Table of Contents
Definition
Aeration in water treatment refers to the process of adding air or oxygen to water in order to improve its quality.
Aeration In Water Treatment: Explanation
Aeration is a water treatment process to eliminate dissolved gases and volatile substances from water by introducing air or oxygen to the water. This results in an improvement in water quality by reducing odor, taste, and color.

The primary objective of aeration in water treatment is to increase the dissolved oxygen amount in the water. Numerous aerobic bacteria require oxygen to break down organic matter and other pollutants in the water, and aeration helps to eliminate certain chemicals, such as iron and manganese, by oxidizing them from the water.
Water treatment facilities use various methods of aeration, such as surface aeration, diffused aeration, and mechanical aeration. Surface aeration involves using fountains, waterfalls, or other equipment to bring air from the surface to the water. Diffusion aeration uses diffusers, such as air stones or membranes, to release bubbles of air or oxygen into the water from the bottom of the treatment vessel. Mechanical aeration uses mechanical devices such as propellers or pumps to mix air and water.
Aeration is a critical stage in the water treatment process because it improves water quality by eliminating dissolved gases and other volatile substances.
Purpose Of Aeration In Water Treatment System
- Aeration is used to remove bad smells in the water.
- Aeration eliminates rid of bad taste in the water.
- To help get rid of iron and manganese in the water.
- To get rid of hydrogen sulfide in the water.
- To get rid of certain chemicals in the water.
- To get rid of ammonia in the water.
- To get rid of nitrogen compounds in the water.
- To get rid of phosphorus in the water.
- To get rid of pesticides in the water.
- To get rid of herbicides in the water.
- To get rid of heavy metals in the water.
- To get rid of radioactive particles in the water.
- To make the water taste and smell better.
- To make the water look better.
- To increase the amount of oxygen in the water.
- To help good bacteria grow in the water.
- To make other water treatment processes work better.
- To make the water safer to drink.
- To protect the environment.
- To save money on water treatment costs.
Types Of Aeration In Water Treatment System
1. Diffused Aeration:
Diffused aeration is the most commonly used method, where small diffusers are used to inject air into the water. Although it is relatively inexpensive and easy to operate, it may not be very efficient in terms of oxygen transfer.
2. Mechanical Aeration:
Mechanical aeration involves using mechanical devices to mix air and water, making it more efficient than diffused aeration. However, it is also more expensive and complex to operate.
3. Static Aeration:
Static aeration involves allowing water to sit in a basin or tank with aeration devices at the bottom. It is the simplest and least expensive method but also the least efficient in terms of oxygen transfer.
Aeration Process
The process of aeration in water treatment involves exposing water to air or oxygen to remove dissolved gases such as carbon dioxide, hydrogen sulfide, and methane, and to increase the oxygen content of the water.
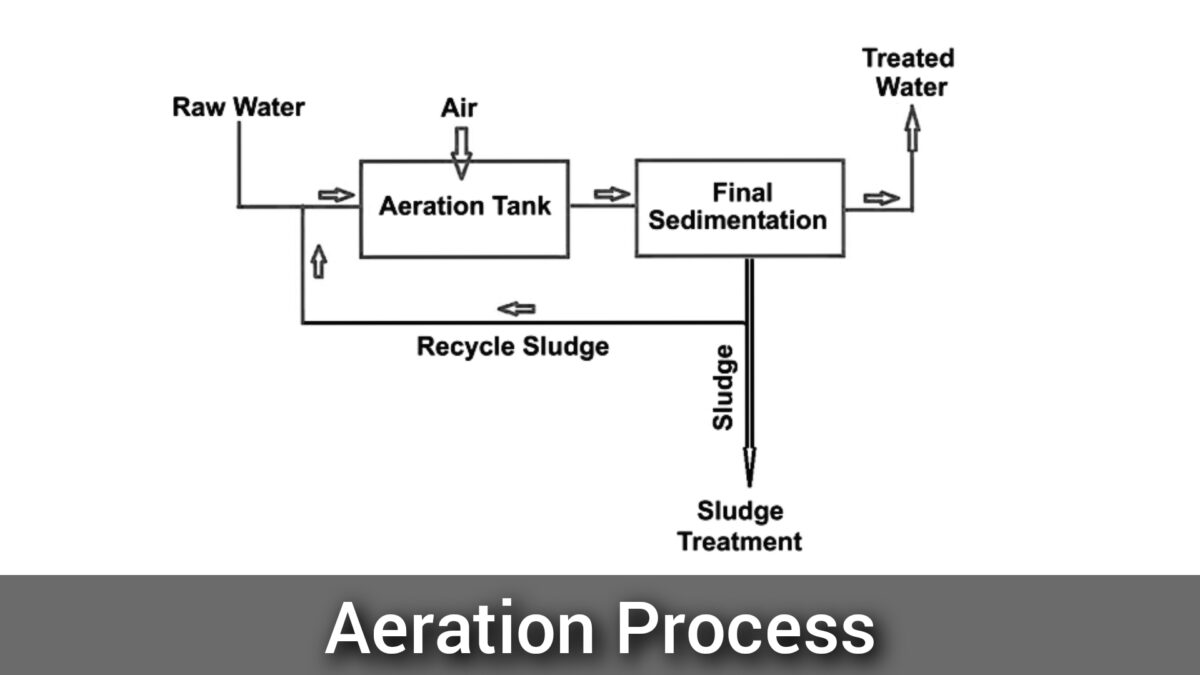
To carry out the process of aeration, water is first mixed with air or pure oxygen, which increases the surface area of the water and allows more contact between the water and the air.
