Table of Contents
What Is Tunnel?
Tunnels are underground passages for roadways, sewers, railways, etc. The ratio of length to width of the tunnel should always be in 2:1. It is enclosed from all sides along the length.
What Are Different Types Of Tunnels?
Classification based upon the usage:
1. Mine Tunnel:

It is used for minerals, ores, and metal extraction from the crust. They are cheaper to build in comparison to other tunnels. It is not much safe since it is meant for permanent occupation.
2. Public Water Tunnel:

It carries sewage, gas, or water for public usage. Earlier these tunnels were used for transporting water into densely populated areas. These were part of aqueduct systems which included an underground chamber and inclined bridge-like constructions by a series of arches.
3. Transportation Tunnel:

It carries railways, pedestrians, the subway, etc.
Classification of tunnel based on the alignment:
4. Off Spur Tunnel:

It is constructed for smaller lengths to get over minor obstacles where curved can’t be allowed.
5. Base Tunnel:
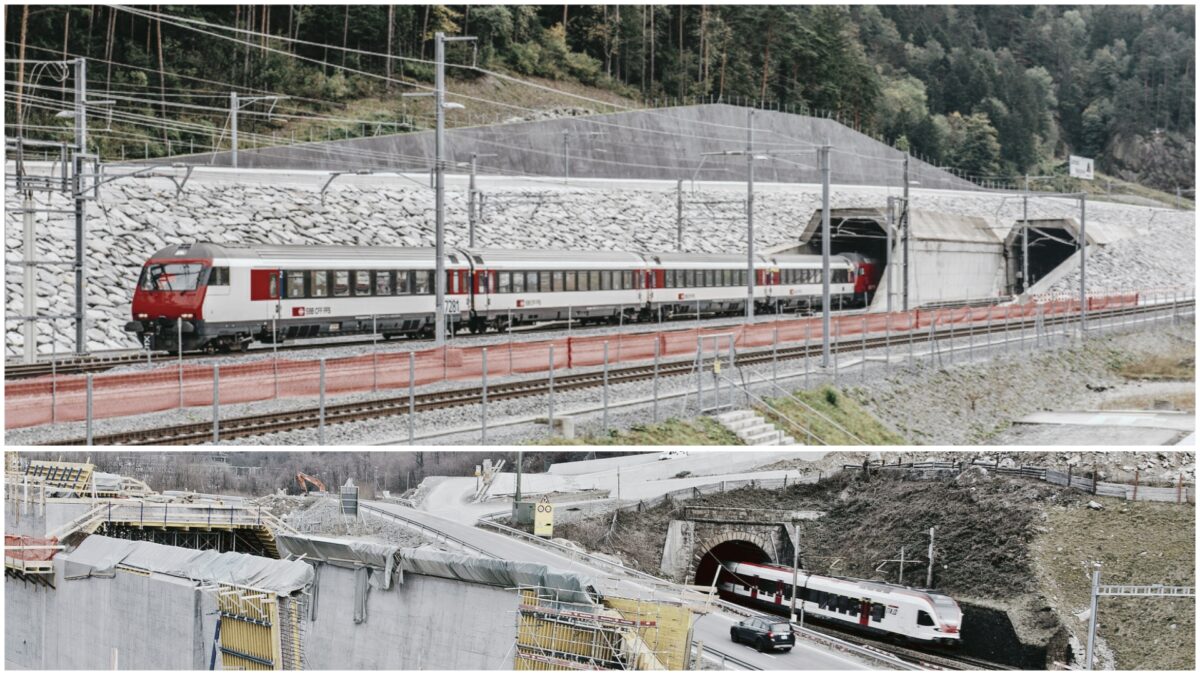

