Table of Contents
What Is Nanofiltration?
Nanofiltration is a process that utilizes membranes with very small pore sizes, typically ranging from 1 to 10 nanometers, to separate different components of a fluid mixture. The pores of the nanofiltration membrane allow particles smaller than 10 nanometers to pass through.
Polymer thin films or metal, such as aluminum, are commonly used materials for creating nanofiltration membranes. Polymer materials like polyethylene terephthalate (PET), polyamide, and polyethersulfone are often used in the creation of “track-etch” membranes. These membranes are created by bombarding the polymer thin film with high-energy particles, which creates tracks that are chemically developed or “etched” into the membrane to form the pores. The resulting pore size is controlled by factors such as pH, temperature, and time during the development process, with pore densities ranging from 1 to 106 pores per cm2.
Metal nanofiltration membranes, such as alumina membranes, are made by electrochemically growing a thin layer of aluminum oxide from aluminum metal in an acidic medium.
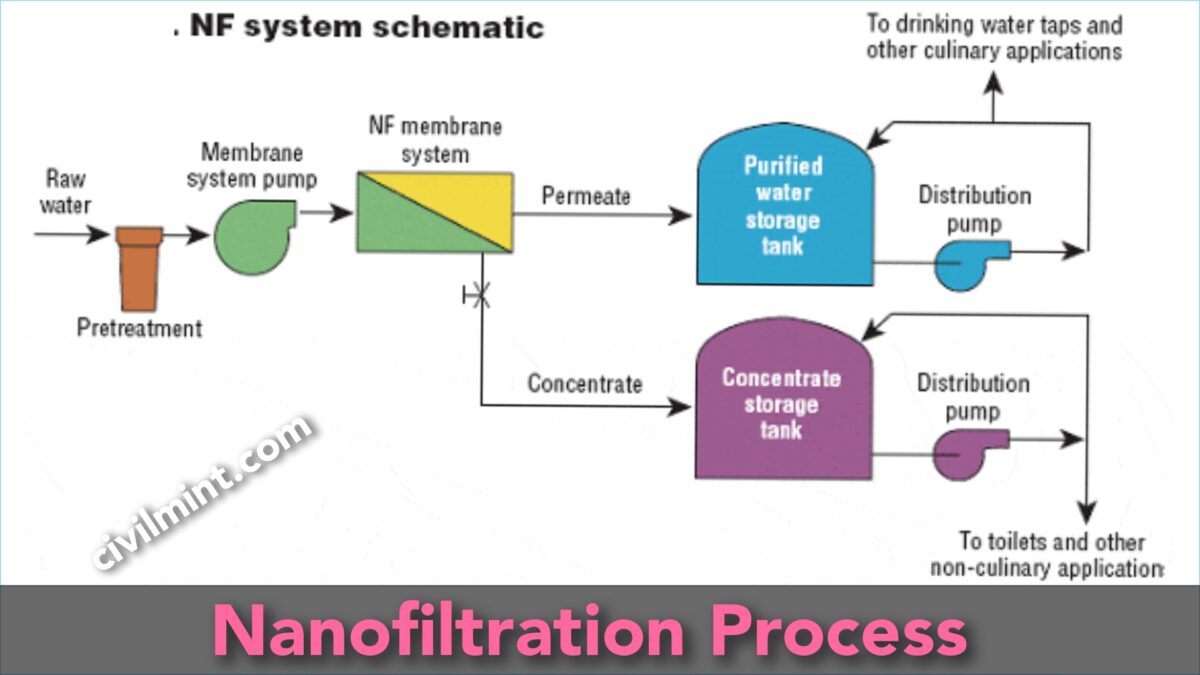
Working Principle Of Nanofiltration
A semi-permeable membrane with very small pores is used to pass a liquid in the working principle of nanofiltration. The membrane retains larger particles, such as dissolved ions and organic molecules, while allowing smaller particles, like water molecules, to pass through. The separation of particles occurs due to a combination of size exclusion, electrostatic attraction, and other molecular interactions.
Nanofiltration finds a variety of applications, such as water treatment, desalination, and separation of organic molecules. It effectively removes contaminants from water and can serve as a pre-treatment step for reverse osmosis. The food and beverage industry also uses nanofiltration for the concentration and purification of products like juices and dairy products
Uses
- Nanofiltration is a process that uses tiny pores to purify fluids. It is commonly used to remove impurities and contaminants from water, such as bacteria, viruses, and organic compounds. It can also be used in the food and beverage industry to concentrate and separate different components of products like fruit juice and dairy.
- Nanofiltration is an effective method for producing clean water and treating wastewater. It can remove harmful contaminants and impurities, making water safe to drink.
- In industries such as oil and gas production, fine chemistry and pharmaceuticals, and medicine, nanofiltration is used for tasks like purifying gas condensates, recovering solvents, and extracting amino acids and lipids from blood and cell cultures.
- Natural essential oils and similar products can be purified and enriched through nanofiltration, which allows for gentle separations and the fractionation of crude extracts.
Advantages Of Nanofiltration
- Softens water without adding extra sodium ions, unlike ion exchangers.
- Performs gentle molecular separation, which can be more cost-effective than other separation processes that require continuous heating or cooling.
- Able to process large volumes and continuously produce streams of products.
Disadvantages Of Nanofiltration
- Limited to membrane pore sizes of only a few nanometers, making it less versatile than other membrane filtration methods.
- Expensive membranes that require regular maintenance and replacement.
- Replacement frequency can be difficult to estimate and may result in premature or delayed replacement.
