Table of Contents
What Are BIM Dimensions?
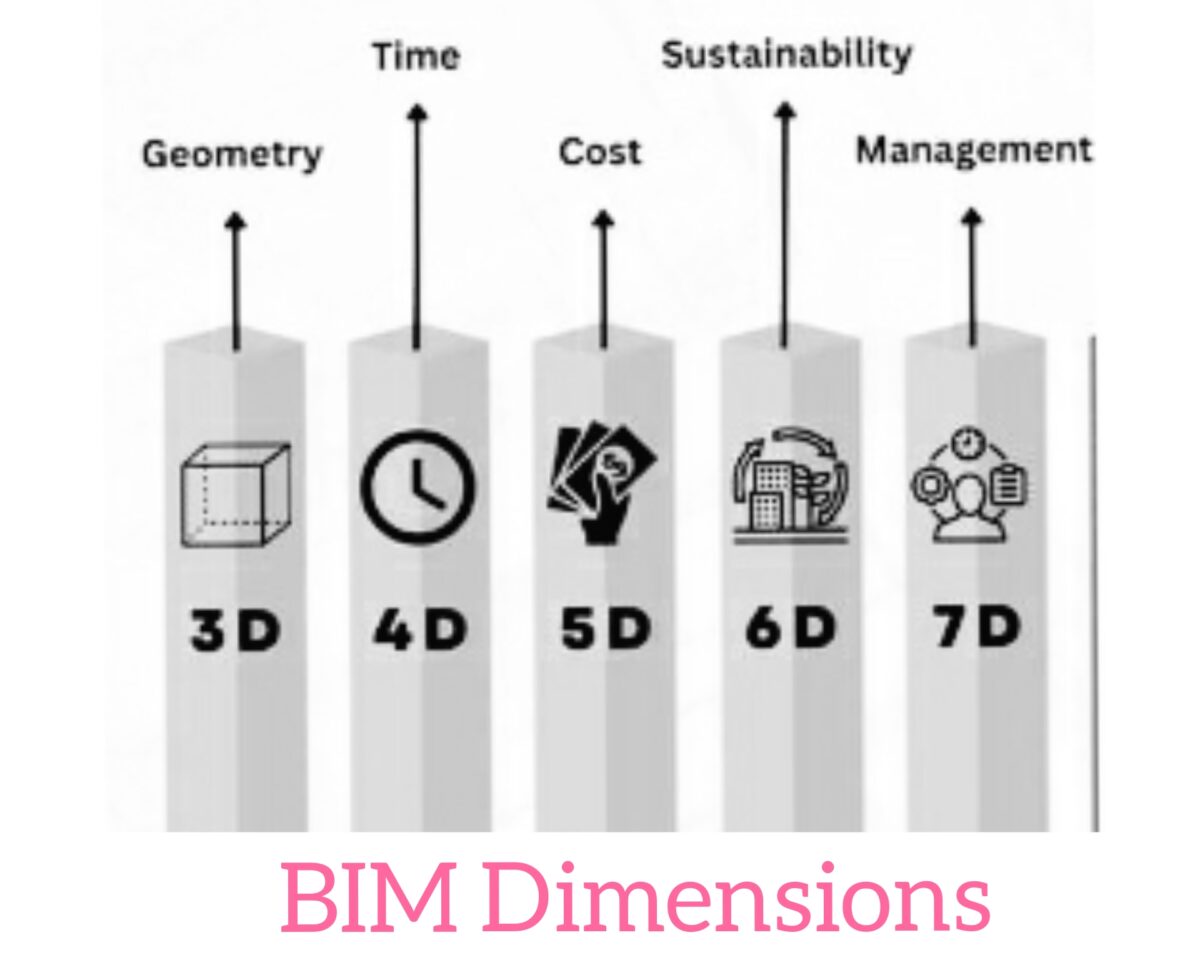
BIM dimensions, which range from 3D to 7D, encompass a spectrum of information that extends far beyond just a visual representation of a building or structure. While three-dimensional (3D) representation remains the foundation, it is the integration of post-dimensionality that elevates BIM from a design tool to a comprehensive ecosystem of information. The incorporation of 3D, 4D, 5D, 6D, and 7D dimensions within a BIM model brings an unprecedented level of clarity and insight to construction projects.