It is constructed in the valley along the natural slope. It is also known as Saddle Tunnel. It is used for transportation by the construction of railway tracks and roadways.
6. Slope Tunnel:
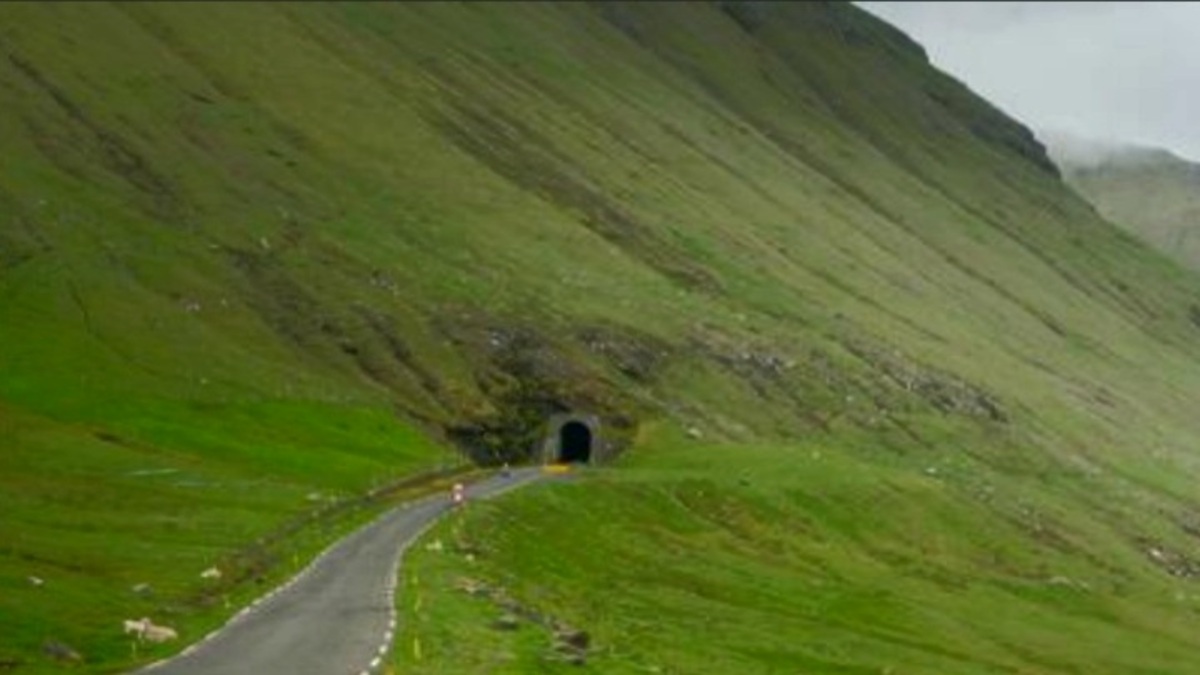

It is constructed upon steep hills and meant for transportation.
7. Spiral Tunnel:
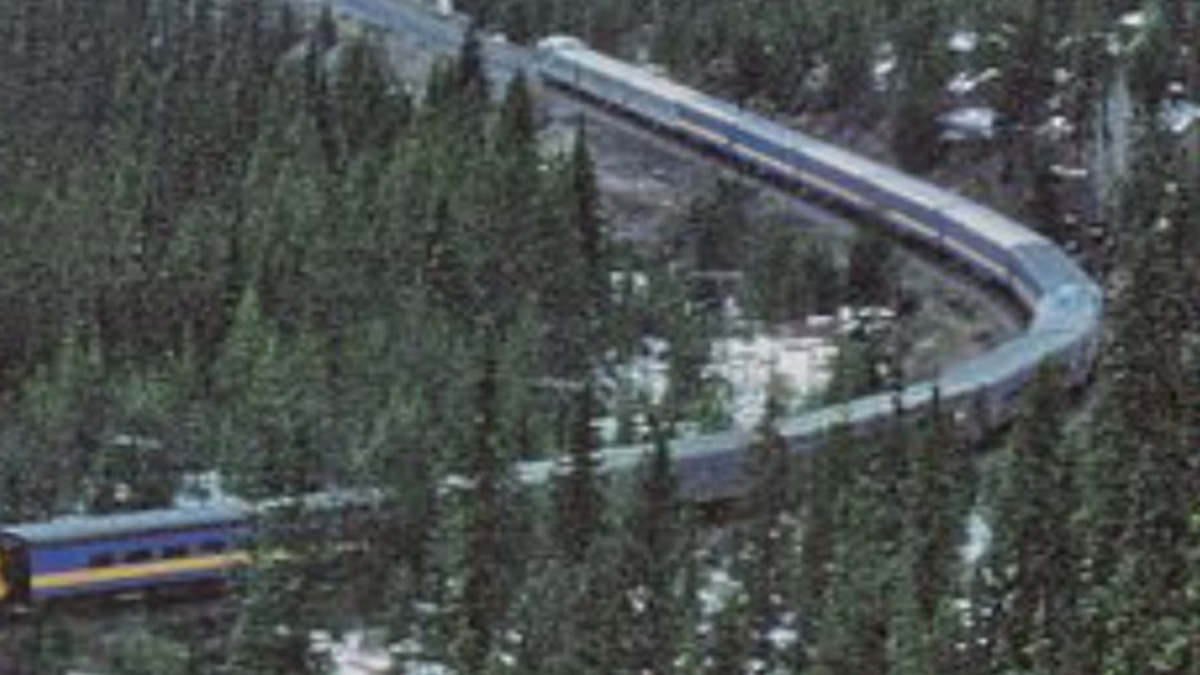

