Table of Contents
Introduction
Electron beam welding is a liquid welding process. Liquid welding is a welding process in which the metal-to-metal connection is in a liquid or molten state.
It is also classified as a new welding process as it uses the kinetic energy of electrons to fuse two pieces of metal together.
Take a look at the below figure to understand it better.
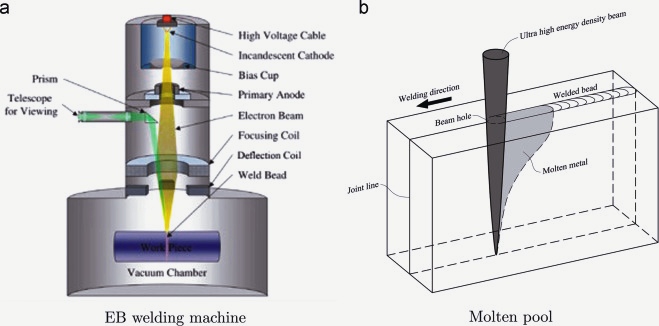
German physicist Karl-Heinz developed this type of welding in 1958. In this welding process, a high beam of electrons strikes the welding plate, where kinetic energy is converted into thermal energy. This heat energy is enough to melt and fuse the workpieces into one piece.
This entire process takes place in a vacuum. Otherwise, the electrons will collide with air particles and lose energy.
Working Principal
Free electrons in vacuum are manipulated by electric and magnetic fields to form narrow beams. When the beam hits a solid, the electrons are converted into heat or kinetic energy. This concentration of energy into a small amount of matter can be precisely controlled electronically and has many advantages.
This welding works on the same principle as electron beam machining. This process uses the kinetic energy of electrons to generate heat. This heat is further used to weld the two welding plates together. When the electron high beam hits the weld plate, its kinetic energy is converted into heat energy. This heat energy is sufficient to fuse two metal sheets together to form a weld.
Uses of Electron Beam Welding
- Used for structural work in the aerospace and marine industries.
- Used to join titanium and its alloys.
- This type of welding is widely used in the automotive industry to join gears, transmission systems, turbochargers, etc.
- Welds electronic connectors in the electronics industry.
- Nuclear and medical industries.