Oxygen from the air or pure oxygen is transferred to the water using a diffuser or other mechanism, such as cascading the water onto a series of trays or plates.
As oxygen is transferred to the water, it reacts with dissolved gases and other impurities, breaking them down into harmless substances that can be removed.
Water is allowed to settle or is subjected to other treatment processes such as filtration or sedimentation to remove remaining impurities or suspended particles.
Various methods can be used to perform aeration, including diffuse aeration, mechanical aeration, and spray aeration, depending on the specific requirements of the water treatment process and the type of contaminant to be removed.
Advantages Of Aeration In Water Treatment:
- Aeration adds oxygen to the water, which supports the survival of aquatic organisms and maintains a healthy ecosystem.
- Aeration helps control unpleasant odors by releasing volatile compounds into the air, reducing the smell.
- Aeration removes dissolved gases like carbon dioxide and methane, which can affect water acidity and the pH balance.
- Aeration aids in the oxidation of metals and minerals, such as iron and manganese, making it easier to remove them from the water.
- Aeration improves water clarity by promoting the settling of suspended particles and reducing turbidity.
- Aeration encourages the growth of beneficial microorganisms that break down organic matter and remove pollutants in wastewater treatment.
- Aeration prevents the formation of excessive algae blooms by mixing and circulating the water.
- Aeration helps regulate water temperature by promoting mixing with the atmosphere, managing thermal pollution.
- Aeration prevents corrosion of water infrastructure by removing corrosive gases and extending the lifespan of pipes and tanks.
- Aeration enhances the aesthetic appeal of water bodies by reducing foul smells, improving clarity, and preventing unsightly algae growth.
Disadvantages Of Aeration In Water Treatment:
- Aeration requires energy-intensive equipment, contributing to increased operational costs.
- Aeration equipment, especially high-powered blowers or compressors, can generate noise and vibration, causing disturbances in the surrounding environment or to nearby residents.
- Aeration can produce aerosols or tiny water droplets that may carry pathogens or contaminants, posing potential health risks if inhaled.
- Aeration may have limited effectiveness in removing certain contaminants, such as specific organic chemicals or heavy metals, requiring additional treatment methods.
- Aeration systems require regular maintenance, including cleaning, inspection, and potential repairs or replacements, to ensure optimal performance and prevent malfunctions or inefficiencies.
Faqs
Aeration adds air to water and wastewater to improve its quality.
Aeration is important because it helps remove impurities and increases oxygen levels in the water.
Aeration can be done by introducing air at the surface, using diffusers at the bottom, or using mechanical devices to mix air into the water.
Aeration promotes the growth of helpful bacteria that break down organic matter, removes gases and odors, and makes the water cleaner.
Challenges include the need for energy-intensive equipment, foaming or splashing issues, oxygen depletion in deep tanks, and the need for regular maintenance of aeration systems.