It is constructed in narrow valleys in the form of loops in the inside of mountains. It enhances the length of the tunnel which avoids a steep slope.
Classification based on the shape of tunnel:
8. D shape Tunnel:
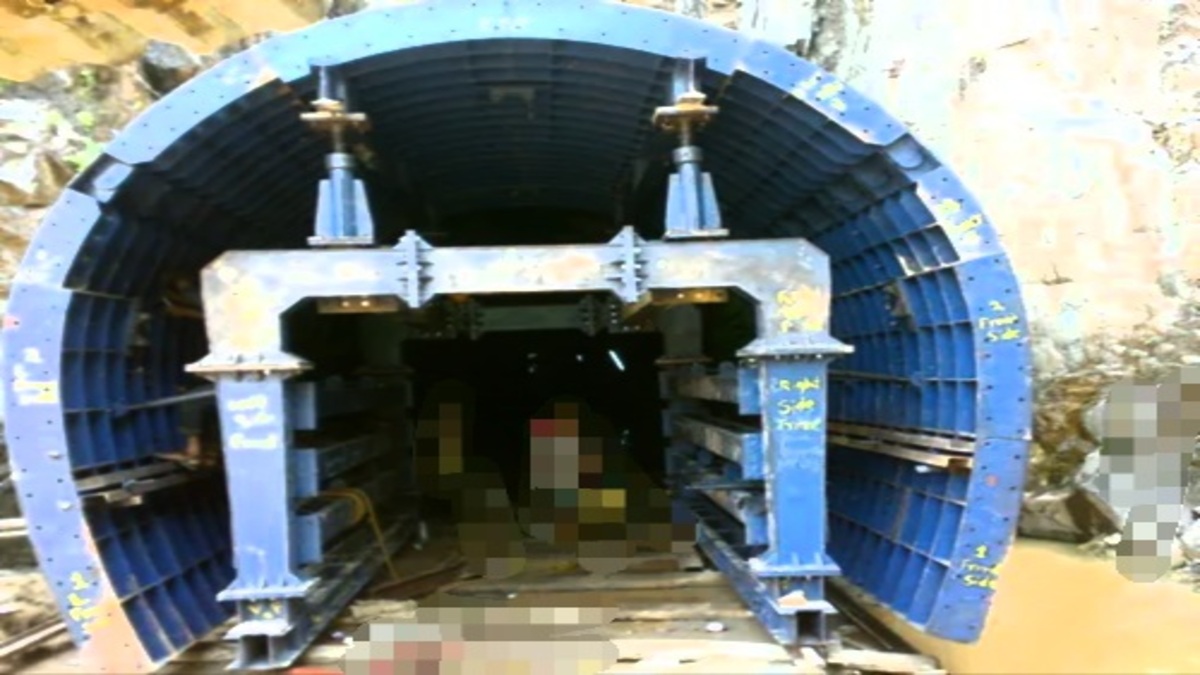

