumps are used to circulate the water in these coats. When water flows through a water jacket, it extracts heat from the engine through a heat transfer process. When the heat of the engine is transferred to the water, it becomes hot. This hot water flows into the radiator. The cooler is equipped with a fan that blows cold air to cool the water. This cold water is pumped back into the water jacket and the entire cycle is repeated. These cooling systems are commonly used in large engines such as trucks, buses, tractors, and automobiles.
Wrapping UP
In general, the cooling system maintains the engine temperature continuously. An engine is a device that converts the chemical energy in fuel into useful mechanical work. When the engine is running, it produces extreme heat. This heat can cause engine damage. Therefore, in order to cool the engine properly, the car uses an engine cooling system
If you like my article please let me know. If you have any questions, please comment below.
I hope you got some knowledge today.
Keep Reading!
Thanks!
Happy Learning!
Cya!