In the world of modern construction and architectural design, a revolutionary approach has emerged that goes beyond traditional methods of project visualization. Building Information Modeling, or BIM, has become a cornerstone of innovation, transforming the way we conceptualize, plan, and execute construction projects. At the heart of this paradigm shift lies the concept of BIM Dimensions, a multifaceted framework that redefines how information is harnessed and presented in a digital form.
In this transformative journey, the 3D dimension provides the spatial foundation, offering a tangible vision for the project. However, because construction projects are not static entities frozen in time, the fourth dimension (4D) steps in, introducing the crucial time element. By saturating the model with a time component, stakeholders can now visualize project progress over time, anticipate potential challenges and optimize timelines.
Further venturing into the world of BIM dimensions, the Fifth Dimension (5D) ushers in the era of financial awareness. Here, the cost dimension intertwines with the spatio-temporal, weaving a complex tapestry of financial data. This marriage of costs, time, and design elements allows stakeholders to make informed decisions that match financial realities.
As the construction industry increasingly embraces sustainability and life cycle considerations, the Sixth Dimension (6D) is emerging. This dimension delves into the life cycle of a project, including maintenance, operation, and longevity. By incorporating comprehensive data about materials, maintenance schedules, and equipment, stakeholders can ensure that a project’s sustainability journey is effective and impactful.
And on the horizon, we see the seventh dimension (7d). While not universally recognized, this dimension hints at a world of other possibilities. It’s the dimension of data analytics, harnessing the power of artificial intelligence and machine learning to gather insights, improve processes, and predict results.
Description Of BIM Dimensions
1. 3D BIM: Visualizing Structures
3D Building Information Modeling (BIM) is a commonly used type of model that displays the three-dimensional aspects (x, y, z) of a structure. This model aids stakeholders, such as architects, engineers, and construction professionals, in visualizing a project before it begins. It provides valuable insight and tools to efficiently plan, design, construct, and manage buildings and infrastructure.
2. 4D BIM: Adding Time Dimension
4D BIM introduces the fourth dimension to the model, representing time. This dimension showcases the project’s duration and schedule. By including a timeline and scheduling information, the model illustrates how the project will evolve over time. This is particularly useful for early-stage conflict detection and enhances site planning and scheduling optimization. It ensures stakeholders are well-prepared by communicating the upcoming stages of construction.
3. 5D BIM: Budget Analysis and Cost Estimation
5D BIM focuses on the financial aspect of a project. It facilitates the visualization of budget analysis and cost estimation over time. This type of model empowers stakeholders to analyze project costs, especially during the initial design and construction scenarios. It’s a valuable tool for estimating costs, comparing predictions with actual costs, and receiving real-time notifications in case of cost overruns.
4. 6D BIM: Enhancing Sustainability
6D BIM is geared towards making structures self-sustainable and energy-efficient. This approach incorporates information that enables stakeholders to evaluate a structure’s energy consumption and predict energy usage during the initial design phase. Utilizing a 6D BIM model contributes to reducing long-term energy consumption and enhancing operational management post-construction.
5. 7D BIM: Facility Management
7D BIM focuses on improving operations and facility management for building owners and managers. This model allows stakeholders to monitor crucial asset data, including status, warranty details, technical specifications, maintenance manuals, and operation guidelines. Essentially, all aspects related to facility management are stored within the building information model. Implementing a 7D BIM model streamlines maintenance processes for contractors and subcontractors, providing comprehensive information about replacement parts and specifications.
You Might Also Like: Revit Families
Conclusion
BIM Dimensions play a vital role in enhancing the project team’s ability to effectively visualize their 3D models. The incorporation of 4D BIM expands this capability by providing real-time information on construction progress. Moving to 5D BIM allows for a comprehensive comparison between the planned and actual costs of a project. The introduction of 6D BIM further simplifies facility management tasks. Ultimately, the use of 7D BIM empowers the project team to achieve enhanced project management competencies.
