There are different types of bearings with different operating principles, materials, lubrication methods, shapes, etc.
Here are the main bearing types:
Table of Contents
Various Types of Bearings
- Ball Bearing
- Roller Bearing
- Linear Bearing
- Bush Bearing
- Thrust Bearing
- Foot Step Bearing
- Anti-friction or Rolling Contact Bearing
- Plain Bearing
- Fluid Bearing
- Magnetic Bearing
- Jewel Bearing
- Flexure Bearing
Let us take a look at these types of bearings.
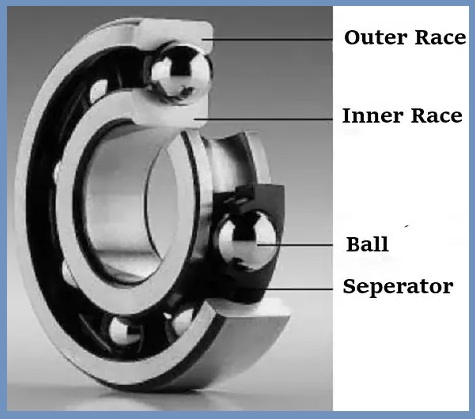
1. Ball Bearing
Ball bearings are one of the most well-known bearing types. It has a small metal ball. This ball is mounted between two metal rings. These metal rings are known as laces. The ball is held in place by an assembly called a cage. While working on ball bearings, there is a small contact area between the race and the ball. These bearings have a limited load capacity and a low friction moment.
2. Roller Bearing
Rolling bearings are designed to maintain the accurate alignment of each component for extended periods of time. It is also capable of withstanding severe transient loads. Therefore, it is ideal for machines that need to be started and stopped frequently. These bearings have a cylindrical rolling element instead of a ball. The ball makes point contact with the race and the rotational movement of the bearing creates line contact. Roller bearings have a very high load capacity.

3. Linear Bearing
Linear bearings have rolling or ball elements. This rolling or ball element is mounted between the two trajectories. These types of bearings are used to give linear motion to the moving parts of the machine. They reduce friction between moving parts of the system where movement works in a straight line. Cabinet drawers and sliding doors are the simplest examples of linear bearings.
The linear bearing has the ability to control speed more accurately than other types of bearings. They have high rigidity and the ability to carry heavy loads. Also, no maintenance or lubrication is required. These bearings are ideal for food processing equipment and packaging machines.

4. Bush Bearing
These bearings have bronze or brass bushings and cast iron bearing housings. This type of bearing has a hole in the bottom plate of the bearing housing to hold the bearing in place.
There is an oil pan hole at the top of the bearing. Bushings are used to lubricate the shaft and bushings. These bearings are ideal for shafts that rotate at low speeds with light loads. This type of solid bearing allows the shaft to be taken in and out smoothly.
The bush bearing has a frictional effect between the inner surface of the bearing and the outer surface of the shaft. And the presence of a lubricating oil film minimizes the resulting friction. Oil rings are considered to be the most efficient and safe type for linear shafts under normal operating conditions.

