Support is a part of a structure that resists loads. it helps structural members to resist force, moment, etc. Support is indicated by reactions that oppose the load.
In this article, we will learn about various types of support and their reactions to Structures. The main function of support is to transfer load from structural members like beams, and slabs to the ground. Support gives stability to the structure.
A structural engineer should have knowledge of types of support & their reactions in structures before designing a structure. Here I have described the most popular types of support used in the structure.
Table of Contents
Types of Support:
- Fix Support
- Pinned or Hinged Support
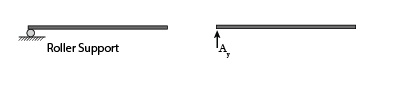
- Roller Support
These are the commonly used support in structural engineering. Let us discuss these 3 types of support with their reactions.
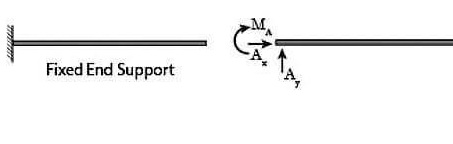
1. Fix Support and Reactions of Fix Support
Fis support is mostly used in building structures. This type of support is also known as rigid support. Fix support resists every type of load and moment. It is restrained against rotation and translation.
Because it is fixed, structural members can not move horizontally/ vertically and can not rotate on their axis. Every type of motion is restricted.


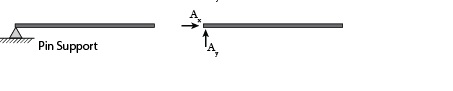
2. Pinned or Hinged Support and Reactions
Pinned support or hinged support can stop vertical and horizontal forces but they are not able to resist a moment. It is restrained only against translation.
In real life, you can see the example of hinged support. The door hinges are an example of hinged support. The door can rotate only on its vertical axis and can not move in the horizontal and vertical directions.
3. Roller Support and Reactions
Roller support only resists perpendicular forces. This type of support can not resist parallel forces or horizontal forces and moments. Roller support can move freely without resisting horizontal forces. This type of support is normally provided in the bridge deck. Roller support in the bridge deck is provided at one end. The main purpose to provide roller support is to allow contraction or expansion of the bridge deck with respect to temperature differences.
Roller support allows and absorbs horizontal movement caused by moving vehicles and seismic activity and provides adequate reaction against these activities.
In the bridge deck, only one end is roller supported and another end is fixed to provide stability to the bridge deck.