It is used where there is a risk of failure due to external pressure due to loosening unstable soil or water. It is best suited for subways.
9. Circular Tunnel:
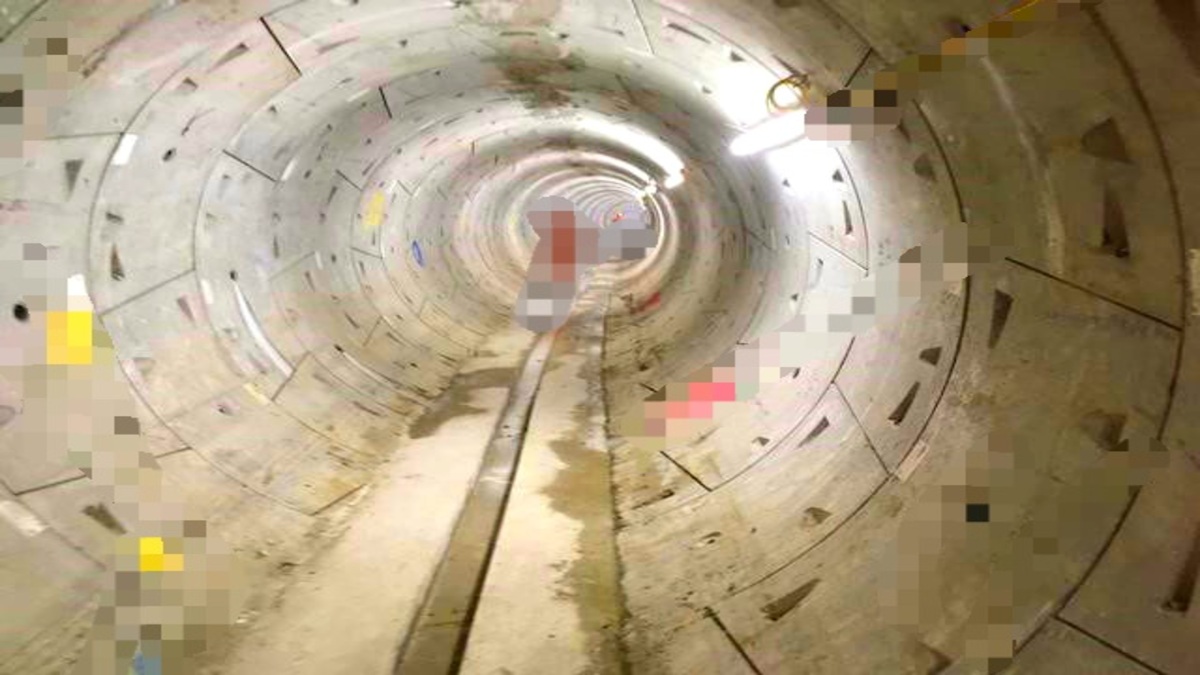

