Parallel seismic pile test is performed to check the quality of pile foundation. It is a non-destructive surface method used to test the quality of pile foundations.
It is used to calculate the length and integrity of pile foundations that are not accessible (too long, too thin, or buried under pile caps).
If we compare other non-destructive surface testing methods, the parallel seismic method is more versatile for determining foundation depth.
This article describes the operation and characteristics of parallel seismic testing in construction.
Table of Contents
How Does Parallel Seismic Pile Test is Performed?
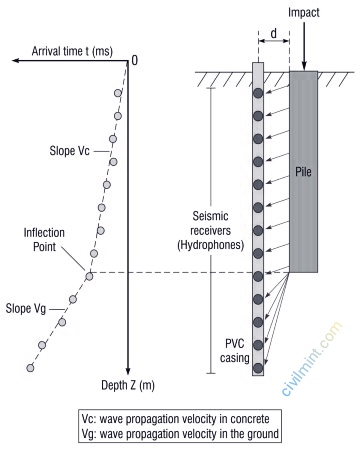
In a parallel seismic system, a borehole is drilled next to the foundation to be tested. The well he is lined with PVC, filled with water and equipped with a series of hydrophones (receivers).
Right now, we are generating seismic waves by hitting structures with hammers. These pressure or shear waves propagating through the foundation are recorded by his hydrophone receiver.
Hydrophones are densely packed every meter. The generated wave travels along the structure at high speed until it reaches the base of the foundation. Beyond the base pedestal, When traveling on the ground, the traveling time will be longer due to the slow wave speed on the ground.
This test is based on measuring the time for these compression or shear waves to reach the receiving station (hydrophone) directly. The point where the velocity drops sharply (the transit time ‘t’ increases) is interpreted as the depth of the structure. The resulting depth-time map determines the depth of the foundation tested.
Similarly, if there are discontinuities or inclusions in the substrate, the signal or wave will be redirected around it, increasing the path length and transit time. It shows the linear deviation of depth versus time plots obtained from parallel seismic tests.
The figure below is an example of parallel seismic resistance test results. The change in slope of the line representing the arrival time of the load impulse as a function of depth indicates the depth of the pile shaft.

Important Characteristics of Parallel Seismic Pile Test
- The boreholes drilled for testing have a diameter of 150 to 200 mm. A borehole is drilled near or very close to the foundation, parallel and close to the structure. Excavate within 1.5m from the foundation.
- Parallel seismic test data becomes more difficult to interpret as the well moves away from the foundation.
- Parallel seismic tests can be performed relatively quickly when testing foundations beneath existing structures. The PS test can be applied to foundations placed on wet ground.
- Applicable to deep foundations such as sheet piles and abutments.
- This test determines pile length, foundation type and foundation scouring formation.
Applications of Parallel Seismic Pile Test
This test is applicable for the following structures.
- Deep Foundations of all types
- Abutment Piers
- Sheet Piles
- Footings
Thanks for reading my article.
Happy Learning!😊
Good By!
