Ball bearing is a popular type of bearing that contains balls to maintain clearance between bearing races. The movement of the balls reduces friction compared to flat surfaces that slide against each other.
Ball bearings are used in machines to transfer motion from one moving part to another and reduce friction between the moving parts. Ball bearings are the most commonly used type of bearing. Ball bearings are used in rolling applications to ensure smooth, low friction movement. Ball bearings provide high performance and long life when transferring loads from the ball to the inner ring.
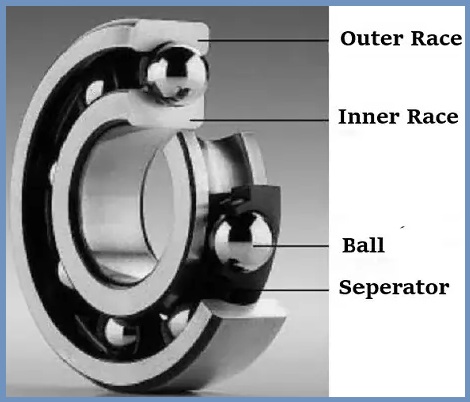
The primary function of ball bearings is to absorb axial and radial loads and reduce rotational friction. Use at least two races to support the ball and transfer the load through the ball.
Most commonly, one race is connected to a rotating component (such as a shaft or hub) and the other race is fixed. As the race spins, so does the ball. As the ball rotates, the coefficient of friction is smaller than the two flat surfaces rubbing against each other.
These valves have a small contact area between the race and the ball. Therefore, the load-bearing capacity of ball bearings tends to be lower than that of other types of bearings. However, these valves can tolerate inconsistencies between the outer and inner rings.
One of the drawbacks of ball bearings is that the balls “flatten” over time and can eventually break if the outer ring is over-pressurized. Therefore, parameters such as rated load should be checked on a regular basis.
Table of Contents
Structure of Ball Bearing
Ball bearing comprises 3 parts as given below.
- Two races (or rings)
- Ball spacer (retainer)
- Rolling elements (ball)
Angular contact ball bearings and radial ball bearings have inner and outer rings. Angular contact ball bearings and radial ball bearings are most commonly used to support radial loads. The outer ring is fixed.
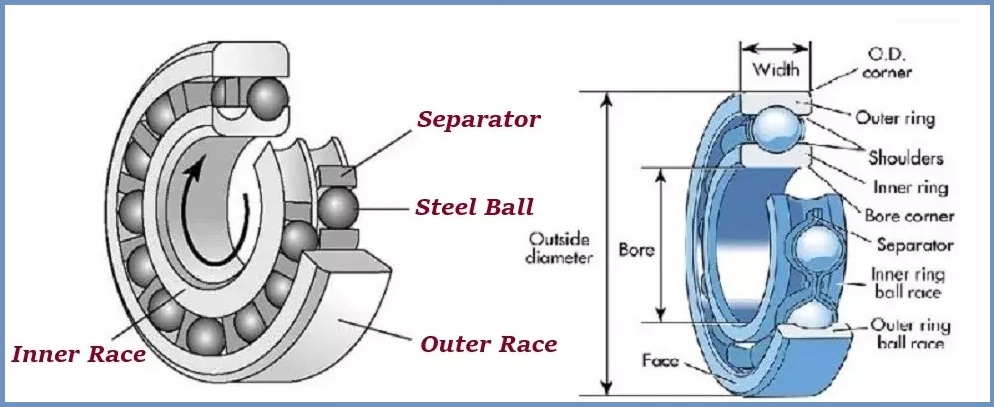
The outer ring helps transfer the radial load from the bearing to the housing. The inner ring is connected to the rotating shaft. This inner race supports and guides the shaft as it rotates.
The rolling element helps carry and transport luggage along the track. The rolling element rotates around the inner ring.
The ball bearings contain a separator that acts as a fence between the balls to prevent the balls from colliding with each other. Thrust ball bearings support axial loads (that is, loads parallel to the axis of rotation). They contain two varieties of the same size.
The Function of Ball Bearing
Ball bearings are the most well-known type of bearing.
Ball bearings have the following functions:
- Carry load
- Reduces friction
- Place the rotating part of the machine
Types of Ball Bearings
- Radial Bearing
- Deep Groove Bearing
- Angular Contact Bearing
- Self-aligning Ball Bearing
- Thrust Ball Bearing
Uses of Ball Bearing
- Ball bearings are used in computer fans and household fans.
- In the watchmaking industry, Jean Lassalle has developed a movement that uses ball bearings to reduce the thickness of the movement. The caliber 1200 uses a 0.20 mm sphere and is only 1.2 mm thick, yet it is still the thinnest mechanical movement.
- Ball bearings are used in many industrial applications such as jet engine shafts, gearboxes, and pulleys.
- Skateboard wheels use two bearings that can handle both radial and axial loads.
- They are used in fidget spinners.
- They are commonly used in piston pumps and centrifugal pumps.