It has strong resistance against external pressure due to water. It is preferred on soft grounds. It is used for the transportation of oil and for laying sewage pipelines. It is the strongest amongst all the shapes and economical as well.
10. Horseshoe Shaped Tunnel:
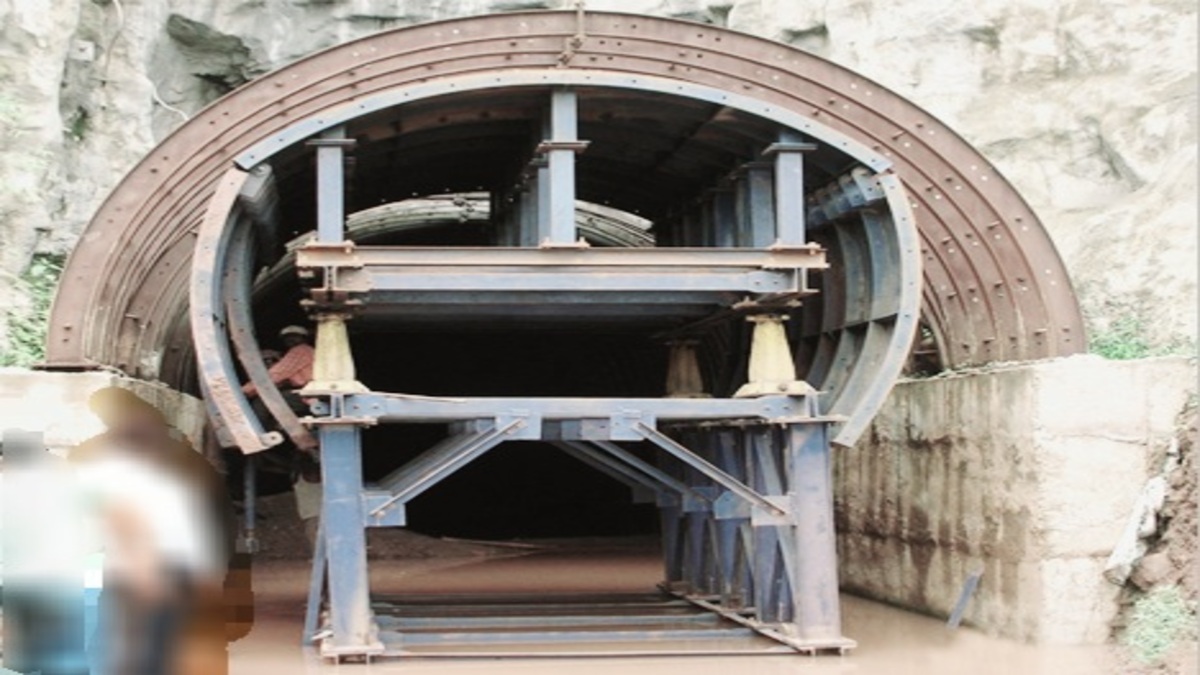

It has a semicircular roof with an arch on the sides. It has the combined advantage of a D shape and circular tunnels. Generally, It is used in railways.
11. Rectangular Shaped Tunnel:
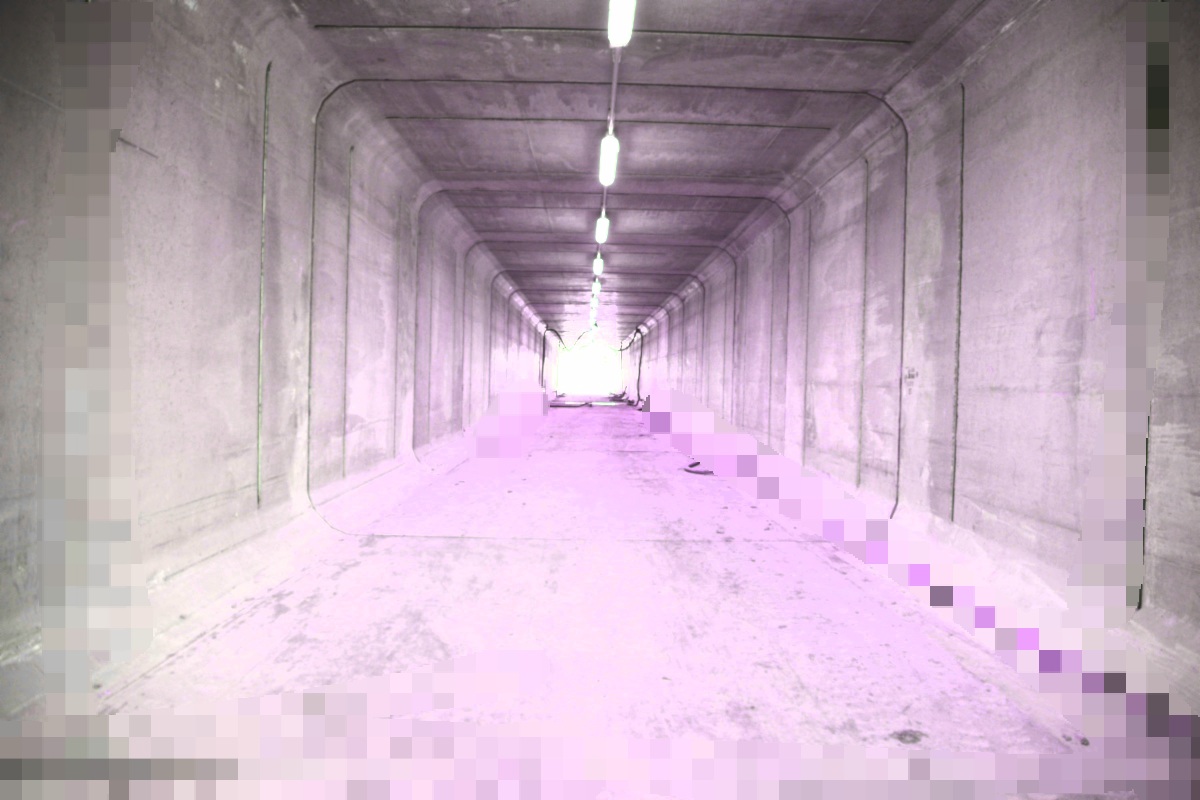