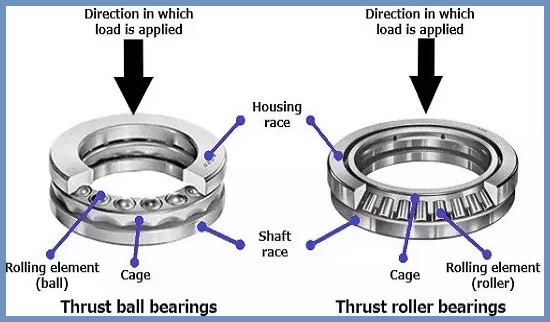
5. Thrust Bearing
For thrusts or thrust bearings, the bearing pressure is axial. There are horizontal or vertical shaft axes. Thrust bearings are called roller bearings when the axis is horizontal. Thrust bearings are called foot bearings when the shaft axis is vertical.
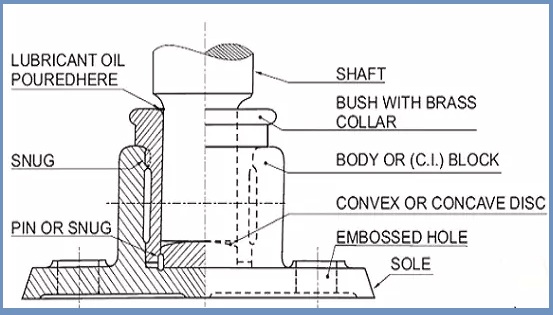
6. Foot Step Bearing
This sort of bearing is fine and perfect for assisting a vertical shaft. These bearings have a bronze bushing and a solid iron block. The shaft`s decreased facet inserts right into a metallic disc. This metallic disc carries concave seating.
The footstep bearing prevents the disc from rotating alongside the shaft by putting the pin partway withinside the disc and partway withinside the block. By becoming into the neck beneath the collar, it prevents the bush from turning with the shaft.
In those bearings, powerful lubrication may be very tough to achieve. The footstep bearings are generally used for low-pace shafts that convey a mild load. Vertical shafts aren’t unusual places in normal energy transmission. The footstep bearings are maximum generally utilized in fabric machines and device rotary tables.
7. Anti-friction or Rolling Contact Bearing
Roller bearings can easily roll on surfaces similar to plain bearings. This process uses hard chrome-plated steel rollers or balls that move within a specially designed cage to produce low-friction bearings.
This bearing has a pure rotational motion between the bearing surface and the shaft. This is because the sliding friction is much higher than the rolling friction.
These bearing types have low starting friction and can be achieved while driving. Therefore, rolling bearings are ideal for machines that need to be started, stopped, and restarted frequently.

8. Plain Bearing
This is one of the simplest types of camps. Includes support surface. However, rolling elements are not included. These bearings are most commonly used for vibration, reciprocating, sliding, and rotary motion.
In these bearings, the journal slides in the bearing while the bearing itself remains stationary. They are attached to the shaft and have a sleeve that fits the hole. They are lightweight, compact in design, and cheaper than other types of bearings. These types also have high elasticity.

9. Fluid Bearing
These types of bearings rely heavily on compressed gas or liquid to carry loads and eliminate friction. Fluid bearings are used instead of metal bearings.
In addition to high vibration and noise levels, fluid mounts are used for machines operating at high loads and speeds. They have high acquisition costs and long useful lives under adverse conditions.

10. Magnetic Bearing
These types of bearings have no physical contact and use the principle of magnetic levitation to hold air in the center of the shaft. Magnetic bearings do not wear and limit the maximum relative motion that can be controlled.
These bearings can automatically adjust the position of the shaft based on the center of gravity, so there are some variations in the shaft design. These offer many benefits for a wide range of applications such as High-speed turbines, centrifuges, and compressors.
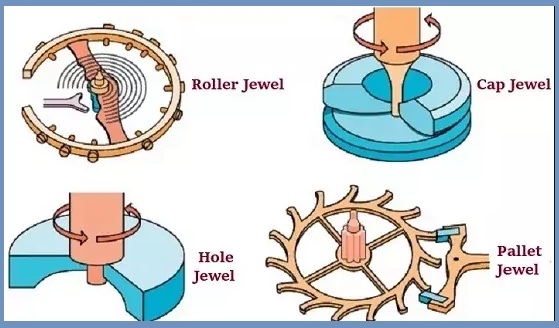
11. Jewel Bearing
The jewel bearing has a totally comparable layout to a simple bearing, however, jewel bearings have jewel-covered spindle holes in preference to a metallic spindle.
The diameter of the holes is a bit bit extra than the shaft diameter. These holes normally have a ring-formed layout. Synthetic ruby, perhaps artificial sapphire, or mineral corundum is used to fabricate the jewels.
The jewel bearings are maximum typically utilized in special commercial programs wherein dimensional accuracy, low friction, and lengthy system provider lifestyles are important. Jewelry bearings are normally hired in mechanical watches.
12. Flexure Bearing
These types of bearings are typically used to maintain degrees of freedom at one or more angles. These are also referred to as part of the compliance mechanism. For applications that require angle compliance, these bearings work like traditional bearings or hinges.
The main advantages of solid-state spherical plain bearings are that they do not require lubrication and generate very little friction. They have a simple design and low cost. They are small, light, and easy to maintain with special equipment.

