Table of Contents
What is Trilateration?
Trilateration is a survey technique in which three distances are measured. Global Positioning System (GPS) is a very popular survey technique based on trilateration concept.
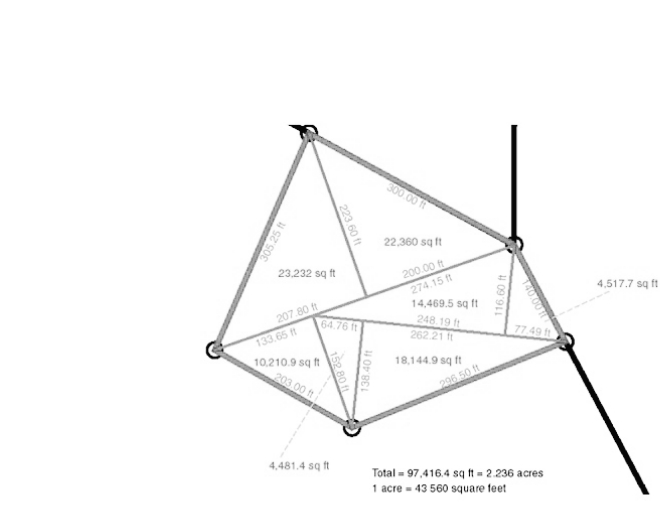
It is very different from triangulation. In triangulation, horizontal angles are measured. Trilateration uses electronic distance measuring devices (EDMs) to estimate the lengths of the triangle sides. Trilateration is the process of creating polygons or quadrilaterals out of a succession of joined or overlapping triangles, with the addition of an additional horizontal angle observation for azimuth control or angle verification.
With the development of EDMIs, trilateration has become more useful because it is extremely exact and precise for establishing and expanding horizontal control.
How It Works?
The measurement area is divided into triangles, and each triangle’s sides are measured individually. The measurement of any trangle is possible. A suitable equipment, such as an electronic one, is used to measure the distances.
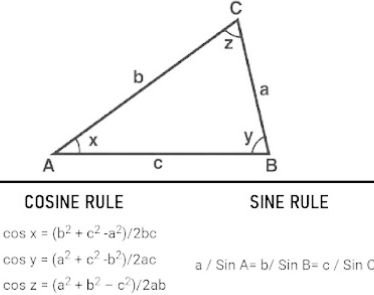
Trigonometric calculations are used to compute the angles of the triangles and the locations of their vertices. The angles are calculated using the sine and cosine rules.
Horizontal angles are occasionally measured in order to verify the precision of the angles calculated from the trigonometric observations.
Following the computation of the triangles’ angles, the trilateration is modified and the station’s coordinates are established.
Uses Of Trilateration In Surveying
The major use of trilateration are in global positioning system. But there are lots of other use cases. They are listed below.
- Trilateration is used to investigate the slow, secular movement in the earth’s crust in seismically active places. This research aids in the development of high-precision engineering projects with scientific and military infrastructure.
- Trilateration is also used in deformation surveys of dams, geothermal areas, structures, regional/local tectonics, and landslides, as well as control expansion or densification for future metropolitan growth, coastline control, inland waterway control, control extension, and densification for land subdivision and construction.
- Utilized for low-order basic topographic surveys.
- Utilized for global positioning systems surveying.
- Used to expand control over topographic mapping from localized small tracts to broader regions.
- EDMs’ increased accuracy makes them ideal for specialized, accurate surveys.
Pros
- Trilateration gives very precise data.
- It is very reliable survey system
- It is cheap .
- Accurate for most circumstances
- Allows for the control of both big and small geographic areas with the least amount of staff.
- Provide the scale control that triangulation is missing.
- It is preferable than the triangulation and traversing methods when done properly.