It is used for hard rocks. It is quite costly and used by pedestrians.
12. Egg Shaped Tunnel:
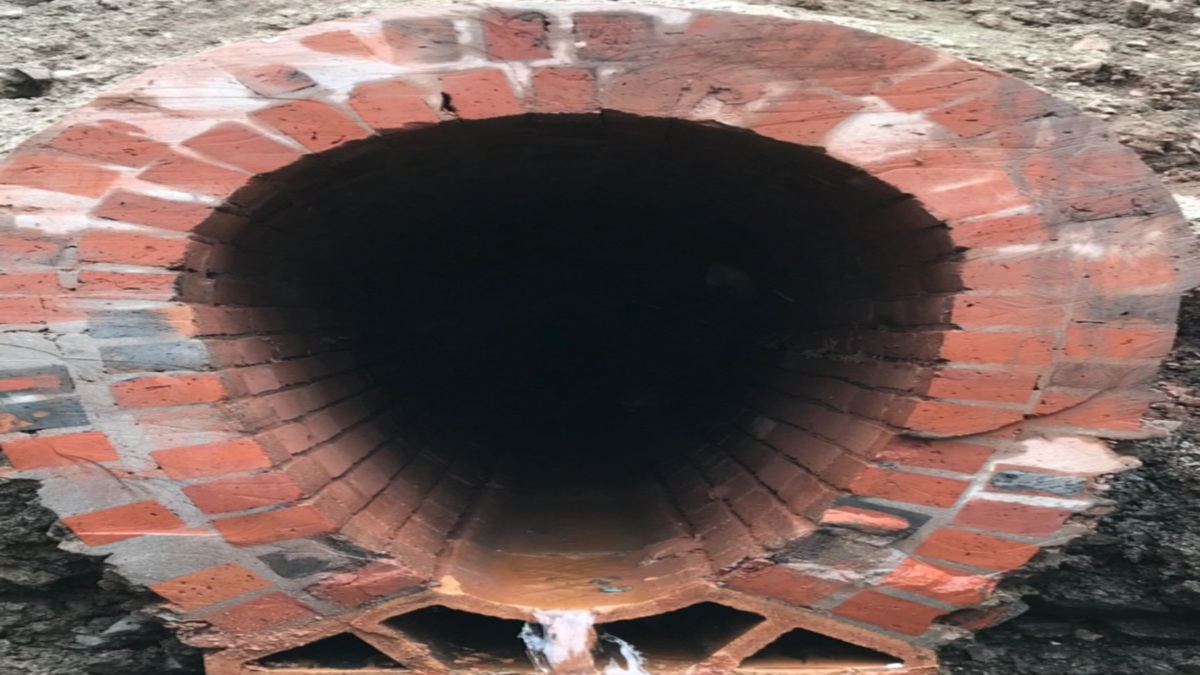

It is used for sewage as it has self-cleansing velocity during dry weather. It is able to resist external and internal pressure.
